- 1Earth and Life Institute, UCLouvain, Belgium
- 2Royal Observatory of Belgium
- 3Université de Liege
- 4European Space Agency
Space weather events are one of the many major factors affecting the escape and evolution of Martian atmosphere. The Sun-planet interaction is affected by several factors such as the heliocentric distance, chemical composition of the atmosphere, solar illumination and its intrinsic magnetic field. Mars has a varied environment of magnetic field. It has little or no intrinsic magnetic field, but there exist some strong, crustal magnetic field patches. Thus, it becomes one of the solar system's best models for understanding the interaction of weakly ionized plasma with a highly irregular magnetic field.
Martian ionosphere owes its existence to the photoionization of neutral species by solar extreme ultraviolet (EUV) and X-ray photons. Martian ionosphere has a stratified structure with two main layers in its electron density profile (Ne). The primary layer (M2 layer) is formed by solar EUV radiation (~20-90 nm) and has a peak electron density at around 120-140 km altitude with a peak density of ~1011 m-3. The second layer (M1 layer) occurs at lower altitude with a peak electron density of ~109 m-3 and is formed by solar soft X-ray and electron impact ionization. The electron densities and the altitudes at which these peaks are very variable.
Radio Occultation (RO) experiments are the first and major explorer of the Martian ionosphere and electron density profiles. RO experiments precisely measure the Doppler shift observed on the link between a planetary spacecraft and Earth, as the spacecraft passes into occultation behind the planet. The RO data can be processed to extract the vertical electron density profiles of the ionosphere. Apart from vertical electron density profiles, RO can also provide density, temperature and pressure profiles of the neutral atmosphere. Thus, it is also a powerful tool to understand the both the neutral atmosphere and ionosphere.
Here we study the effect of solar flares and coronal mass ejections on the whole Martian atmosphere using the publicly available Mars Express radio occultation data from ESA Planetary Science Archive (PSA). For this, we selected two major solar disturbed periods occurred during 6th to 13th of June 2011 and 16th February to 31st March 2015. Using the Level 2 data we calculated the Ne profiles in the ionosphere as well as the temperature profiles of lower atmosphere. We also compare our results with numerical models and available measurements like MARSIS and Langmuir probe on NASA's MAVEN in the selected period.
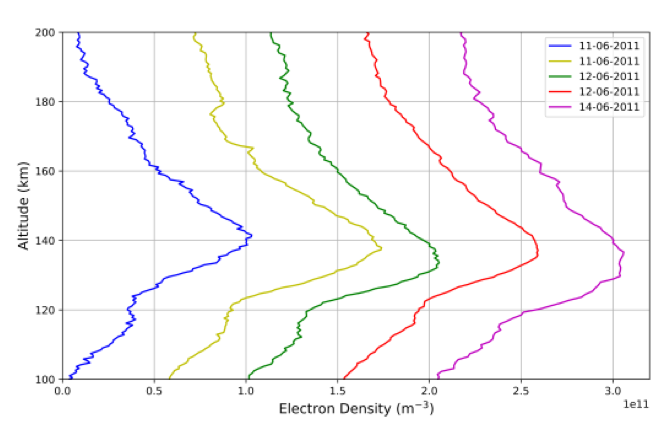
Figure 1: a. Electron density profiles observed by MEX on 2011 following a solar event on the 8th of June 2011.
How to cite: Krishnan, A., Karatekin, Ö., Verkercke, S., Henry, G., and Witasse, O.: Effect of Solar Event on Mars Atmosphere, Europlanet Science Congress 2022, Granada, Spain, 18–23 Sep 2022, EPSC2022-673, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2022-673, 2022.

