TP4
Session assets
Please decide on your access
Please use the buttons below to download the presentation materials or to visit the external website where the presentation is linked. Regarding the external link, please note that Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
Forward to presentation link
You are going to open an external link to the presentation as indicated by the authors. Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
We are sorry, but presentations are only available for users who registered for the conference. Thank you.
Oral and Poster presentations and abstracts
Abstract
On 2017-09-27 at 18:56:12 UT a large meteoroid impacted the lunar surface, causing an impact flash with a duration of 1.12 seconds. Using Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera images, and the PyNAPLE (Python NAC Automatic Pair Lunar Evaluator) software pipeline, the resultant crater was identified. The crater is located at latitude φ= 8.0288, longitude λ = -76.546, approximately 14km east of the crater Glushko. The asymmetrical morphology of the ejecta blanket indicates the direction of impact was from the south, and impacting incidence angle was <30o.
Introduction
Lunar impacts are monitored on a regular basis, by both amateur and professional groups [1,2,3]. Since the first confirmed recording of a lunar impact flash in 1999, at least 600 confirmed impact flashes have been observed.
This large volume of data has let to several studies on both the properties of the impactor, and the thermal evolution of the impact itself [4,5,6]. These studies make use of the observed brightness of the flash, and the most likely parent meteoroid stream to calculate the total energy and temperature of the impact, and estimate the resultant crater size.
Very few of these impact craters have located [7] however, as finding metre scale craters and linking them to an observed impact with certainty is difficult. By identifying the resultant crater from an observed impact flash, valuable ground truth data can be obtained to help constrain the energy of the impact through use of crater scaling laws. The ejecta pattern of the impact can also tell us important information about the trajectory of the impactor.
Impact Flash
At 18:56:10 UT on 2017-09-27, a meteoroid impacted the lunar surface. The impact was observed by SdR UAI Luna members Bruno Cantarella and Luigi Zanatta, using a dual telescope system capturing with ZWO ASI120MM cameras, running at 25fps in one telescope, and 30fps in the other. It was also confirmed to be observed by Stefano Sposetti in Gnosca, Switzerland, ruling out the possibility the flash being a false detection.
The flash lasted 29 frames in the 25fps camera, giving it a duration of 1.12s. The first 22 frames are shown in Fig. 1. Its peak luminosity is reached in the second frame after only 0.04s, with the peak quantum efficiency of the camera at 590nm.
Figure 1: The first 22 frames of the 2017-09-27 impact flash.
As there were no meteor streams active at the time of the impact, it is concluded that the impactor belonged to the sporadic meteor background.
Crater Detection
The PyNAPLE software [8] was utilised in order to search for the resultant impact crater in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Narrow Angle Camera images (LRO NAC).
PyNAPLE works by searching for all before-after LRO NAC image pairs for a given time and location on the lunar surface, and running them through several operations which calibrate, map project, register, and align the images in order for pixel by pixel division to occur. This produces a final image in which similarities have cancelled out, and changes between the images are highlighted.
The crater, Fig. 2, was discovered in both LRO NAC images M1315871095R and M1344064055L, taken in 2019 and 2020 respectively, and and is absent from any images of the location from pre-2017.
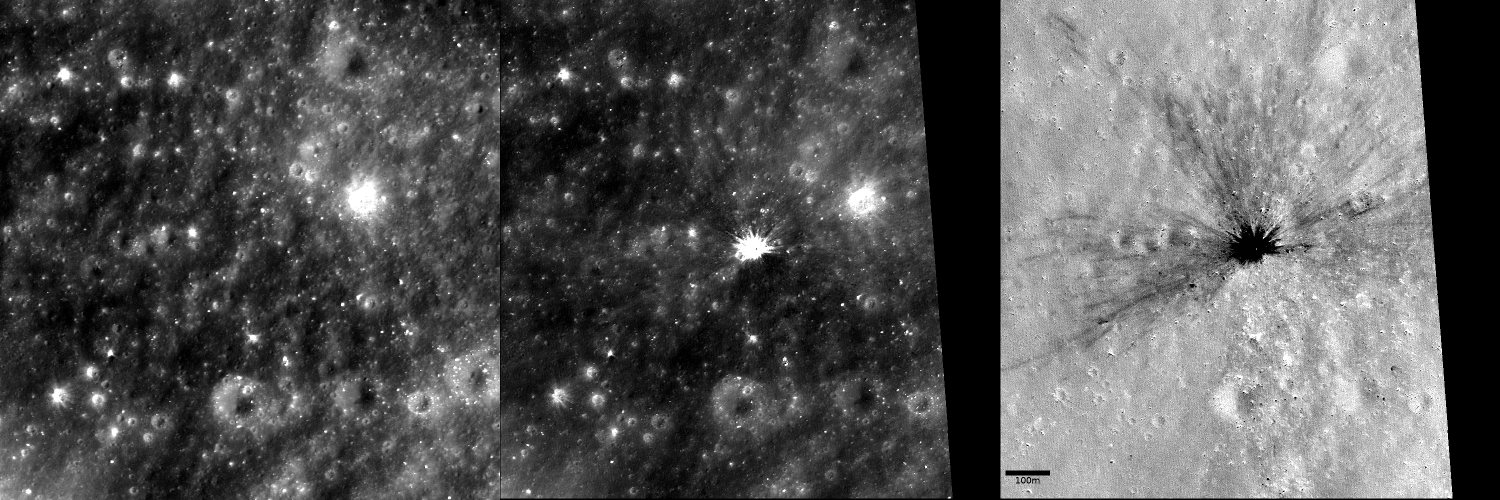

Figure 2: The crater formed during the 2017-09-27 lunar impact. Left: The ‘before’ image M1180620010R. Centre: The ‘after’ image M1315871095R. Right: The resultant image from dividing M1315871095R by M1180620010R.
Crater Analysis
The ejecta blanket and newly exposed regolith are higher albedo than the surrounding undisturbed material. Consequently, in the current LROC images the fresh regolith is overexposed, and no measurements as the craters diameter can be made, although the extent of the ejecta can be measured up to 600m away from the point of impact. This prevents the calculation of impact energy by employing crater scaling laws at this time. As the LRO is still collecting images, however, once new images of the site get released, these calculations will be possible.
The ejecta blanket of the impact crater tells us some information on the impact. The asymmetrical morphology of the ejecta blanket, shown in Fig. 3, is formed by the meteoroid impacting with an angle below ~30o incidence, according to Shuvalov’s findings for projectiles below 100m in size [9]. The exclusion zone towards the bottom of the image containing no ejecta is indicative of the up-range direction of the impactor being towards the bottom of the image.
Knowing the direction of the impact is important as incidence angle plays a large part in a number of crater scaling laws [10], but also as a way to differentiate potential parent meteoroid streams if there were multiple possible candidates.
Figure 3: The cropped ratio image, with a threshold applied to highlight only the ejecta blanket.
The presence of smaller exclusion zones within the ejecta blanket are likely due to effects caused by the local terrain.
Future Work
Once new images of the crater are collected and released by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, a size measurement for the impact crater can be obtained. This will allow for the application of crater scaling laws to calculate the impacting kinetic energy, and to solve backwards through current impact flash methodologies.
Bibliography
[1] Madiedo et al (2010) Advances in Astronomy, 2010:167494
[2] Xilouris et al (2018) A&A , 619, A141
[3] Suggs et al (2008) Earth Moon and Planets, 102:293298
[4] Avdellidou and Vaubaillon (2019) MNRAS, 484, 5212-5222
[5] Madiedo et al (2018) MNRAS, 480, 5010-5016
[6] Bonanos et al (2018) A&A, 612, A76
[7] Suggs et al (2014) Icarus, 10.1016
[8] Sheward et al (2019) EPSC-DPS2019, Abstract 1032-1
[9] Shuvalov (2011) Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 11, 1713-1718
[10] Horedt and Neukum (1984) Earth moon and Planets, 31, 265-269
How to cite: Sheward, D., Cook, A., Avdellidou, C., Delbo, M., Cantarella, B., Zanatta, L., Sposetti, S., and Lena, R.: Lunar Surface Change Detection with PyNAPLE: The 2017-09-27 Lunar Impact Flash and Impact Crater, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-590, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-590, 2021.
Abstract
A number of attempts have been done to detect of lunar impact flash observations by various researchers in last 20 years. One of the systematically research of lunar impact flash observations has been done at İSTEK Belde Observatory since 2017. We report the very first results of two first lunar impact flashes detected from Turkey.
Introduction
Interplanetary space is full of meteoroids, cometary fragments and debris. Occasionaly these objects impact to the surface of the Moon at high velocities. During these events the kinetic energy of the impactor is converted to thermal energy and give out an optical signature detectable with small instruments. Impact flashes are rapid events that in most cases escape attantion due to low amount of signal. Monitoring the night side of the Moon increases capturing an impact flash due to higher contrast. For this reason impact observations are carried out between 5-10 and 20-25 ages of the Moon. Impact events are beneficial providing information on impact energy, impactor mass, impactor source, temperature of the event [1,2,3,4,5,6]. We present the first report of two impact flashes on December 12, 2017 from Turkey.
Observation and method
ISTEK Belde Observatory (IBO) is located on the Asian shore of the historic Bosphorus waterway at 41o 01' 48'' N latitude and 29o 02' 32'' E longitude at an altitude of 150m. The observatory houses a Meade LX600 16'' Schmidt-Cassegrain f/8 telescope as the primary instrument. By using f3.3 focal reducer and Celestron Skyris 274M (1600×1200 px) monochrome camera, the telescope provides 24x30 arcminute field of view. The camera is operated at 15 fps. The time signal is acquired by network synchronisation. On 2017 December 12th a number of consecutive 10 minute observations each providing 9000 frames were inspected by LunarScan [7] and ZEPAZO software. Two impacts were detected and the signal is converted into visual magnitudes using MaximDL aperture photometry routine. For magnitude calculation three reference stars HD111662, HD111663 and HD111692 with known V magnitudes are used. These stars were within 1/4° from the impact sites and they were imaged in close succession with same air mass and exposure time. The impact flashes are detected at 82o.8 E, 8o.3 N (Flash 1) and 33o.7E , 16o.3N (Flash 2) selenographic coordinates. The photometric data are provided in Table 1 and location of flashes on the Moon are shown in Figure 1.
Figure1: Flash 1- 82o.8 E, 8o.3 N and Flash 2 - 33o.7E , 16o.3N Selenographic coordinates.
Table 1: Information of lunar impact flashes.
| Flash 1 | Flash 2 | |
| Time | 04:19:30.866 | 04:20:04.400 |
| Duration | 0.533(s) | 0.466(s) |
| Peak Magnitude | 7.98 | 7.48 |
| Radiated Energy (J) | 1,96x106(J) | 2.33x106(J) |
Analysis and results
Magnitudes of the flashes are calculated using Pogson formula mf =ms+2,5log(fs/ff), where mf, ms are the magnitudes of the flash and the reference star respectively, fs and ff are the observed fluxes of the flash and the reference star. The peak magnitudes of the flashes are 7.98 and 7.48 for Flash 1 and Flash 2, respectively. The radiated power P, in watts m-2, of an impact flash can be calculated using P=κ x 10-M/2.5Δλ , where κ is the flux density in W m-2 µm-1for a magnitude 0 source (κ=3,75x10-8) [8], M is the aparent magnitude of the flash and Δλ is filter passband (Δλ=500nm), in µm. The observed energy Ed is calculated by integrating power equation with respect to time. The radiated energy which emitted as light on the lunar surface Er, can be estimate by means of the relation Er=EdπƒR2 where R is the Earth-Moon distance (R=386605km), in m, when the flash occurs, f is a factor discribes the anisotropy degree of the light emission process (f=2 for the lunar surface and f=4 for the high altitude on the lunar soil)[9]. We conclude the observed events released energy 1,96x106 J and 2.33x106 J for Flash 1 and Flash2 respectively. These flashes are the first of their kind observed from Turkey; these event provided valuable insight on performance of the observatory instruments and reduction software.
References
[1] Ortiz J. L., Aceituno F. J., Aceituno J., A search for meteoritic flashes on the Moon, A&A, 343, L57,1999.
[2] Ortiz J. L., Sada P. V., Bellot Rubio L. R., et al., Optical detection of meteoridal impacts on the MoonNature, 405, 921, Nature, 2000.
[3] Suggs R. M., Moser D. E., Cooke W. J., Suggs R. J., The flux kilogram-sized meteoroids from lunar impact monitoring, Icarus, 238, 23, 2014.
[4] Madiedo J. M., Ortiz J. L., Organero F., et al., Analysis of Moon impacrt flashes detected during the 2012 and 2013 Perseids, A&A, 577, A118, 201, 2015.
