- 1IAPS-INAF, Rome, Italy (mauro.ciarniello@inaf.it)
- 2Osservatorio Astronomico, INAF, Trieste, Italy
- 3Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie, Universitá degli Studi di Napoli Parthenope, Naples, Italy
- 4Université Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, IPAG, Grenoble, France
- 5Institut Universitaire de France (IUF), Paris, France
- 6LESIA, Université Paris Cité, Observatoire de Paris, Université PSL, CNRS, Sorbonne Université, Meudon, France
- 7Institute of Planetary Research, German Aerospace Center (DLR), Berlin, Germany
- 8Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany
- 9Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, INAF, Naples, Italy
Remote sensing data of comets 9P/Tempel 1 and 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P hereafter) indicate the occurrence of water-ice-rich spots on the surface of cometary nuclei [1-5]. These spots are up to tens of metres in size and appear brighter and bluer than the average surface at visible wavelengths.
In addition, the extensive observation campaign performed by the Visible and InfraRed Thermal Imaging Spectrometer (VIRTIS, [6]) and the Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System (OSIRIS, [7]) during the Rosetta escort phase at 67P revealed a seasonal cycle of the nucleus colour. This is characterised by blueing of the surface while approaching perihelion followed by progressive reddening and restoral of the original colour along the outbound orbit. The temporal evolution of the colour has been interpreted in previous studies as the result of increasing exposure of water ice at smaller heliocentric distances [8, 9], however, an explanation of such seasonal cycle in the context of a quantitative cometary activity model was not yet been provided.
Recently, in [10] we showed that the seasonal colour cycle observed on comet 67P is determined by the occurrence of the above-mentioned water-ice-rich spots (referred to as Blue Patches – BPs –, given their colour). This can be explained in the context of activity models [11, 12] of pebble-made cometary nuclei [13], i.e. in terms of nucleus surface erosion induced by H2O and CO2 ices sublimation, driving the cometary activity.
According to the scenario proposed in [10] (Fig. 1), the presence of the BPs is due to the exposure of subsurface sub-metre-sized Water-ice-Enriched Blocks (WEBs) thanks to surface erosion triggered by CO2 sublimation ejecting decimetre-sized chunks [12]. The WEBs are composed of ice-rich pebbles (dust-to-ice mass ratio δ=2, [14]), embedded in a matrix of drier pebbles (δ>>5) forming most of the nucleus. Once exposed to illumination as BPs, the WEBs are eroded by water-ice sublimation ejecting sub-cm dust [11]. By means of dedicated spectral and thermophysical modelling, we match the nucleus colour temporal evolution measured by the VIRTIS Mapping channel in the 0.55-0.8 µm spectral range. In doing this, we take into account the competing effects of CO2- and H2O-driven erosion that expose and remove the BPs, respectively, and are seasonally modulated by the insolation conditions, primarily depending on the heliocentric distance.
The new nucleus model proposed in [10], implying an uneven distribution of water ice in cometary nuclei, reconciles the compositional dishomogeneities observed on comets (the BPs) at macroscopic (up to tens of metres) scale, with a structurally homogeneous pebble-made nucleus at small (centimetre) scale, and with the processes determining the cometary activity at microscopic (sub-pebble) scales.
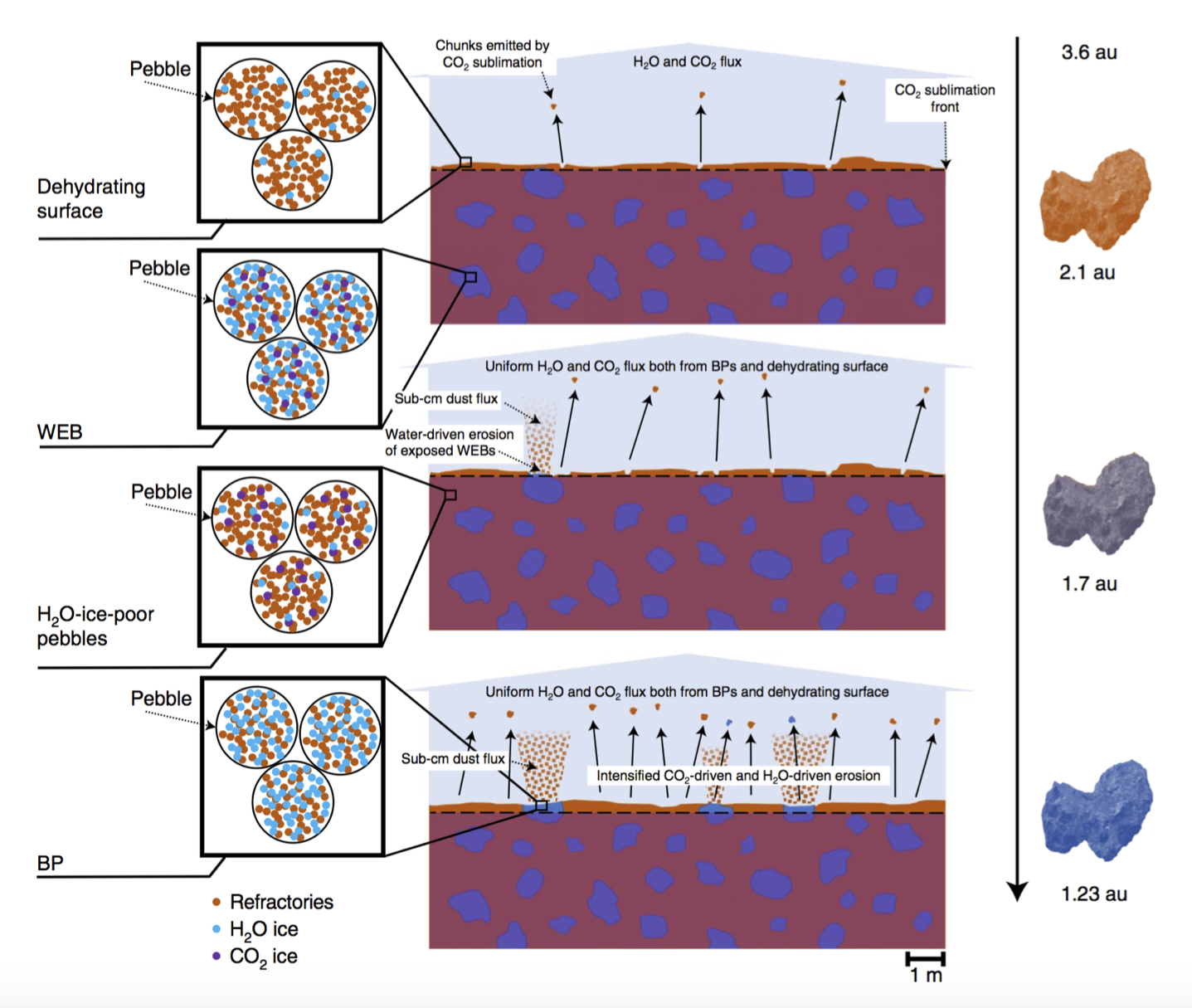
