Ice Giants Net Flux Radiometer (IG-NFR) Electrical Architecture
- 1Catholic University of America
- 2Nasa Goddard Space Flight Center
From the Ice Giants Pre-Decadal Survey Mission Report 2017 (IGPDS), a Net Flux Radiometer (NFR) was identified in the IGPDS report as a complementary payload for a probe mission to the Ice Giants. In this paper, we will focus on the electrical architecture of an advanced NFR that is applicable to both Uranus and Neptune. The NFR contains seven spectral channels to measure energy flux from 0.2-300 μm region. The NFR rotates clockwise and anti-clockwise at 5 different viewing angles sequentially and each channel projects an unobstructed 5° field-of-view (FOV) into the atmosphere. It would enable the scientists to determine an ice giant’s atmospheric heat balance and the tropospheric 3D flow which will lead to deeper understanding the plant’s radiation, region of solar energy deposition and the atmospheric conditions [1], [2], [3], [4]. In this design, thermopile sensors are used as the detector to convert radiation energy to electrical signal. Those thermopiles are uncooled and passive detector which help to reduce overall size, weight and power (SWaP) factor of the instrument. However, the readout noise is dominated by low-frequency noise which limited the resolution of the instrument. To overcome such problem, an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) with multi-channel analog-to-digital converter has been developed to reduce the low frequency noise of the readout system. A field-programmable-gate array (FPGA) has been integrated to the readout system to truly sample seven channels of the ASIC simultaneously. In this paper, we will go over the details of the ASIC and how to use it with the FPGA to implement the readout system for the advanced NFR. Figure 1 shows the system block diagram of the instrument [5], [6], [7].
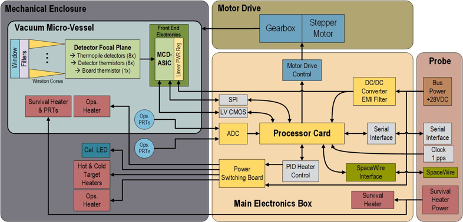
Figure 1: System block diagram of the instrument
[1] Aslam, S., et al., (2019). International Planetary Probe Workshop 2019, Oxford, UK
[2] Aslam, S., et al., (2020). Space Science Reviews, 216(1)
[3] Aslam, S., et al., (2018). 49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2018, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, Volume: LPI Contrib. No. 2083, 2675
[4] Aslam, S., et al., (2021). EPSC Abstracts Vol. 15, EPSC2021-144, 2021 European Planetary Science Congress 2021
[5] Tran, D., et al., (2020). Sensors and Systems for Space Applications XIII 11422, 1142205.
[6] Tran, D., et al., (2020). Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 1233.
[7] Quilligan, G., et al., (2021). IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science.
How to cite: Tran, D., Aslam, S., Gorius, N., Quilligan, G., and Nehmetallah, G.: Ice Giants Net Flux Radiometer (IG-NFR) Electrical Architecture, European Planetary Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-449, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-449, 2021.