[5] Bonanos et al., NELIOTA: first temperature measurement of lunar impact flashes, A&A, 612, 2018.
[6] Madiedo, J.M., et al., First determination of the temperature of a lunar impact flash and its evolution, MNRAS, 480, 5010-5016, 2018.
[7] Gural, P. Meteoroid environments workshop, MSFC 2007.
[8] Bessel, M.S., Castelli, F., and Plez, B. 1998. Model atmospheres broad-band colors, bolometric corrections and temperature calibrations for O-M stars. A&A, 333, 231-250.
[9] Bellot Rubio, L. R., Ortiz, J. L., Sada, P. V., Luminous efficiency in hypervelocity impacts from the 1999 lunar Leonids, AJ, 542, L65, L68, 2000.
How to cite: Acar, M. and Ateş, A. K.: Two Successive Lunar Impact Flashes: First lunar impact detection from Turkey, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-498, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-498, 2021.
Abstract
We present the contribution of our team to ESA's P3-NEO-I project, where we have been responsible for the detection and analysis of lunar impact flashes. These events provide key information about the impact processes taking place when meteoroids hit the Moon, and also allow to quantify the impact hazard of asteroids and comets for Earth. We also focus on the development of a new system for lunar impact flashes observations which has been deployed at the Calar Alto Observatory (Spain). This system can observe these events simultaneously in three different wavelengths by means of high-frame-rate and high-resolution CMOS cameras.
1. Introduction
The identification and analysis of flashes produced by the impact of meteoroids on the lunar surface is one of the techniques suitable for the study of the flux of interplanetary matter impacting the Earth. This method has the advantage that the area covered by one single detection instrument is much larger than the atmospheric volume monitored by meteor detectors on Earth. Our team at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) has been involved in the observation and analysis of these events since 1997 [1]. Since then, impact flashes have been unambiguously detected during the maximum activity period of several major meteor showers by using this technique, and flashes of sporadic origin have been also recorded [2].
For the detection of lunar impact flashes we have employed telescopes endowed with high-sensitivity CCD video cameras. Most of out telescopes are Schmidt-Cassegrain instruments with an aperture ranging between 28 to 50 cm, although some observational campaigns have been also performed with much larger instruments, such as, for instance, the 3.5 m telescope located at the Calar Alto Observatory [3].
During the last decade we have performed important improvements in the systems employed to detect these flashes. Most of these advances involved the use of faster cameras with higher resolution working at different wavelengths. In this work we focus on the systems employed by our team in the framework of ESA's P3NEOI project, and also on a new fast multiwavelength system deployed at the Calar Alto Observatory.
2. Contribution to the P3NEOI project
Since 2019 our team is member of a consortium of eight astronomical observatories leaded by the company Deimos Space, This consortium presented a technical proposal to the ESA ITT AO/1-9591/18/D/MR "P3NEOI: observational support from collaborating observatories". We are responsible for the work package (WP) dedicated to the detection and analysis of lunar impact flashes. One of the aims of this WP is the quantification of the flux of interplanetary matter that impacts our planet. For this purpose we have employed several telescopes located at three observatories in Spain: La Sagra, La Hita, and Sevilla. New instrumentation has been tested within this WP, including CMOS cameras with a maximum frame rate of 168 fps at full resolution (1920x1200 pixels). A sample impact flash recorded with one of these devices is shown in Figure 1. The main advantages of these cameras in relation to previously-employed imaging devices have been analyzed. One of their main utilities is related to their ability to obtain light curves with enhanced resolution. The monitoring in different wavelengths has also provided the temperature of lunar impact flashes.
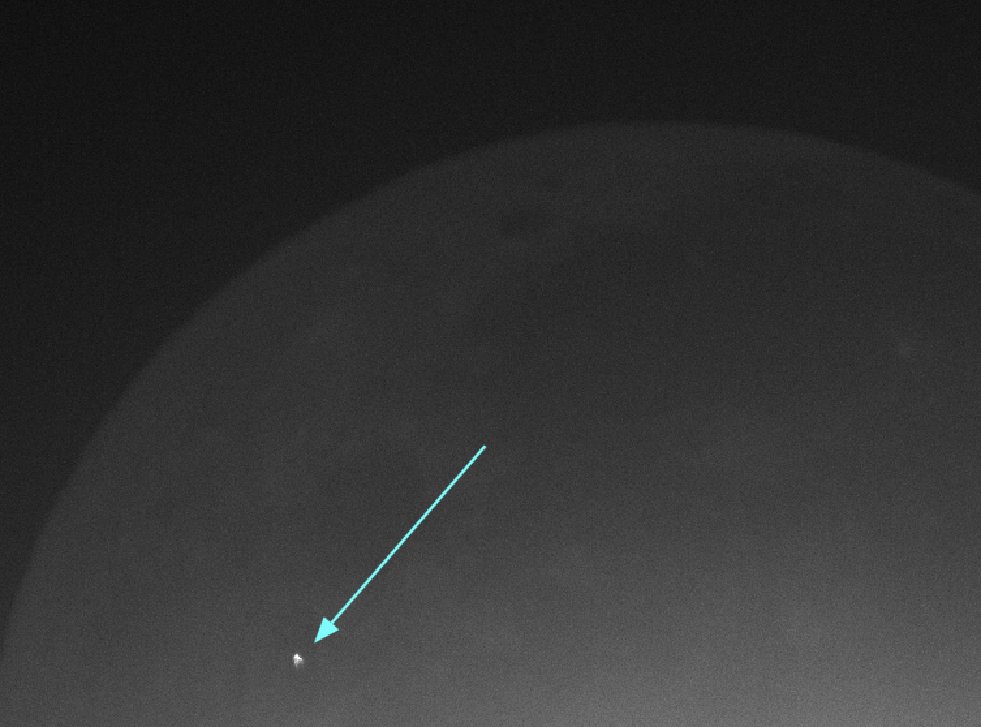

Figure 1. Lunar impact flash recorded in the framework of the ESA P3NEOI project on 27 May 2020 at 20h48m49s UT, with a peak apparent magnitude of 5.5.
3. New instrumentation at CAHA
Our team has deployed a new telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory (Spain) and one of its goals is to observe lunar impact flashes. This instrument has an aperture of 60 cm and employs a set of high-speed CMOS cameras (with a frame rate of 300 fps) that can observe, simultaneously, at three different wavelengths: namely, I, V and R. The telescope, which has been founded by the Spanish Ministry for Science and Innovation, is located within a dedicated 4-m automated dome and works in a coordinated way with the rest of instruments we are currently employing at different observatories in our country. Figure 2 shows an image of this new instrument, which can be controlled remotely. This new telescope has implied an important step for the analysis of the collision of meteoroids with the lunar ground.
Figure 2. The new 60 cm telescope deployed at the Calar Alto Observatory.
References
[1] Ortiz, J.L. et al., J., 1999. A search for meteoritic flashes on the Moon. Astron. Astrophys. 343, L57–L60.
[2] J.L. Ortiz, et al., 2000, Optical detection of meteoroidal impacts on the Moon. Nature 405, 921–923.
[3] Madiedo J. M., Ortiz J. L., Yanagisawa M., Aceituno J. and Aceituno F. (2019b). "Impact flashes of meteoroids on the Moon". Meteoroids: Sources of Meteors on Earth and Beyond, Ryabova G. O., Asher D. J., and Campbell-Brown M. D. (eds.), Cambridge, UK. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9781108426718, 2019, p. 136-158
How to cite: Madiedo, J. M., Ortiz, J. L., Morales, N., Santos-Sanz, P., Organero, F., Ana, L., and Fonseca, F.: Development of new systems for the observation of lunar impact flashes and the IAA participation in the ESA P3NEOI project, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-754, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-754, 2021.
Introduction
The intense, short-lived, self-luminous plume (or ‘impact flash’) produced from a hypervelocity impact is frequently observed on the lunar surface [1-4]. Laboratory measurements of these impact flashes (e.g. Figure 1) can also be acquired to determine parameters such as the target and impactor composition, or size/mass of the impactor [5-9]. Previous work has shown that the emission intensity from hypervelocity impacts tends to increase at higher impact velocities [10-15]. The relative intensity of atomic and molecular emission lines/bands originating from both projectile and target materials can also be used to determine approximate temperatures reached during impact [16-20].
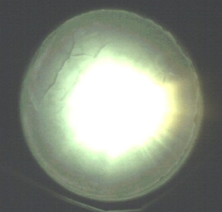
Figure 1: Photograph of a hypervelocity impact flash from a 3 mm aluminium projectile impacting a water ice target at 4.51 km s-1.
Current understanding of icy Solar System bodies, such as Europa and Enceladus, suggests they may contain favourable environmental conditions to synthesise biologically significant molecules such as amino acids, fatty acids, sugars and heterocyclic bases. Ground-breaking impact experiments [21-24] have demonstrated that complex organic molecules can be formed during hypervelocity impact events that are ubiquitous throughout the Solar System. Consequently, laboratory impact flash measurements from icy targets can be utilised to constrain the temperatures required for the shock-synthesis of these biologically important species. This preliminary study utilises emission spectra for the temperature measurement of impacted salt-water ice using different projectile speeds and materials.
Experimental
The University of Kent two-stage light-gas gun (LGG) [25] was used to horizontally accelerate a 3 mm aluminium or 4.3 mm Nylon projectile into salt-water ice targets composed of 20 g NaCl in 1 L of deionized water inside a sterilised 100 mm diameter, stainless steel container with their surfaces aligned at 90o to the shot line. Specific impact parameters for each experiment are summarised in Table 1.
|
Shot ID |
Projectile Material |
Impact Speed / km s-1 |
|
1 |
3 mm 7075 Aluminium |
6.03 |
|
2 |
3 mm 7075 Aluminium |
6.29 |
|
3 |
4.3 mm Nylon 6 |
6.90 |
|
4 |
4.3 mm Nylon 6 |
5.99 |
Table 1: Experimental parameters for impact flash measurements from salt-water ice targets.
The target mixture was frozen to -120 °C, with the temperature increasing to approximately -50 °C during the evacuation process of the LGG target chamber (to 50 mbar), prior to firing. A manual focus, 50 mm, F1.2, Nikon NIKKOR lens was aligned with the front viewport of the LGG target chamber and focused onto the end of a 0.5 mm internal diameter core of a fibre optic cable connected to an Ocean Insight Red Tide USB-650 spectrometer to record the impact flash spectrum.
Results and Conclusions
Figure 2 shows an example impact flash spectrum recorded using this methodology, with Na, Al and Zn atomic emission lines and AlO molecular bands clearly visible. The Al, AlO and Zn emission originate from the 7075 Al projectile (containing ~6% Zn). The relative intensities of the averaged Na 589 nm and 819 nm doublet emission lines originating from the target material were used to determine approximate peak temperatures for each impact experiment using a Boltzmann distribution calculation as outlined by Unnikrishnan et al. [26].
