How to access and download the scientific data of Korean space exploration using KARI Planetary Data System
- 1Korea Aerospace Research Institute, Future Innovation Research Center, Daejeon, Republic of Korea (kl0630@kari.re.kr)
- 2HANCOM InSpace Co. Ltd., Daejeon, Republic of Korea (dskim@inspace.re.kr)
1. Introduction:
The Republic of Korea inaugurated its space exploration era by launching Danuri lunar orbiter on August 5, 2022. As of now, Danuri is conducting scientific missions in a lunar polar orbit at an altitude of 100 km. Initially scheduled for a one-year mission (nominal mission) until December 2023, its mission has been extended until December 2025. These scientific missions are conducted by five scientific instruments onboard Danuri, and the scientific data obtained from these instruments have been accessible to the public since January 2024.
The science mission payload of Danuri includes four Korean-developed instruments such as a Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (KGRS), a Wide-angle Polarimetric Camera (PolCam), a Magnetometer (KMAG), and a Lunar Terrain Imager (LUTI), as well as an internationally collaborative instrument, ShadowCam, developed by Arizona State University with funding from NASA.
2. KARI Planetary Data System:
The KARI Planetary Data System (KPDS) comprises functionalities designed to deliver scientific data to the developers of Danuri’s scientific instruments, which are research institutes and universities in Korea, to collect processed data from these developers, and to manage these datasets. Furthermore, KPDS includes functionalities to make the scientific data and supplementary data accessible to the public via its website(Figure 1).
All scientific data released to the public and managed for archiving in KPDS are compliant with the NASA PDS4 standard. To ensure compliance, all data uploaded to KPDS undergo PDS4 standard validation immediately upon upload.