Figure 1. 67P surface gets bluer approaching perihelion as a consequence of the progressive exposure to sunlight of subsurface WEBs (from Figure 4 in Ciarniello et al., 2022, Nature Astronomy, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-022-01625-y). The comet nucleus is made of two types of pebbles, both including refractories and CO2 ice, with different water ice content: pebbles with high content of H2O ice form the WEBs, while H2O-ice-poor pebbles represent the rest of the nucleus. CO2 ice is stable beneath the CO2 sublimation front at depths >0.1 m [12]. Approaching perihelion, the CO2 ice sublimation rate increases, eroding the surface by chunk ejection and exposing the WEBs. Once exposed, WEBs lose CO2 and are observable as BPs. Water-ice sublimation erodes the BPs ejecting sub-cm dust from their surface and preventing the formation of a dry crust [11]. The BPs survive until their water-ice fraction is sublimated, producing the observed surface blueing. Please refer to ref. [10] for complete details.
References
[1] Sunshine, J. M. et al. (2006) Science 311, 1453–1455.
[2] Filacchione, G. et al. (2016) Nature 529, 368–372.
[3] Raponi, A. et al. (2016) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 462, S476-S490.
[4] Barucci, M. A. et al. (2016) Astron. Astrophys. 595, A102.
[5] Oklay, N. et al. (2017) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 469, S582–S597.
[6] Coradini, A. et al. (2007) Space Sci. Rev. 128, 529–559.
[7] Keller, H. U. et al. (2007) Space Sci. Rev. 128, 433–506.
[8] Fornasier, S. et al. (2016) Science 354, 1566–1570.
[9] Filacchione, G. et al. (2020) Nature 578, 49-52.
[10] Ciarniello, M. et al. (2022) Nat. Astron. doi:10.1038/s41550-022-01625-y.
[11] Fulle, M. et al. (2020) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 493, 4039–4044.
[12] Gundlach, B. et al (2020). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 493, 3690–3715.
[13] Blum, J. et al. (2017) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 469, S755–S77.
[14] O’Rourke, L. et al. (2020) Nature 586, 697–701.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Italian Space Agency (ASI, Italy; ASI-INAF agreements I/032/05/0 and I/024/12/0), Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES, France), and Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-und Raumfahrt (DLR, Germany) for supporting this work. VIRTIS was built by a consortium from Italy, France and Germany, under the scientific responsibility of IAPS, Istituto di Astrofisica e Planetologia Spaziali of INAF, Rome, which also led the scientific operations. The VIRTIS instrument development for ESA has been funded and managed by ASI (Italy), with contributions from Observatoire de Meudon (France) financed by CNES and from DLR (Germany). The VIRTIS instrument industrial prime contractor was former Officine Galileo, now Leonardo Company, in Campi Bisenzio, Florence, Italy. Part of this research was supported by the ESA Express Procurement (EXPRO) RFP for IPL-PSS/JD/190.2016. D.K. acknowledges DFG-grant KA 3757/2-1. This work was supported by the International Space Science Institute (ISSI) through the ISSI International Team "Characterization of cometary activity of 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko comet". This research has made use of NASA’s Astrophysics Data System.
How to cite: Ciarniello, M., Fulle, M., Raponi, A., Filacchione, G., Capaccioni, F., Rotundi, A., Rinaldi, G., Formisano, M., Magni, G., Tosi, F., De Sanctis, M. C., Capria, M. T., Longobardo, A., Beck, P., Fornasier, S., Kappel, D., Mennella, V., Mottola, S., Rousseau, B., and Arnold, G.: Seasonal evolution unveils the internal structure of cometary nuclei, Europlanet Science Congress 2022, Granada, Spain, 18–23 Sep 2022, EPSC2022-105, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2022-105, 2022.