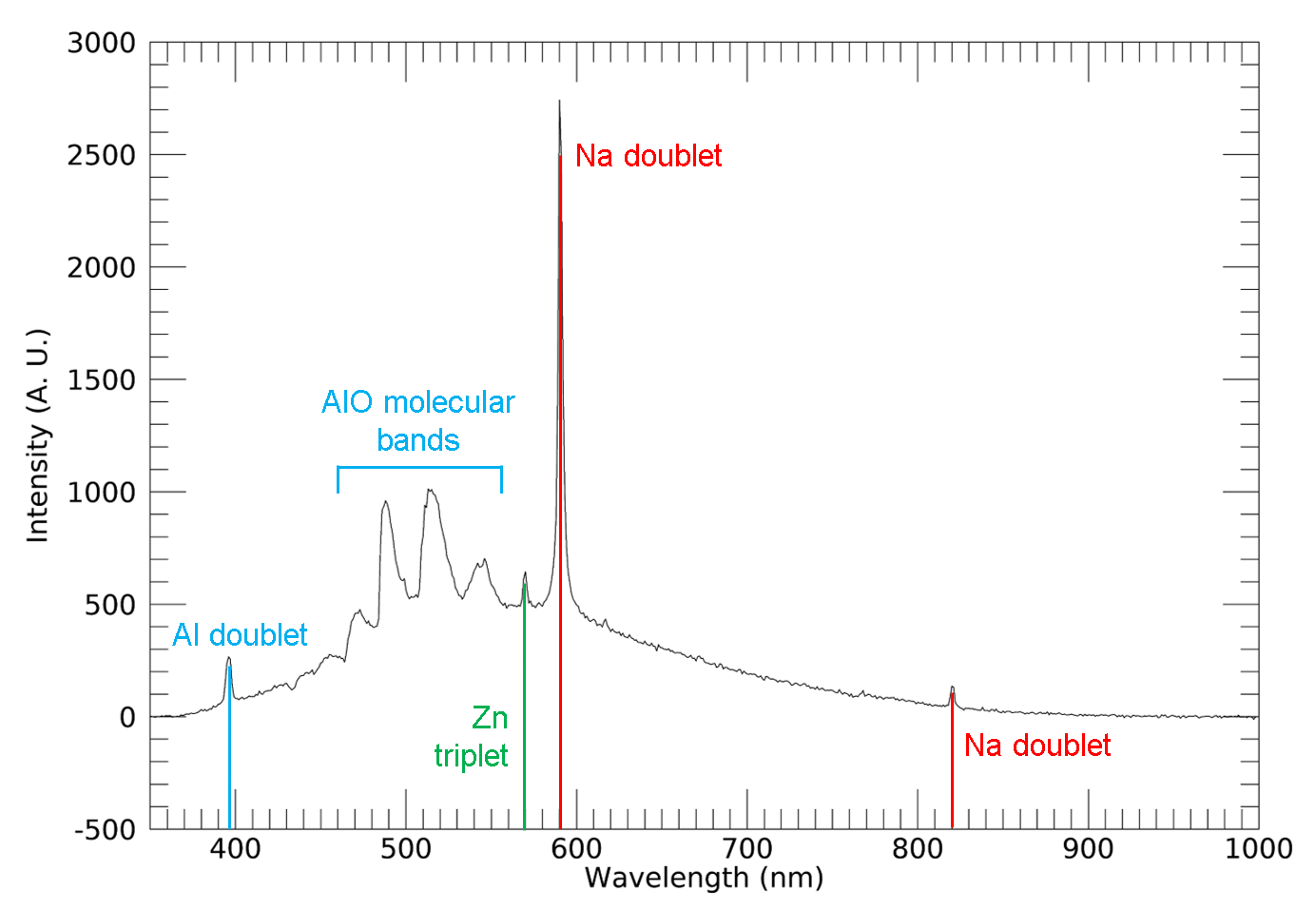
Figure 2: Impact flash emission spectrum from a 3 mm Al projectile impacting a salt-water ice target 6.03 km s-1. Labelled Na atomic lines were used for peak temperature determination.
All determined temperatures using this method were between 3000 K and 3420 K. Furthermore, shots 1 and 4, with similar impacts speeds, showed a small temperature difference of 140 K despite the distinctly different projectile material properties. This suggests that the calculated peak temperature is derived primarily from the target material. This observation may be a result of the method only utilising Na emission lines originating from the salt-water ice. Future work will constrain the calculated temperatures more precisely using spectra from shots at a wider range of impact speeds. These experiments should also provide an approximate correlation of impact energy and resulting temperature to be ascertained. Additional measurements with improved spectral resolution will further increase the precision of the determined temperatures and allow complimentary calculations using atomic emission lines originating from the projectile (e.g. the Al doublet at ~395 nm).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the STFC for financially supporting this work and Mark Price for IDL support.
References
[1] Uesugi K. (1993) Adv. Astronaut. Sci., 84, 607. [2] Yanagisawa, M. & N. Kisaichi (2002) Icarus, 159, 31. [3] Bozanos A.Z. et al. (2018) A&A, 612, A76. [4] Madiedo J.M. et al. (2018) MNRAS, 480, 5010. [5] Eichhorn G. (1976) Planet. Space Sci., 24, 771. [6] Lawrence R.J. et al. (2006) IJIE, 33, 353. [7] Ernst C.M. & Schultz P.H. (2007) Icarus, 190, 334. [8] Goel A. et al. (2015) IJIE, 84, 54. [9] Avdellidou C. & Vaubaillon J. (2019) MNRAS, 484, 5212. [10] Gehring J.W. & Warnica R.L. (1963) 6th HVIS Conference Proceedings. [11] Jean B. & Rollins T.L. (1970) AIAA J., 8, 1742. [12] Eichhorn G. (1975) Planet. Space Sci., 23, 1519. [13] Burchell M. et al. (1996) Icarus, 122, 359. [14] Ernst C.M. & Schultz P.H. (2002) Lunar Planet. Sci., XXXIII, Abstract #1782. [15] Sugita et al. (2003) J. Geo. Res. 108(E12), 5140. [16] Tsembelis K. et al. (2008) IJIE, 35, 1368. [17] Yafei H. et al. (2019) IJIE, 125, 173. [18] Tandy J.D. et al. (2014) J. Appl. Phys., 116. [19] Mihaly J.M. et al. (2015) J. Appl. Mech., 82. [20] Schultz P.H. & Eberhardy C.A. (2015) Icarus, 248, 448. [21] Martins Z. et al. Nature. Geo., 6, 1045, (2013). [22] Sugahara H. & Mimura K. (2014) Geochem. J., 48, 51. [23] Sugahara H. & Mimura K. (2015), Icarus, 257, 103. [24] Umeda Y. et al. (2016), J. Biol. Phys., 42, 177. [25] Burchell M.J. et al. (1999) Meas. Sci. Technol., 10, 41. [26] Unnikrishnan et al. (2010) Pramana J. Phys., 74, 6.
How to cite: Tandy, J., Spathis, V., Wozniakiewicz, P., and Alesbrook, L.: Emission Spectroscopy for the Temperature Measurement of Salt-Water Ice during Hypervelocity Impact, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-630, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-630, 2021.
Introduction: Impactors several tens up to 200 m in size are likely to suffer complete disruption and to produce large airbursts, similarly to the Tunguska event over Russia in 1908 [e.g., 1]. Observations and numerical modeling of medium sized impacts producing large airbursts have shown that such impacts represent an important fraction of extraterrestrial matter accretion to Earth, with Tunguska-like events occurring every 100 to 10,000 years, which is notably more frequent than crater-forming impact events. However, little is known about occurrences of such airburst events in the geological record, principally because of the lack of readily identifiable evidences such as impact craters. Finding residues of such events is thus critical for assessing the complete impact history of the Earth. Here we present the discovery of extraterrestrial particles in the Sør Rondane Mountains, Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, which were produced during a “touchdown” impact event ca. 430 ka ago, when a large airburst vapor jet interacted with the Antarctic ice sheet.
Material and Methods: Twenty nine igneous particles were recovered from glacial sediment collected during the 2017-2018 BELAM (Belgian Antarctic Meteorites) expedition that took place in the Sør Rondane Mountains, Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. Glacial sediment was sampled from a flat eroded summit in the Walnumfjellet (WN) area. 10Be exposure age of nearby summits suggest that the first sampled area has been continuously exposed over the last 870 ka [2]. About half the particles are compound spherules consisting of two or more spherules fused together. The petrography and mineralogy of 18 particles were determined at the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences of Brussels, Belgium. Their major and trace element compositions were determined at the Museum für Naturkunde of Berlin, Germany, and at Florida State University, USA, respectively. Oxygen isotopic compositions were determined by means of secondary ion mass spectrometry at the CRPG of Nancy, France.
Results: The mineralogy of the particles consists of olivine and spinel, with minor interstitial glass. On the basis on their internal textures and spinel content, we identify four groups of particles: 1/ the spinel-rich particles (SR; N = 9; ≥19% vol. spinel); 2/ Porphyritic olivine (PO; N = 5; <10% vol. spinel); 3/ Barred olivine (BO; N = 3; <10% vol. spinel); and 4/ one cryptocrystalline (CC; ⁓15% vol. spinel). The bulk major and trace element compositions of the particles are chondritic, pointing to a meteoritic origin. Spinel chemistry in SR particles is characterized by an Fe3+/Fetot of 77-89, where in porphyritic olivine particles, Fe3+/Fetot is lower at 60-62. Bulk spinel chemical compositions suggest highly oxidizing conditions during the formation of SR particles, suggesting that they formed in the lower atmosphere, whereas conditions were much less oxidizing for SP particles [3]. Chemistry and similarities to textural groups in BIT-58 impact particles suggest that all WN particles formed during a single impact event. However, age incompatibly prevents a pairing of WN particles with the impact event recorded in BIT-58. On a petrological and chemical level, WN particles match ⁓430 ka old impact particles found as layers in EPICA Dome C and Dome Fuji (i.e. L1 and DF2641, respectively) [4; 5], suggesting a continental distribution. A likely scenario is the disruption of a large (i.e. at least 100 m in size) chondritic asteroid over Antarctica ~430 ka ago. Oxygen isotopic signatures of WN particles are characterized by a highly negative δ18O, ranging from -35 to -52‰, and Δ17O ranging from -0.5 to - 1.2‰, consistent with oxygen isotopic compositions of L1 and DF2621 particles. Highly negative δ18O values are also consistent with interaction with the Antarctic icesheet during formation of the particles. This suggests that WN, L1 and DF2621 particles were produced during a touchdown impact, which occurs when the jet of melted and vaporized meteoritic material resulting from a large airburst reaches the surface, in this case the Antarctic icesheet, at high velocity. Numerical simulations of a projectile with a diameter of 100 to 150 m entering Earth’s atmosphere at a velocity of 20 km s−1 and an impact angle from 15° to 90° support such a touchdown scenario and, in particular, explain the complex chemical and isotopic conditions leading to the formation of the four observed textural groups SR, SP, BO and CC.
Conclusion: We report the discovery of meteoritic ablation spheres from the Sør Rondane Mountains. Their chondritic chemistry, coupled with characteristic spinel chemical compositions and oxygen isotopic signatures show that they formed in the lower atmosphere during a large touchdown event over the Antarctic icesheet. Combining chemical and isotopic composition with a numerical model help understanding the complex formation processes occurring during this unique impact event over Antarctic likely ~430 ka ago.
References: [1] Artemieva N. A. and Shuvalov V. V. (2016) Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 44: 37–56. [2] Suganuma Y. et al. (2014) Quat. Sc. Rev. 97: 102-120. [3] Van Ginneken M. et al. (2010) Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 293: 104–113. [4] Narcisi B. et al. (2007) Geophys. Res. Lett. 34: (2007) [5] Misawa K. et al. (2010) Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 289: 287–297. [5] H. Motoyama (2007) Eos Trans. AGU 88, abs. #C51A-0076.
How to cite: Van Ginneken, M., Goderis, S., Artemieva, N., Debaille, V., Decrée, S., Harvey, R., Huwig, K., Hecht, L., Yang, S., Kaufmann, F., Soens, B., Humayun, M., Van Maldeghem, F., Genge, M., and Claeys, P.: A large meteoritic event over Antarctica ca. 430 ka ago inferred from chondritic spherules from the Sør Rondane Mountains., Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-679, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-679, 2021.
Description of the CdC
Campo del Cielo (CdC, Figure 1) is a 4000-year-old [1, 2] strewn field in the south of the Chaco province, Argentina, which was caused by an impact of IA iron octahedrite [3]. This strewn field has an extremely elongated pattern extending over an area of ~14 km (downrange) by ~3.5 km (lateral). Other known terrestrial strewn fields are much smaller: the Sikhote-Alin in Siberia is 1.2 km long, the Kaalijarv in Estonia is 1 km, and the Morasko strewn field in Poland extends over a length of 0.4 km. Another interesting characteristic of CdC is that a lot of depressions found within the strewn field are not impact craters but penetration funnels [4] in which intact meteorites could be found including 30-ton-weight fragments.
Method
This study presents an attempt to reconstruct the Campo del Cielo impact event, i.e., to estimate the minimal pre-atmospheric mass and velocity of the meteoroid, its fragmentation during the atmospheric entry, and to compare the resulting strewn field with the observed one.
The process of meteoroids entering atmosphere can be described with an ordinary differential equation system, which combines drag, gravity and ablation with some kinematic equations [5]. In addition, most meteoroids fragment along their trajectory due to dynamic (ram) pressure caused by the atmosphere. To get good approximate solutions, with inexpensive computational power, we use semi-analytical approaches, like the Pancake and Separate Fragment Model in combination with statistics, such as the Size-Frequency-Distribution, to describe the fragmentation process.
The impact of dense material onto a porous target results in funnels formation instead of an impact crater [6] if the impact velocity is below a critical value. To simulate funnel formation, we use the iSALE-2D shock physics code [7] with initial conditions consistent with the atmospheric entry model.
Atmospheric Model Constraints
- The largest recovered fragments with a mass of ~30 tons each (El Gancedo, 30.8 tons, found in funnel No. 24 and El Chaco, 28.84 tons, found in funnel No. 10) were not fragmented upon landing, but penetrated the surface to form funnels.
- The distance between the largest crater (No. 3) and the most distant small meteorite found in situ (No. 26, 3.09 tons) is ~14 km.
