- 1The Open University, School of Physical Sciences, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom
- 2Space Science and Technology Department, STFC/RAL, UK
We present the OpenMARS reanalysis dataset (https://doi.org/10.21954/ou.rd.c.4278950), a publicly available resource developed to support the planetary science community in atmospheric and climate studies of Mars. The OpenMARS dataset combines a state-of-the-art Martian Global Circulation Model (MGCM) with data assimilation techniques to produce a dynamically consistent, gridded record of the Martian atmosphere over multiple Mars years. Data assimilation—routinely used in terrestrial weather and climate studies—offers a powerful framework for Mars by combining sparse, irregular satellite observations with a physically based model. This yields a complete and coherent picture of the atmospheric state that cannot be derived from observations or models alone.
OpenMARS utilises observations from multiple spacecraft and has been used to support a wide array of research topics, such as atmospheric dynamics, dust and water ice transport (Figure 1), chemical cycles, surface-atmosphere interactions, and climate variability. Studies leveraging OpenMARS have explored phenomena ranging from regional dust storms and polar processes to planetary waves and seasonal cycles, making it a valuable resource for both modelling and observational studies of the Martian climate system. These reanalyses are not only critical for advancing our scientific knowledge but are increasingly valuable for operational planning, especially as Mars exploration enters a new phase that includes long-duration robotic missions and future human exploration. Accurate atmospheric data are essential for entry, descent, and landing (EDL) planning, surface operations, and understanding environmental hazards.
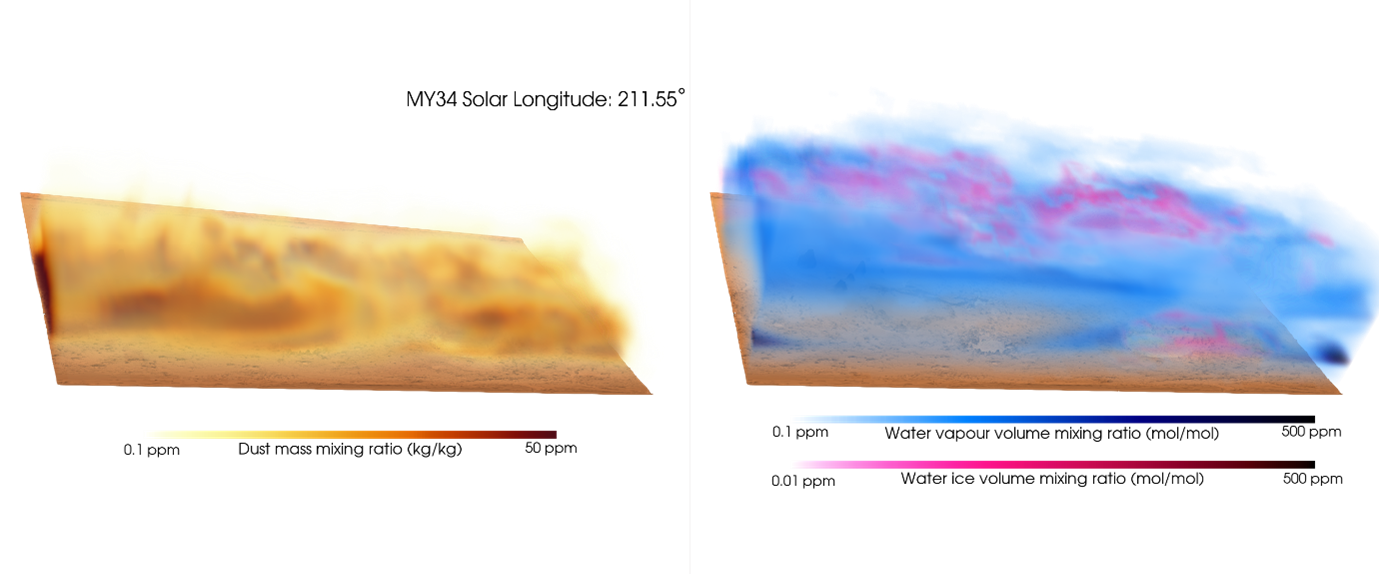
Figure 1: Sample output from the OpenMARS reanalysis dataset during the global dust storm in 2018.
We are actively working to update the OpenMARS dataset through multiple avenues including upgrading to the latest MCS v6 retrievals, which provide improved vertical coverage and retrieval quality. In response to feedback from the community, we are also exploring the inclusion of additional output variables and diagnostics relevant to current research needs. We encourage the community to make use of OpenMARS in their investigations and welcome suggestions for future enhancements. As a community-driven resource, OpenMARS aims to support the broad goals of planetary science and the practical requirements of future Mars missions.
How to cite: Holmes, J. A., Rajendran, K., Streeter, P. M., Patel, M. R., and Lewis, S. R.: OpenMARS: A Global Reanalysis Dataset for Martian Atmospheric Studies and Exploration, EPSC-DPS Joint Meeting 2025, Helsinki, Finland, 7–12 Sep 2025, EPSC-DPS2025-583, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc-dps2025-583, 2025.