KPDS, developed through collaboration between the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), one of the Korean government-funded research institutes, and HANCOM InSpace Co. Ltd., one of the space companies in the Republic of Korea, fulfills these roles. Specifically, KPDS is the Republic of Korea's inaugural public release and management system for scientific data in space exploration.
KPDS website offers users convenient access to scientific data through filter-based and keyword-based search functionalities (Figure 2). Additionally, users can directly access desired data through directories on the KPDS website without the need for separate search functions. Also, KPDS website features a Thumbnail Viewer for scientific datasets, providing users with thumbnail images. Users can perform simple image modifications such as brightness, gamma, hue, contrast, sharpness, and additional adjustments of the thumbnail images, as well as compare among selected thumbnails, if thumbnails are available. Additionally, it offers a Metadata Viewer for accessing metadata of scientific datasets compliant with the PDS4 standard. Furthermore, KPDS provides various information regarding Korea's space exploration and the utilization of scientific data, enabling general users to easily and efficiently utilize the scientific data obtained from Korea's space exploration missions.
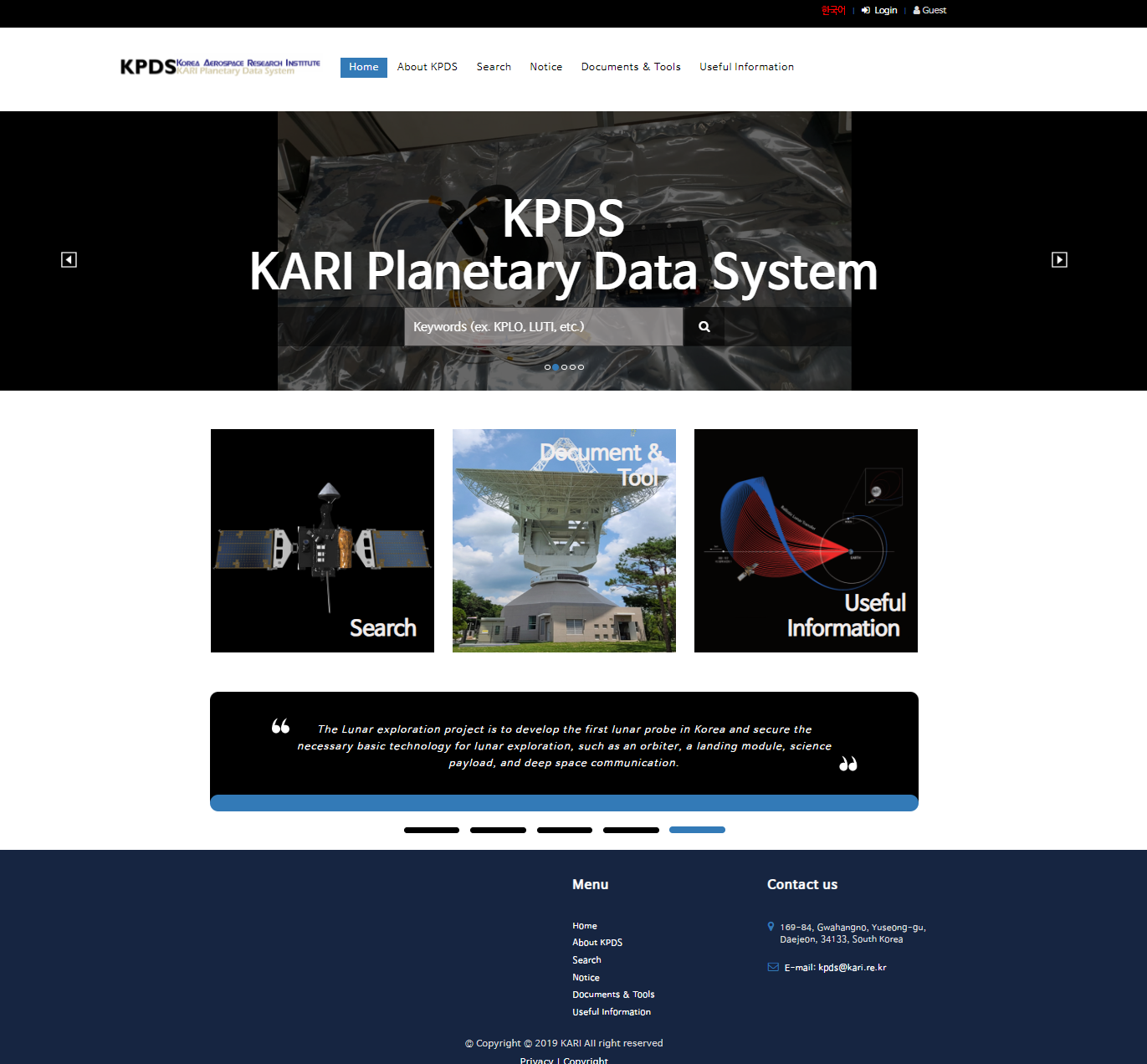
Figure 1. KPDS Website Main Page
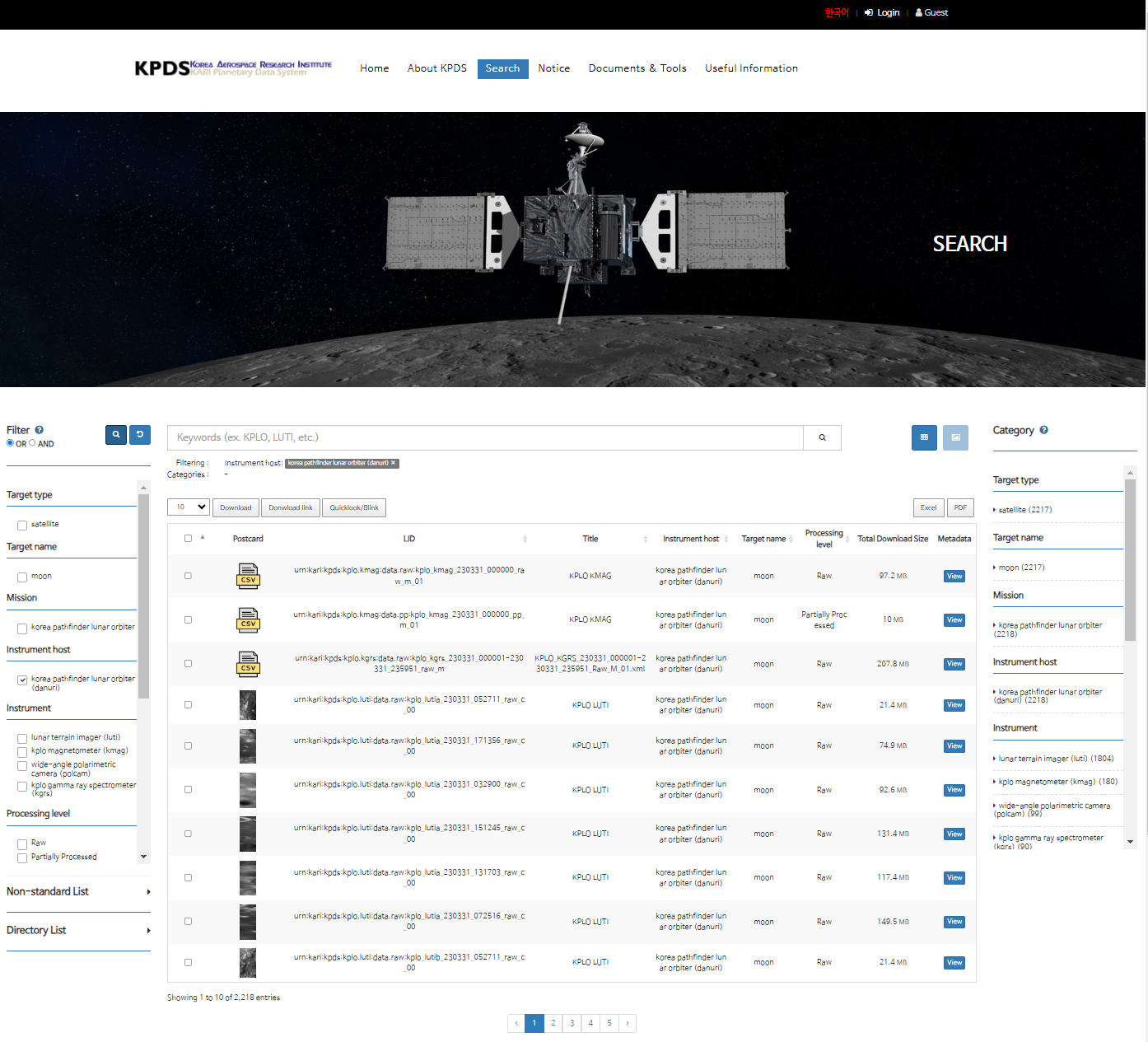
Figure 2. KPDS Website Search Page
How to cite: Kim, J. H. and Kim, D.: How to access and download the scientific data of Korean space exploration using KARI Planetary Data System, Europlanet Science Congress 2024, Berlin, Germany, 8–13 Sep 2024, EPSC2024-163, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2024-163, 2024.