- There are 4 impact craters with a diameter range from 65 to 115 m.
Results
Preliminary analysis of impact experiments and numerical models shows that in the CdC case (iron projectile and loess as a target) funnel formation and projectile survivability is possible at impact velocities below 1 km/s. The iSALE models confirm this estimate: the 1 km/s is probably the upper limit of impact velocity allowing survivability of high strength iron meteoroids impacting into loess. Such low impact velocity requires a specific entry scenario with an extremely shallow entry angle.
Figure 2 shows, that for the vaporization dominated regime (ablation coefficient of 0.01 s2/km2) a fragment with initial mass of 90-100 tons (immediately after fragmentation at an altitude of 20 km) and initial velocity of 16 km/s reaches the surface with velocity below 1 km/s if the entry angle is in the range of 7 - 16° to horizon. Several runs for variated speed of meteoroid at disruption in the range of 12-20 km/s show a possible angle range up to 18.5° and a mass range of 60-150 tons for the largest funnel-forming fragments.
To get a match between calculated and observed expand of the strewn field (~14.03 km), the trajectory angle at the point of disruption should be at least 13° (at a speed of 20 km/s) or up to 15° for lower speed of 12 km/s).
We also reconstructed the mass and velocity of the four crater-forming fragments using pi-scaling-laws (Figure 3). Their summed mass near the surface is at least 3028 tons (at a speed of 18 km/s) and up to 3692 tons (at a speed of 14 km/s). Its corresponding mass at the disruption point is 5348 and 6779 tons, respectively.
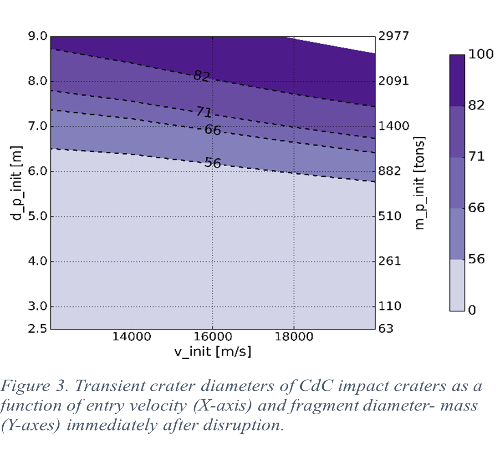
Those results represent just one possible scenario which assumes one fragmentation event from a number of possible scenarios. This scenario suggests that the Campo del Cielo strewn field was formed after an atmospheric entry of a minimal ~9000 tons in mass iron meteoroid (~13 m in diameter) at a shallow entry angle of ~16° and a speed of 14-18 km/s. The meteoroid was severely fragmented during the atmospheric passage: crater-forming fragments (with a final mass of 520 - 1150 tons impacted the surface with a velocity of 4 – 6.5 km/s at an angle of ~14°; funnel-forming fragments (5 – 31 tons, Fig. 4) and small meteorites (3 - 5 tons) landed with velocities < 1 km/s at various angles up to 45° (the smaller the meteorite, the more it is decelerated, and the steeper is the impact angle).
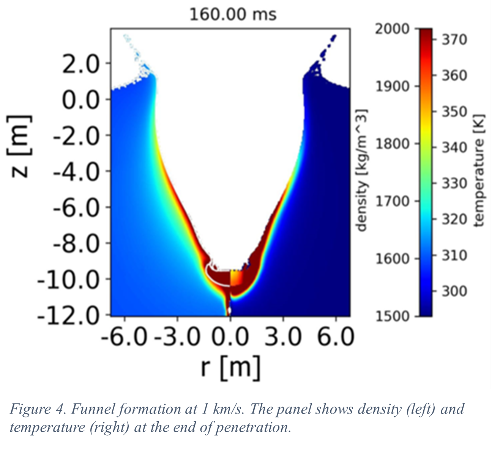
Discussion: We successfully reproduced the length of the CdC strewn field, but its lateral extension is substantially smaller than the observed one. The main reason of this discrepancy is the uncertainty of the repulsion coefficient in case of catastrophic fragmentation and complex behavior of small fragments. The survivability of large fragments (~30 tons) is indeed possible. However, the dependence of funnel’s length on fragment mass (and hence, its velocity) requires additional runs. Also, post-impact collapse of penetration funnels cannot be resolved without 3D models.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the funding from the ESA project P3-NEO-VIII. The authors are grateful to Shawn Wright for the update of CdC field observations.
References
[1] Cassidy W. A. and Renard M. L. 1996. M&PS 31:433–448.
[2] Cassidy W. A. et al. 1965. Science 149: 1055–1064.
[3] Liberman R. G. et al. 2002. 37:295–300.
[4] Vesconi M. A. et al. 2011. M&PS 46:935–949.
[5] Artemieva N. A. and Shuvalov V. V. 2001. JGR 106:3297–3310.
[6] Kadono T. 1999. Hypervelocity impact into low density material and cometary outburst. PSS 47: 305–318.
[7] Wünnemann K. et al. 2006. Icarus 180: 514–527.
How to cite: Artemieva, N., Schmalen, A., and Luther, R.: Modeling Campo del Cielo strewn field, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-106, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-106, 2021.
An increasing number of newly formed impact craters on Mars have been detected in the last 15 years. These small craters are normally identified via dark spots in lower resolution images that formed during the impact process, presumably through the removal or disturbance of bright surface material [1]. Later higher resolution images revealed single craters or crater clusters, which form when impactors fragment in the atmosphere, within those halos [1,2]. Due to this detection method, most of the new impact sites found are in dusty regions, which imposes an observational bias [3]. Newly formed clusters consist of two to thousands of individual craters and can be tightly clustered or spread out over hundreds of meters [2]. Since the InSight (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) mission landed on Mars in 2018 [4], the search for newly formed impact craters has become even more important, because identifying impacts in seismic signals could provide further constraints on both the atmospheric and solid-body effects of impact cratering process on Mars, as well as help place further constraints on the properties of the uppermost layer of the crust. As one of InSight’s mission goals is to estimate the current impact rate on Mars, the seismic detection of impacts is also crucial [4].
The aim of this new study is to describe the properties of the complete catalog of known newly formed craters on Mars and examine correlations between different crater cluster properties. We investigated 559 crater clusters and 493 single craters detected between 2008 and 2020 using 25 cm/px HiRISE images. The locations and diameters were noted for each single crater, as well as for every individual crater within a cluster down to 1 m diameter. This was done using ArcMap (ArcGIS) software with the three-point method of the CraterTools add-in [5]. We describe the cluster characteristics, such as the number of craters within a cluster, largest crater in a cluster, cluster effective diameter, cluster dispersion, elevation of the impact sites, and the variation in sizes of craters within a cluster.
More than half of the new impact sites form as clusters. We did not find any differences between the spatial distribution of single and crater clusters across Mars. The mapped crater clusters from this study consist of 2 to 2334 individual craters. More than half of all clusters (58%) consist of 10 craters or less. Crater clusters containing more than 100 craters are rare. With regard to the sizes of craters within crater clusters, we found that for highly populated clusters, the majority of craters are very small, and clusters with few craters have a tendency for craters that are more equal in size. Clusters having large effective diameters contain more equally sized craters. Our results show the full range of parameter spaces that are possible for cluster properties, which can help validate theoretical atmospheric fragmentation models.
References:
[1] Malin M. C. et al. (2006) Science, 314, 1573-1577.
[2] Daubar I. J. et al. (2019) JGR, 124, 958-969.
[3] Daubar I. J. et al. (2013) Icarus, 225, 506-516.
[4] Banerdt B. W. et al. (2020) Nature, 13, 183-189.
[5] Kneissl T. et al. (2011) Planet. Space Sci., 59, 1243-1254.
How to cite: Neidhart, T., Miljković, K., Sansom, E. K., Daubar, I. J., Collins, G. S., Eschenfelder, J., Gao, A., and Wexler, D.: Updated statistics for crater clusters on Mars, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-570, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-570, 2021.
Silicate nanoparticles, otherwise referred to as very small grains (VSGs) [1], occur in various astrophysical environments. These grains experience substantial processing (e.g., amorphization) during their lifetime in the diffuse interstellar medium due to events such as grain-grain collisions and irradiation [2]. Moreover, several studies have pointed out that the main building blocks of these silicates are O, Si, Fe, Mg, Al and Ca, all elements that are among the principal constituents of the Earth’s surface [3], thus leading to the name “astronomical silicates”. However, the structure and chemical evolution together with the origin of these grains are still poorly understood and intensively debated [4,5].
The aim of this study is the simulation of space weathering processes on olivine single crystals by liquid phase pulsed laser ablation (LP-PLA). The study of the resulting structure of both the target and the ablated material together with their chemical evolution has been carried out by a multiple technique characterization. In particular, spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering measurements, analyses of the electrostatic properties and reactivity to acids and bases on the obtained colloidal solutions of the ablated nanoproducts have been performed and coupled with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM).
Selected olivine target crystals (Fo87) from the São Miguel island (Azores) were analyzed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). LP-PLA experiments were performed with a Nd:YAG laser focused via a singlet lens onto the surface of the target, which was fixed at the bottom of a polystyrene box filled with 4 ml of deionized water (type 1) to immerge it completely. Laser pulses of 5 ns and 100 mJ simulate the timeframe and energy exchange occurring during grain-grain interstellar collisions [6] and they generate a plasma plume at the crystal/liquid interface. The rapid cooling induced by the confining liquid layer brings about the condensation of the chemical vapor it contains with production of a colloidal solution of nanoparticles. These solutions were analyzed by dynamic light scattering techniques and optical absorption spectroscopy in the range from 200 nm to 1100 nm (6.20 eV - 1.13 eV). Absorption measurements on the colloidal solutions have been compared against reference colloidal solutions dispersed in deionized water (i.e. mesoporous silica [SiO2] nanoparticles, brucite [Mg(OH)2] nanoparticles, aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3] nanoparticles, chrysotile [Mg3Si2O5(OH)4] nanotubes, and synthetic forsterite [Mg2SiO4] nanoparticles). Moreover, additional absorption analyses have been carried out as a function of the addition of known aliquots of sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide solutions. TEM/EDS analyses were then performed on the ablated nanoparticles deposited via electrophoresis on C-coated Cu grids and compositional variations of the ablated target were determined by X-ray photo-emission spectroscopy analyses.
The size distribution of LP-PLA synthesized nanoparticles is typically multimodal due to aggregation phenomena. Aggregation is consistent with the measured ζ-potential, which is negative with a relatively low absolute value, within the range 30-50 mV. Nonetheless, a recurrent mode is centered at about 2 nm (hydrodynamic diameter) and it is consistent with the measured size distribution obtained by transmission electron microscopy analysis (average nanoparticles diameter around 3-5 nm). Optical absorption measurements on the ejected material show a main band around 215 nm. This feature is very similar to the “B2 band” reported in several studies on silica glass [7] and ascribed to oxygen vacancies, but its nature is still far to be fully understood. We also found that this feature at 215 nm is very common among both Si and Mg compounds (e.g., Si-oxide, Mg-hydroxide, chrysotile). Moreover, additional absorption bands in the range 240-350nm are observed suggesting the formation of new space weathering products as result of the ablation process.
Therefore, these results suggest that substantial chemical processing might be expected during space weathering of “typical” interstellar grains into VSGs. Moreover, coupling these experimental results with remote sensing datasets will provide fundamental information about the origin and evolution of these silicate grains.
Acknowledgments: M.M is supported by the SIMP PhD thesis award.
References: [1] Witt A. N. (2000) Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 105(A5), 10299-10302. [2] Carrez P. et al. (2002) Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 37, 1599-1614. [3] Henning T. (2010) Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 48, 21-46. [4] Draine B. T. (2003) Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 41, 241-289. [5] Escatllar A. M. et al. (2019) ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 3, 2390-2403. [6] Loeffler M. J. et al. (2016) Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 51, 261-275. [7] Skuja L. N. et al. (1984), Solid State Communications, 50, 1069-1072.
How to cite: Murri, M., Capitani, G., Fasoli, M., Monguzzi, A., Calloni, A., Bussetti, G., and Campione, M.: Astronomical silicate nanoparticle analogues produced by pulsed laser ablation on olivine single crystals, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-111, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-111, 2021.
Introduction: Many meteorites have shock metamorphic textures, such as deformation and melting features under polarizing microscope. These shock features have been used to explore a variety of shock histories on meteorite’s parent bodies. A number of shock experiments have been conducted to estimate the shock pressure, which the shock metamorphic textures formed (e.g.,[1]). The previous experiments have been conducted mainly with uniaxial shock-recovery techniques (e.g., [2]). However, the conventional method can only obtain one data set at specific pressure per shot and is difficult to conduct a number of shots due to the destruction of metal containers. There is another technique pertaining to shock recovery, that is, the use of decaying shock waves. This method was applied to shock recovery of single olivine crystals with a high-power laser [3]. In this study, we extend this technique to macro rocky materials with the size of >10 mm using a two-stage light gas gun. Since we used a projectile much smaller than a metal container, a decaying compressive pulse propagates into the target, resulting in shocked samples compressed at various pressures. Our method allows us to reduce the effect of reflected waves from the wall of the container, which is a well-known problem in conventional shock recovery experiments.
Methods: We conducted the shock recovery experiments with a two-stage light gas gun at the Planetary Exploration Research Center of Chiba Institute of Technology, Japan [4]. We used marble and basalt as experimental samples. The samples were shaped into cylinders with a diameter of 30 mm and a height of 24 mm, sealed in a titanium (Ti) container, and covered with a Ti or Al front plate. The impact velocity was 7 km/s on average. The samples were cut across the epicenter and made into thin sections. We used an optical microscope and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to observe shocked samples in detail. We also conducted numerical calculations under the same conditions as the experiments with the iSALE shock physics code [5-7] to estimate the peak pressure distributions in the samples.
Results and Discussion: We numerically estimated an allowable range of peak pressure in a recovered sample to be ~20 GPa around the epicenter and ~1 GPa around the rear surface of the sample. In the recovered marble sample, we found that calcite exhibited undulatory extinction which is one of the known shock metamorphic textures. The total number of calcite grains showing undulatory extinction decreased with increasing distance from the epicenter. The threshold pressure required for the production of undulatory extinction was estimated to be about 2 GPa, which is close to the Hugoniot elastic limit of calcite [8]. This suggests that plastic deformation leads to the formation of undulatory extinction in calcite. In the case of the recovered basalt sample, plagioclase and pyroxene showed undulatory extinction, and plagioclase does not exhibit mosaicism and vitrification. These observation results indicate that an experienced pressure is up to 20 GPa. In addition, shock melt veins (<4 µm wide) were found to be formed at a distance of 1–2 mm from the epicenter. We estimated that the experienced pressure of the materials at the locations of shock melt veins is about 10 GPa with the iSALE calculation. Therefore, the shock textures, which are the co-existence of undulatory extinction in silicates and shock melt veins, are produced at 10 GPa compression. The shock pressures estimated by the iSALE calculation are consistent with those based on the petrological and mineralogical observations of the recovered samples in this study.
Conclusion: We developed a method to collect shocked samples with a variety of shock pressures (1–20 GPa). Additionally, the peak pressures at the location where the shock features are found are quantitatively estimated with a combination of observation and shock physics modeling. These shock indicators may be useful to estimate the shock histories of chondrite parent bodies.
Acknowledgments: We appreciate the developers of iSALE, including G. Collins, K. Wünnemann, B. Ivanov, J. Melosh, and D. Elbeshausen. We also thank T. Davison for the development of the pySALEPlot.
References: [1] Stöffler, D. et al. (2018) Meteoritics & Planet. Sci. (MaPS), 53, 5-49. [2] Yamaguchi, A. et al. (2003) Springer Science+Business Media, LLC. pp. 29–45. [3] Nagaki, K. et al. (2016) MaPS, 51, 1153-1162. [4] Kurosawa, K. et al. (2015) Journal of Geophysical Research Planets (JGR), 120, 1237-1251. [5] Amsden, A. A., et al. (1980) LANL Report LA-8095. 101 p. [6] Ivanov, B. A., et al. (1997), IJIE, 20, 411. [7] Wünnemann, K., et al. (2006) Icarus, 180, 514. [8] Ahrens, T. J. & Gregson, Jr, V. G. (1964) JGR, 69, 4839-4874
How to cite: Ono, H., Kurosawa, K., Niihara, T., Mikouchi, T., Genda, H., Tomioka, N., Sakaiya, T., Koundo, T., Kayama, M., Koike, M., Sano, Y., Satake, W., and Matsui, T.: Shock recovery of rocks with a variety of shock-induced pressure at a single shot, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-175, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-175, 2021.
Introduction: We present a shock-recovery setup to study the melting of genuine troilite and its migration into the surrounding silicate host [1-4], a process responsible for optical darkening in ordinary chondrites [5-6] between 40-60 GPa [3]. We combine a numerical approach [7] with a reverberation shock-recovery experiment [7-10] to calibrate our experimental requirements and verify or falsify our numerical results predictions. Because shock-recovery experiments are expensive, numerical models allow us to identify the optimum experimental conditions. Moreover, natural (precious) meteoritic samples do not allow for an all-parameter controlled experimental set-up, many phases can interact in shock settings [2-4], e.g., the eutectic properties of troilite change when Fe-metal is present [11], affecting the troilite melting efficiency.
Our work aims at identifying shock darkening enhancing parameters by using numerical models to narrow down experimental parameters to an ideal setup. We do this by using olivine and troilite minerals only, thus disposing of chondritic materials. Moreover, the simplification of the starting mineral setup (peridotite and troilite) ensures an uncorrupted study of the genuine melt behavior of troilite.
By succeeding shock melt migration of troilite, we aim to characterize the melt using various analytical methods. The experimental run products will be investigated by scanning electron microscopy, electron microprobe analyses, spectral analyses, x-ray tomography, and optical microscope observations. Identifying melt production and migration relevant parameters will improve our understanding of shock metamorphism and shock-darkening processes.
Methods: The outline of the shock experiment is summarized in Fig. 1. The sample consists of a 20 mm × 1.5 mm thick peridotite disk (Tulppio, Finland; Fo91). Previously synthesized powdered troilite (FeS, [12]) is filled into sub-mm drilled holes atop or beneath the peridotite disk. Powdered troilite promotes shock melting by pore crushing [2].
In classic shock-recovery experiments [8,9] a steel flyer plate (2 mm thick) is accelerated towards a steel container containing the sample. The shock wave propagates in sample after passing a 3 mm thick steel interface (driver plate). Reverberations occurring at bottom/top interfaces between sample and steel container equalize pressures in sample to the pressure in steel. A tantalum foil is used to protect the sample from iron contamination from the sample container.
Using the shock physics code iSALE-2D [13], we reproduce this setup: a half-disk of olivine for simulating peridotite (ANEOS for Fo90) with a 0.5 mm half-sphere of troilite (Tillotson EoS, [2]) surrounded by 0.06 mm thick tantalum (Tillotson EoS, [7]), all inserted in steel (ANEOS for iron) with the 3 mm thick steel driver plate above, are hit by a 2 mm thick steel flyer plate. We vary the impact velocity of the flyer plate (2000–2800 m/s), the troilite porosity (0–20%), its position in olivine (on top, at bottom) and record the following: pressure and temperature at nominal input (before reverberation) and peak of the shock (after reverberation) for olivine and troilite. We interpolate pressure and temperature values with Hugoniot data and estimate the effective entropy input from the reverberation in pressure units.
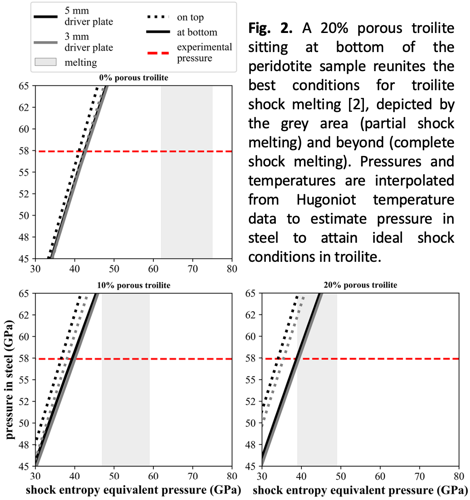
Expected results: The best conditions to induce melting of troilite are summarized in Fig. 2. A more in-depth illustration of the shock-wave propagation in the numerical models is shown in Fig. 3a-b. We estimate that a 20% porous troilite powder is necessary to induce melting of troilite upon release of the shock wave [2]; for good measure, we compared results for a 3- and 5-mm thick driver plate. We also observed that it is more efficient to melt 20% porous troilite that sits beneath the olivine disk. By observing the propagation of the shock wave, we see that reflected shock waves (first from bottom, lastly from top of the sample) which interfere with previous initial shock waves result in equalization of the pressure to the initial pressure in steel.
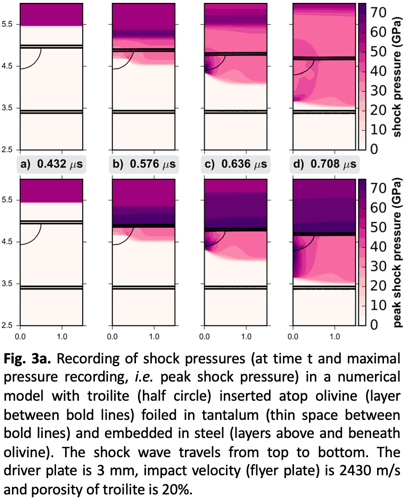
Outlook: The numerical study helps to set up optimum experimental conditions of the shock experiment in terms of phase positions within the sample (troilite top or bottom placement) and sample composition. With the planned experiment, we hope to observe shock-darkening of the troilite/peridotite assemblage, which will help to provide leads on similar processes observed in ordinary chondrites.
References:
[1] Stöffler et al. (2018) Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 53, 5–49. [2] Moreau et al. (2018) Phys. Earth Planet. In., 282, 25-38. [3] Moreau et al. (2019) Icarus, 332, 50-65. [4] Moreau and Schwinger (2020) Phys. Earth Planet. In., 310, 106630. [5] Kohout T. et al. (2014) Icarus, 228, 78-85. [6] DeMeo F. E. and Carry R. P. (2014) Nature, 505, 629-634. [7] Moreau (2019) Ph.D. thesis, Unigrafia, Helsinki, 60 pp. hdl.handle.net/10138/300084. [8] Langenhorst and Deutsch (1994) Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 125, 407–420. [9] Langenhorst and Hornemann (2005) EMU Notes Mineral. 7, 357–387. [10] Schmitt (2000) Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 35(3), 545-560. [11] Mare et al. 2014) Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 49, 636–651. [12] Moreau et al. (2021) Meteorit. Planet. Sci., in prep. [13] Wünnemann K. et al. (2006) Icarus, 180, 514-527.
How to cite: Moreau, J.-G., Stojic, A. N., Jõeleht, A., Plado, J., and Hietala, S.: A shock-recovery experiment to study shock melting of troilite in ordinary chondrites, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-34, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-34, 2021.
Introduction: Shock metamorphism in ordinary chondrites [1] is driven by impact events between asteroids. One effect of shock is the darkening of the lithology, which happens at two different stages of the shock intensity scale, at shock stage C-S7 (>70 GPa, whole rock melting, [1]) or between shock-stage 5 and 6 (40–60 GPa, metals and iron sulfides melt veins [2−7]). The darkening affects reflectance spectra of ordinary chondrites and, consequently, of asteroids. If an asteroid fragment of the S-complex asteroids is shock-darkened, its spectra will be similar to C/X-complex asteroids. This would affect the generally accepted spectroscopy-derived distribution of asteroids in the Main Asteroid Belt [7,8].
We investigate the impact conditions on rubble-pile asteroids in order to study the shock stage distribution and the mass of possibly shock-darkened asteroidal fragments. The distribution of porosity in rubble-pile asteroids depends on the internal structure [9]. The aim of the research is to highlight what type of rubble-pile asteroid collisions can explain the abundance of high shock stage materials [10] and the abundance of shock-darkened asteroidal fragments within the asteroid population.
Methods: We use the iSALE code [11] to simulate hypervelocity impact processes. We used the ε-α compaction model [11] for porosity, strength properties from [12] and an ANEOS for dunite to represent the material of the projectile and asteroid. We applied cylindrical-symmetry 2-D Eulerian gridwith Lagrangian tracers to study the distribution of peak shock pressures [13,14]. We apply numerical models of simplified rubble-pile structures of asteroids and study: a) The distribution of peak shock pressures (shock metamorphism). b) Quantification of shock-darkened material in the rubble-pile asteroid as well as in the escaping material. The model of a rubble-pile asteroid of 5 km in diameter is represented by several porous boulders of varying sizes surrounded by loose material. For the different impact scenarios, we varied the impact velocities (4−10km/s), the projectile diameters (800-1600m) and the porosities of the boulders (10−30%) as well as the porosity of the loose material (75−100%).
Results and discussion: The distribution of peak shock pressures strongly depends on both: impact velocity and projectile size (Fig.1a, b). Scenarios with cases considering higher boulder porosities (30%) only result in a small decrease of pressure (Fig. 1c, left panel) and thus lower shock stages are experienced as the shock wave is dampened by the compaction of porosity.
On the one hand porosity is responsible for an overall energy absorption but can on the other hand lead to localized pressure amplifications. Larger porosities of loose material (Figure 1c, right panel; here empty space) do not lead to significant differences compared to the case with porosities of 75% (Fig. 1a, left panel). We also observe that the rubble-pile asteroid is almost completely destroyed and porosity of the loose material is crushed out by the shock wave.
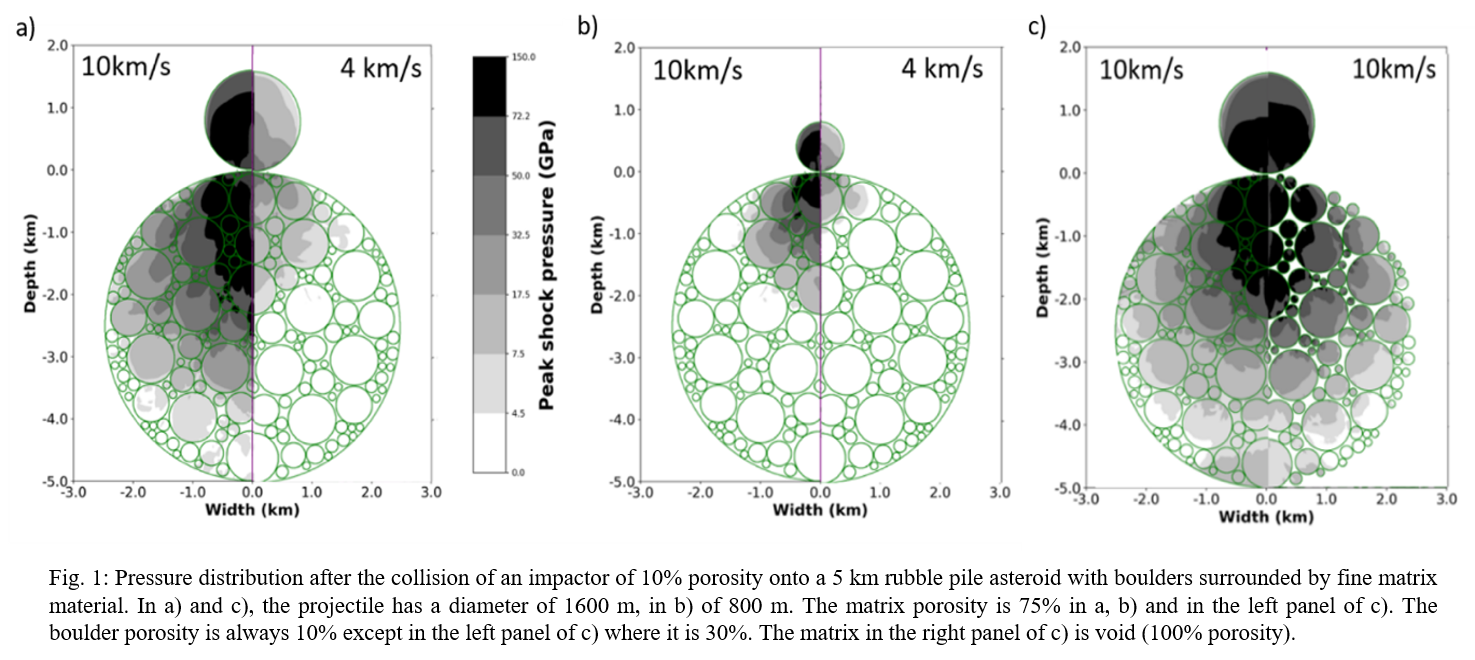
We also determined the efficiency of shock-darkening, which is defined as the shock-darkened mass in the rubble-pile asteroid normalized to the projectile mass (mt/mp). As shown in Fig. 2, the efficiency of shock-darkening increases significantly with increasing impact velocity and is dependent on the porosity of the boulders (compare squares and triangles in Fig. 2). For the most energetic impacts (large impactor and large impact velocities of 10 km/s) an efficiency of eight is reached, which correspond to about 30% of the asteroid being shock-darkened. Increasing the porosity of the boulders from 10 to 30% decreases the efficiency to about half the value. However, the effect remains stronger for larger impact velocity. By decreasing the impact velocity, the efficiency decreases linearly. For the lowest considered impact velocities shock-darkening is not efficient anymore.
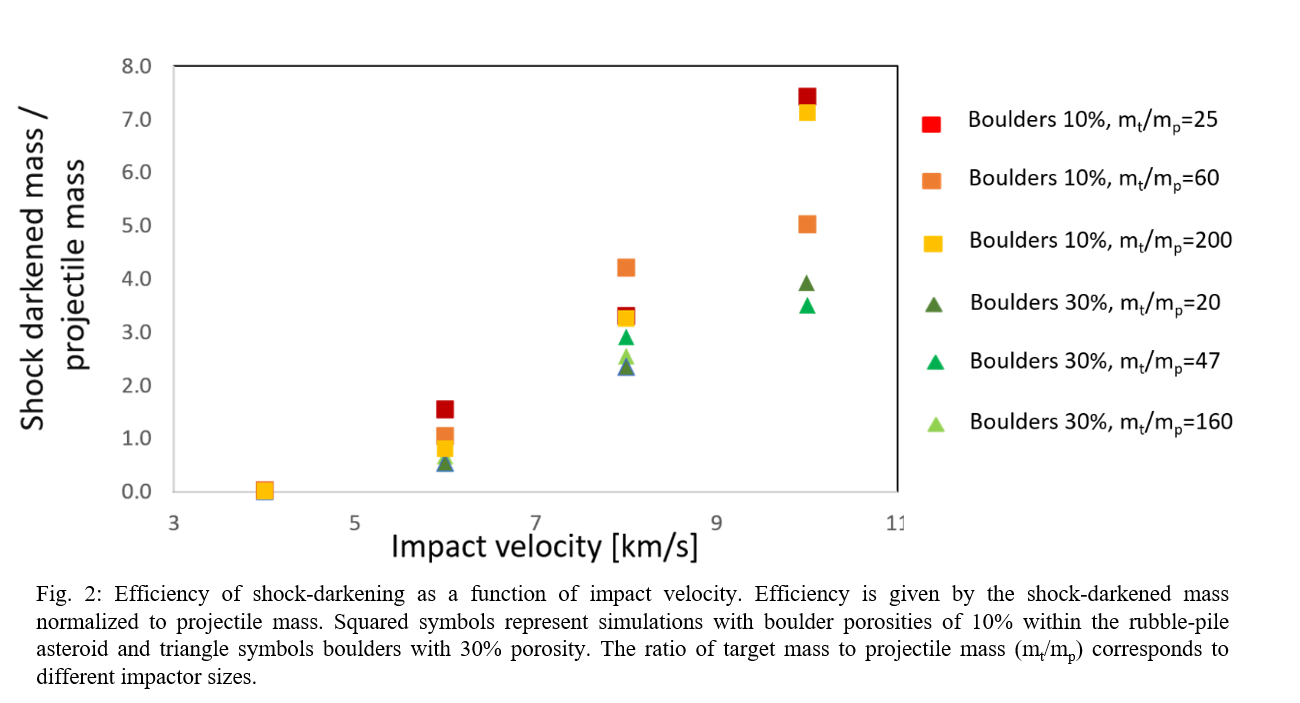
In Fig. 3 we show the results from the investigation of the ejecta for different collision scenarios. For the largest impactor, almost the entire asteroid material is already escaping at 6 km/s (cp. red squares). For those cases up to 90% of the asteroid mass is escaping. Considering lower impact velocities, only for the larger impactor a sufficient amount (~50%) of material is escaping. An increase of boulder porosity has a pronounced negative effect on the amount of escaping mass: only a small percentage between 1% and 8% of the total asteroid mass will escape. Fig. 3b and c show the escaping shock-darkened mass with respect to total escaping mass (b) and to the total shock-darkened mass in the rubble-pile (c). Only a small portion of the total escaping mass is actually shock-darkened, for almost all collision scenarios less than 6% (Fig. 3b). It can be shown that for the most energetic impact between 15 and 45% of the shock-darkened mass in the rubble-pile asteroid are escaping from the asteroid (Fig. 3c).
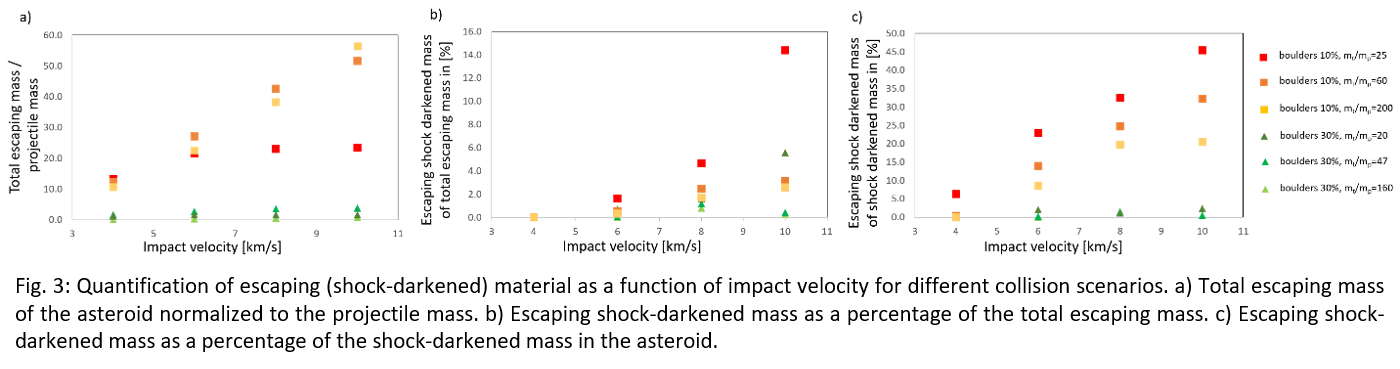
To conclude, high levels of shock metamorphism in ordinary chondrites require impacts with high velocities (8−10km/s) and large projectiles in order to exceed at least 20% of target mass within the C-S5, C-S6 and C-S7 shock stage distribution in rubble-pile asteroids as well as a sufficient amount of shock-darkened escaping material.
Acknowledgments: Our thanks go to the iSALE developers. This work is supported by the Academy of Finland and the European Regional Development Fund and the programme Mobilitas Pluss (Grant No. MOBJD639).
References: [1] Stöffler et al. (2018) Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 53, 5-49. [2] Moreau J. et al. (2017) Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 52(11), 2375-2390. [3] Moreau J. et al. (2018). Phys. Earth Planet. In., 282, 25-38. [4] Moreau J. et al. (2019). Icarus, 332, 50-65. [5] Moreau J. and Schwinger S. (2020), 310, 106630. [6] Kohout T. et al. (2020) Astron. Astrophys., 639, A146. [7] Kohout T. et al. (2014) Icarus, 228, 78-85. [8] DeMeo F. E. and Carry R. P. (2014) Nature, 505, 629-634. [9] Housen and Holsapple (2003) Icarus, 163, 102-119. [10] Bischoff et al. (2018) Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 1-14. [11] Wünnemann K. et al. (2006) Icarus, 180, 514-527. [11] Asphaug et al. (1998) Nature, 393, 437-440. [12] Cremonese et al. (2012) Planet. Space Sci., 66, 147-154. [13] Elbeshausen et al. (2009) Icarus, 204, 716-731. [14] Elbeshausen and Wünnemann (2011) Proc. 11th Hypervelocity Impact Symposium 2010.
How to cite: Güldemeister, N., Moreau, J., Kohout, T., Wünnemann, K., and Luther, R.: High Pressure Shock Metamorphism in Rubble-pile Asteroids using Numerical Simulations, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-468, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-468, 2021.
The crust on Mars has been structurally affected by various geologic processes such as impacts, volcanism, mantle flow and erosion. Previous observations and modelling point to a dynamically active interior in early Martian history, that for some reason was followed by a rapid drop in heat transport. Such a change has significantly influenced the geological, geophysical and geochemical evolution of the planet, including the history of water and climate. Impact-induced seismic signature is dependent on the target properties (conditions in the planetary crust and interior) at the time of crater formation; Thus, we can use simulations of impact cratering mechanics as a tool to probe the interior properties of a planet.
Contrary to large impacts happening in Mars’ early geologic history, the present-day impact bombardment is limited to small meter-size crater-forming impacts (in the atmosphere and on the ground), which are also natural seismic sources (Daubar et al., 2018, 2020; Neidhart et al., 2020). Impact simulations, in tandem with NASA InSight seismic observations (Benerdt et al., 2020, Giardini et al., 2020), can help understand the crustal properties over the course of Mars’ evolution, including the state of Mars’ crust today. Our most recent numerical investigations include: estimating the seismic efficiency and moment from small meter-size impact events, tracking pressure propagation from the impact point into far field, transfer of impact energy into seismic energy, etc (Rajsic et al., 2020, Wojcicka et al., 2020). Understanding coupling between impact crater formation process with the generation and progression of seismic energy can help identify small impact everts in seismic data on Mars. We also looked at the same process on the Earth (Neidhart et al., 2020) and the Moon (Rajsic, et al., this issue).
Since the landing of the NASA InSight mission on Mars, there was a dozen known new impacts (Miljkovic et al., 2021). However, all but one impact occurred much too far away (3000 to 8400 km distance from the InSight lander) to be within the detectability threshold estimates (Teanby et al., 2015; Wojcicka et al., 2020). About 50% of the observed craters were likely single impacts and the other 50% were evidently cluster craters with less than 40 individual craters in the largest cluster. The largest single crater was ~14 m in diameter, and the largest crater in a cluster was ~13 m (Neidhart et al., this issue), consistent with crater cluster observations (Daubar et al., 2013). The one impact that had a possibility of being detected by SEIS was 1.5 m in diameter at 37 km distance (Daubar et al. 2020).
Considering that orbital imaging is limited in space and time, these known new impacts represent only a fraction of the total number of impacts that have occurred on Mars in the last ~2 years. According to impact flux calculations (Teanby and Wookey, 2011), there should have been ~3000 detectable craters, larger than 1 m in diameter, formed on Mars since InSight landed. If any of these unobserved impacts have been large enough and close enough to InSight to detect seismically, we have not yet discerned them in the seismic data.
References:
Banerdt, W.B. et al. (2020) Nature Geosci. 13, 183-189.
Giardini, D. et al. (2020) Nature Geosci. 13, 205-212.
Daubar, I.J. et al. (2020) J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 125: e2020JE006382.
Wójcicka, N. et al. (2020) J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 125, e2020JE006540.
Rajšić et al. (2021) J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 126, e2020JE006662.
Daubar et al. (2013) Icarus 225, 506-516.
Teanby, N.A. & Wookey, J. (2011) PEPI 186, 70-80.
Neidhart, T. et al. (2020) PASA, 38, E016.
Teanby, N.A. et al. (2015) Icarus 256, 46-62.
Miljkovic, K. et al. (2021) LPSC, LPI Contribution No. 1758.
How to cite: Miljkovic, K., Rajsic, A., Neidhart, T., Sansom, E., Wojcicka, N., Collins, G., and Daubar, I.: Numerical modelling of recent impacts on Mars and contribution to InSight mission science, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-459, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-459, 2021.
Introduction: A possible source of seismic activity on Mars is meteoroid impacts [5]. Nevertheless, in the first Martian year of the the NASA InSight Mission [2] no signal has been unambiguously associated with an impact event [4]. This calls for further investigation of meteorite strikes and the relationship between impact conditions and the seismic signals they generate. One of the ways to understand the seismic signature of meteoroid impacts is to analyze already existing data from other planetary bodies.
During the Apollo era, over one thousand seismic signals were recorded on the Moon [e.g. 12]. Part of the Apollo seismic experiments were artificial impacts of Lunar modules (LM) and Saturn booster drops (S-IVB). Artificial impacts are considered large scale controlled experiments, because the exact position of the crater and the impactor parameters that made it are known. In this work, we model S-IVB artificial impacts on the Moon, using the iSALE-2D shock physics hydrocode [e.g., 1, 3, 21]. We simulated both the crater formation and the pressure wave propagation and attenuation. We examined size of the crater, cratering efficiency, impact momentum transferred to the target and two seismic parameters: seismic efficiency and seismic moment, and compared these measurements to the existing data [e.g., 10, 8, 7].
One challenge with modelling the S-IVB artificial impacts is the realistic presentation of the projectile. The Apollo S-IVB boosters were hollow aluminum cylinders, with a very low bulk density of 23 gcm−3 and mass of 14 t. The booster was 17.8 m long and 6.6 m in radius. The impact speed at the ground level was 2.54-2.66 kms−1. The drop angle was reported to be between 13.2◦ and 35◦ from vertical. [e.g., 14, 19]. There were five such impacts, and they all impacted into mare basalts and made elliptical craters (long and short axis in between 29.71 m and 38.7 m) with a central mound (crater depth was roughly estimated to 2-3 m) [e.g., 14].
Numerical modelling: All simulations in this work used the iSALE-2D shock physics hydrocode [e.g., 1, 3, 21]. To exclude any influence of target properties, all simulations used the same uniform target model of a 44% porous basaltic regolith [20, 15]. The mass and impact velocity of the projectile in our simulations were the same in all simulations and consistent with the experi- ments. Given the axial symmetry of the mesh geometry employed, we investi- gated five simplified representations of the irregularly shaped projectile. Three cases had a geometry of right-cylinder, with 90% porosity and different dimen- sions: 1. 11.7 m radius and height 0.5 m; 2. 5.8 m radius and 2 m height; 3. 0.992 m radius and 16.7 m height. The last two cases were spheroids: one was non-porous aluminum sphere with 1.06 m radius and the other one was 90% porous and had a radius of 2.3 m [13,21]. To calculate momentum transfer, the vertical component of the seismic moment and seismic efficiency we use approaches described extensively in previous studies [9, 7, 20, 15].
Here, we focus only on the vertical component of the seismic moment Mz [11, 7, 20]. To calculate seismic efficiency we used the same approach described in numerous previous work [e.g., 9, 20, 15].
Results: The shape of the projectile has a substantial effect on crater for- mation but little effect on the seismic signature of the impact. The largest crater was formed in Case 3, while the best agreement with observed crater properties was provided by Case 1 (for depth) and Case 5 (diameter). The porosity of the projectile affected the size of the mound at the bottom of the crater, which supports the idea that the observed central mounds at the bottom of the ob- served craters are projectile remenants [14]. The seismic efficiency k 10−6 and seismic moment Mz4 1010 Nm were of the same order of magnitude for all cases. This seismic efficiency is in agreement with lower estimates of [10], and the seismic moment is consistent with the scaling proposed in [17, 16, 20, 6].
Conclusion: We have successfully replicated the S-IVB artificial impacts on the moon with iSALE2D, producing craters that are consistent with obser- vations in their approximate dimensions and morphology. The simulations also constrain the seismic efficiency and seismic moment of the artificial impacts, which are relatively insensitive to the density and shape of the impactor. The low seismic efficiency determined here for artificial impacts on the Moon may help explain the non-detection of impacts by InSight in the first Martian year of operating. Moreover, the insensitivity of seismic moment to impactor density and shape suggests that results from the Apollo seismic experiment of these artificial impacts are useful analogs for small impacts on Mars that can be used to better inform their detectability by InSight [17, 16, 20, 6].
[1] Amsden A.A. et al. 1980. Technical report.
[2] Banerdt B.W. et al. 2020. Nature Geoscience, pages 1–7.
[3] Collins G.S. et a. 2004. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 39(2):217–
[4] Daubar I.J. et al. 2020. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 125(8).
[5] Daubar I.J. et al. 2018. Space Science Reviews, 214(8):1–68.
[6] Fernando B. et al. 2020 Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
[7] Gudkova T. et al. 2015. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 427:57–65.
[8] Gudkova TV et al. 2011. Icarus, 211(2):1049–1065.
[9] Guldemeister & Wunnemann K.2017. Icarus, 296:15–27.
[10] Latham G. et al. 1970. Science, 170(3958):620–626.
[11] Lognonne P. et al. 2009. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 114(E12).
[12] Lognonne & Mosser B.1993. Surveys in Geophysics, 14(3):239–302.
[13] Lundborg N. 1968. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, volume 5, pages 427–454.
[14] Plescia J.B. et al. 2016. Planetary and Space Science, 124:15–35.
[15] Rajsic A., et al. 2021. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
[16] Teanby N.A. 2015. Icarus, 256:49–62.
[17] Teanby N.A. & Wookey J. 2011. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 186(1-2):70–80.
[18] Tillotson J.H. Technical report.
[19] Wagner RV., et al. 2017. Icarus, 283:92–103,
[20] Wojcicka N. et al. 2020. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 125(10)
[21] Wunnemann K., et al. 2006. Icarus 180(2).
How to cite: Rajšić, A., Miljković, K., Wojcicka, N., Onodera, K., Collins, G., Kawamura, T., Lognonne, P., Wieczorek, M., and Daubar, I.: Numerical modelling of the artificial impacts on the Moon, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-710, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-710, 2021.
Near-Earth Asteroids visited by spacecraft display a depletion in the number of small craters (< 100 m). For example, the fractured monolith 433 Eros (Thomas et al., 2005), and the rubble piles 25143 Itokawa (Michel et al., 2009), 162173 Ryugu (Noguchi et al., 2021), and 101955 Bennu (Daly et al., 2020) all show a depletion in small craters. Models of the crater populations on Eros and Itokawa indicate that the depletion can be explained by seismic shaking induced by meteorite impacts (e.g., Thomas et al., 2005; Richardson et al., 2004; 2005; Michel et al., 2009). The effects of seismic activity occur in the active layer, the uppermost layer of the regolith. Previous models of seismic shaking that recreate crater populations have used a broad range of active layer depths, ranging from 0.1 m to 5 m across various models for Itokawa and Eros (Richardson et al., 2004; 2005; 2020; Michel et al 2009; Susorney et al., 2021). However, the actual regolith thickness is poorly constrained or unknown in many cases.
In this study, the uncertainty introduced into seismic shaking models from the assumed active layer thickness is investigated by comparing the relative timescales of crater relaxation (crater erasure). We use the Richardson et al., (2004) seismic shaking model, as modified by Michel et al., (2009) for Itokawa with impactor populations from O’Brien and Greenberg (2005). Our results show that decreasing the active layer depth leads to a nonlinear increase in the time to erase a crater. The total increase in time to erasure for a crater 20 m in diameter when changing from regolith depths of 5 m to 0.1 m is over three magnitudes, mostly accommodated between depths of 1 m to 0.1 m. We also investigated the relative timescales of crater erasure for craters of different sizes. Increasing the crater diameter leads to a non-linear increase in crater erasure time, with a 103 increase in erasure time when the diameter is increased from 5 m to 100 m.
The high sensitivity of crater erasure time on active layer depth and crater size implies that care should be taken when inferring surface properties, in particular asteroid surface age, time since a resetting event, or depth/diameter comparisons between asteroids with different crater populations.
References
Daly, R.T., Bierhaus, E.B., Barnouin, O.S., Daly, M.G., Seabrook, J.A., Roberts, J.H., Ernst, C.M., Perry, M.E., Nair, H., Espiritu, R.C., Palmer, E.E., Gaskell, R.W., Weirich, J.R., Susorney, H.C.M., Johnson, C.L., Walsh, K.J., Nolan, M.C., Jawin, E.R., Michel, P., Trang, D., Lauretta, D.S., 2020. The Morphometry of Impact Craters on Bennu. Geophys. Res. Lett. 47, e89672. doi:10.1029/2020GL089672
Michel, P., O'Brien, D.P., Abe, S., Hirata, N., 2009. Itokawa's cratering record as observed by Hayabusa: Implications for its age and collisional history. Icarus 200, 503–513. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2008.04.002
Noguchi, R., Hirata, N., Hirata, N., Shimaki, Y., Nishikawa, N., Tanaka, S., Sugiyama, T., Morota, T., Sugita, S., Cho, Y., Honda, R., Kameda, S., Tatsumi, E., Yoshioka, K., Sawada, H., Yokota, Y., Sakatani, N., Hayakawa, M., Matsuoka, M., Yamada, M., Kouyama, T., Suzuki, H., Honda, C., Ogawa, K., Kanamaru, M., Watanabe, S.-I., 2021. Crater depth-to-diameter ratios on asteroid 162173 Ryugu. Icarus 354, 114016. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2020.114016
O'Brien, D.P., Greenberg, R., 2005. The collisional and dynamical evolution of the main-belt and NEA size distribution, Icarus 178, 179
Richardson, J.E., Melosh, H.J., Greenberg, R., 2004. Impact-induced seismic activity on asteroid 433 Eros: a surface modification process. Science 306, 1526–1529. doi:10.1126/science.1104731
Richardson, J.E., Melosh, H.J., Greenberg, R.J., O'Brien, D.P., 2005. The global effects of impact-induced seismic activity on fractured asteroid surface morphology. Icarus 179, 325–349. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2005.07.005
Richardson, J.E., Steckloff, J.K., Minton, D.A., 2020. Impact-produced seismic shaking and regolith growth on asteroids 433 Eros, 2867 Šteins, and 25143 Itokawa. Icarus 347, 113811. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2020.113811
How to cite: Allen, N., Susorney, H., and Teanby, N.: The role of regolith thickness in seismic shaking on asteroids, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-118, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-118, 2021.
Numerous small bodies inevitably lead to cratering impacts on large planetary bodies during planet formation and evolution. As a consequence of these small impacts, a fraction of the target material escapes from the gravity of the large body, and a fraction of the impactor material accretes onto the target surface, depending on the impact velocities and angles. Here, we study the mass of the high-speed ejecta that escapes from the target gravity by cratering impacts when material strength is neglected. We perform a large number of cratering impact simulations onto a planar rocky and icy targets using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. We show that the escape mass of the target material obtained from our numerical simulations agrees with the prediction of a scaling law under a point-source assumption when vimp > ~ 10 vesc, where vimp is the impact velocity and vesc is the escape velocity of the target. However, we find that the point-source scaling law overestimates the escape mass up to a factor of ~ 70, depending on the impact angle, when vimp < ~ 10 vesc (Figure 1). Using data obtained from numerical simulations, we derive a new scaling law for the escape mass of the target material. We also derive a scaling law that predicts the accretion mass of the impactor material onto the target surface upon cratering impacts by numerically evaluating the escape mass of the impactor material. Our newly derived scaling laws would be useful for predicting the erosion of the target body and the accretion of the impactor for a variety of cratering impacts that would occur on large rocky and icy planetary bodies during planet formation and collisional evolution from ancient times to today (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of cratering impacts (left) and velocity distribution of the ejecta (right). High- and low-speed ejecta are launched closer to and farther from the impact point, respectively; that is, the escape mass is launched from the vicinity of the impact point (left). Irregular-shaped objects in the left panel indicate ejecta of target and impactor materials (the total amount and their fractions depend on the impact condition). The point-source scaling law is characterized by a unique slope in the velocity distribution, while direct SPH simulations of cratering impacts demonstrated that high-speed ejecta would have a steeper slope for the velocity distribution (the gray line in the right panel). This discrepancy leads to an overestimation in the escape mass when using the point-source scaling law, depending on the considered escape velocity of the target vesc.
Figure 2. Impact angle-averaged scaling laws for rocky (red lines) and icy (blue lines) bodies as a function of vimp/vesc. Left: the escape mass of the target material (Mesc,tar) normalized by impactor mass (mimp). Middle: the accretion mass of the impactor material onto the target surface (Macc,imp/mimp). Right: total escape mass (Mesc,tot = Mesc,tar + Mesc,imp in a unit of mimp; Mesc,tot > 1 indicates a net erosion and vice versa for a net accretion). Examples of typical outcomes of cratering impacts on different solar system bodies under different contexts are indicated by the labels in each panels.
How to cite: Genda, H. and Hyodo, R.: Erosion and accretion by cratering impacts on rocky and icy bodies: Formulation of scaling relations for high-speed ejecta, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-154, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-154, 2021.
Abstract
The elongated crater population on Mars is of great interest in planetary sciences [1]. In 1982, 1988 and 2000 three datasets were established using Viking images [1,2,3]. In 2011 a new and improved set of data with 261 craters and a database including up-to-date images taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) onboard ESA’s Mars Express were established [4] and continuously updated [5]. Based on the crater shape [6] and the ejecta deposit [7] the direction of impact can be estimated. Since this is not always a straightforward determination, it was decided to check whether the topographic profile could help in ambiguous cases.
1. Introduction
Impact cratering is one of the fundamental processes in shaping the surface of terrestrial planets. Even though most impact structures have a circular shape, a small fraction of elongated craters formed by oblique impacts can be observed. Using the recently developed Mars Express database, the current study focuses on the impact direction of elongated craters on Mars.
2. Motivation for the study
One major driver for conducting this study is the ongoing discussion of the decaying moonlets hypothesis, which might be an explanation for at least a fraction of the elongated crater population on Mars, as well as the unsolved origin of the Martian moons, Phobos and Deimos [5,9].
3. Direction of impact
As a precondition the crater orientation is analysed and a strong correlation to the crater age can be stated. For the identification of the impact direction a two-stage process is applied and this presentation shows the usefulness of the procedure. A first estimation is based on the crater shape [6] and the ejecta deposit [7]. Figure 1 shows a crater example and table 1 the summarized results for the elongated crater population on Mars. Subsequently, the estimation is reviewed by an analysis of the topographic crater profiles, which result from the pressure distribution during impact [8]. Figure 2 presents the corresponding profile for the first example crater. This review process indicates the validation of the results of the first stage. For craters with morphological characteristics not allowing a distinct identification of the impact direction in stage one this approach helps to improve the dataset dramatically (figures 3 and 4).
4. Figures
Figure 1: Estimation of impact direction based on crater shape and ejecta deposit for example crater 1
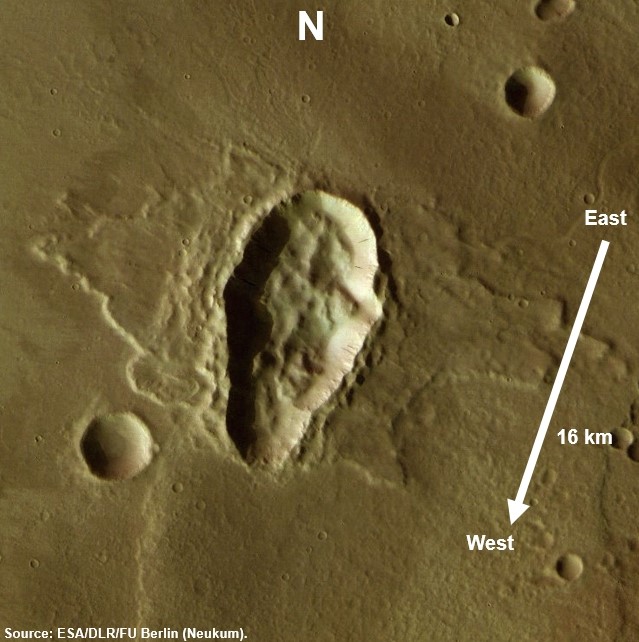
Figure 2: Altitude profile of example 1 based on HRSC MOLA blended DEM (200m) confirms East to West impact direction
Figure 3: Distinct identification of impact direction based on crater shape and ejecta deposit difficult for example crater 2
Figure 4: Altitude profile indicates West to East impact direction
5. Table
Table 1: Direction of impact
Acknowledgements
B. Buchenberger sincerely thanks O. Witasse for more than a decade of great cooperation and friendship that gave him the opportunity to work on such wonderful topics like this.
References
[1] Schultz, P. H. and Lutz-Garihan, A. B.: Grazing Impacts on Mars: A Record of Lost Satellites, Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 87, p. 84-96, 1982.
[2] Barlow, N. G.: Crater Size-Frequency Distributions and a Revised Martian Relative Chronology, Icarus, Vol. 75, p. 285-305, 1988.
[3] Bottke, W. F., Love, S. G. et al.: Interpreting the Elliptical Crater Populations on Mars, Venus and the Moon, Icarus, Vol. 145, p. 108-121, 2000.
[4] Buchenberger, B., Witasse, O. et al.: Elongated craters on Mars revisited: Test of the decaying moonlets hypothesis? EPSC-DPS Joint Meeting, p. 738, 2011.
[5] Sefton-Nash, E., Faes, Z. et al.: The Orbit Planes of Impactors that Formed Elongated Martian Craters, EPSC, p.286, 2017.
[6] Burchell, M.J., Robin-Williams, R. et al.: The SMART-1 lunar impact, Icarus, Vol. 207, p. 28-38, 2010.
[7] Melosh, H.J.: Impact Cratering - A Geologic Process, Oxford University Press, New York, p. 101, 1996.
[8] Pierazzo, E. and Melosh, H. J.: Melt Production in Oblique Impacts, Icarus, Vol. 145, p. 252-261, 2000.
[9] Craddock, R.A.: Are Phobos and Deimos the result of a giant impact? Icarus, Vol. 211, Iss. 2, p. 1150, 2011.
How to cite: Buchenberger, B., Sefton-Nash, E., and Witasse, O.: Analysis of topographic profiles of elongated craters on Mars, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-492, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-492, 2021.
Introduction: Recent studies have shown some terrestrial impact structures to possess ejecta ramparts similar to martian impact craters, e.g. Lonar crater in India [1], and Ries crater in Germany [2]. Nonetheless, the formation of ejecta rampart structures is still controversial and several formation models have been proposed to explain the rampart formation process (see review by [3]).
The 26 km diameter Ries crater in Germany is a relatively pristine, complex impact crater characterized by two distinct ejecta lithologies. The built up of the continuous ejecta blanket by a polymict lithic breccia, called Bunte breccia, generally composed of mainly unshocked to weakly shocked sedimentary target clasts, minor amounts of crystalline basement fragments, and reworked surficial sediments [4], overlain by patches of shocked and partly melted crystalline basement material, called suevite [6, 7], is well exposed in several outcrops within the outer rim (see Aumühle Fig.1A).
This study focuses on the trackability of the ejecta layers transition and the documented thickening of the ejecta deposits [2] by ground-penetrating radar (GPR) in Aumühle. We plan to assess the capability of the GPR method for an analogue of particular importance, Lonar crater. Since, Lonar crater occurred in basalts of the Deccan Plateau [5,6], it represents a target lithology that is comparable to the massive basaltic plateaus on Mars.
Methods: The GPR study for Ries crater is investigating the subsurface contact between Bunte breccia and suevite with a bi-static 50MHz-200MHz antenna configuration for constant separation traversing profiles. The spatial arrangement of the profiles in grids allows a reconstruction of the boundary layer (contact plane). In addition, the attenuation of the radar signal has to be studied for layered ejecta deposits, as present in Aumühle, and in a not yet determined basaltic analogue.
Studies prospective: The continuous ejecta blanket of Lonar crater extends to an average distance of 1 km from the crater rim (Fig.1B) and is reported to be divided into two ejecta types as well [8, 9, 10]. An apparent thickening of the ejecta deposits is observable in its distal parts similar to rampart structures on mars [1, 11]. If the Ries study provides a feasible concept, this study will be extended to the distal ejecta parts at Lonar.
Acknowledgments: We thank the “Wissenschaftliche Gesellschaft, Freiburg im Breisgau” for funding the field trip to Ries crater.
References: [1] Maloof et al. 2009 Geological Society of America Bulletin 122:109–126. [2] Sturm et al. 2013 Geology, 41, 531-534. [3] Weiss and Head 2018 Meteoritics & Planet. Sci., 53, 741-777. [4] Hörz et al. 1983 Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 21, 1667-1725. [5] Osae et al. 2005 Meteoritics & Planet. Sci., 40, 1473–1492. [6] Stöffler 1977 Geologica Bavarica, 75, 443-458. [7] Von Engelhardt 1997 Meteoritics & Planet. Sci., 32, 545-554. [8] Fredriksson et al. 1973 Science, 180, 862–864. [9] Kumar et al. 2014. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 119, 2029–2059 [10] Kiik et al. 2020 Geosciences 10, 417. [11] Wulf et al. 2019 Earth. Planet. Sc. Lett., 506, 209-220. [12] USGS Earth Explorer website.
How to cite: Wilk, J. and Wulf, G.: Impact excavation processes studied by Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) on terrestrial analogues for Mars., Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-799, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-799, 2021.
Introduction: The Late Triassic Rochechouart impact structure, Massif Central, France, has been suggested to be one of the largest impact structures in western Europe. A pre-erosion diameter of 40-50km has been proposed [1]. However, the lack of a distinct crater morphology hampers estimates of its dimensions and, thus, an assessment of the event magnitude. A deep erosional level is expected, ~1100 m of basement rocks have been eroded since exhumation was initiated in the Cretaceous [2]. However, a graded suevite at Chassenon (north-central part of the area of impactites) indicates a remarkably complete infill sequence [1]. The suevite resembles resurge deposits known to represent the uppermost parts of impact-generated infill sequences in marine-target craters (e.g., Lockne, Tvären, Chicxulub [3]). The 121.7m deep SC2 hole at Chassenon, intersects 88m of suevite and 25m of basement breccia before reaching a more intact gneissic basement [4]. The lower Rhaetian age of the event [5] places the impact paleogeographically at an isthmus between the Tethys Sea in the south and the Rhaetian Sea to the north [6] following a transgression initiated at that time [7].
Methods: The core logging of SC2 follows the same methodology (i.e., line-logging) as in the studies forming the base for Eq. 1 [3]. This allows analysis of the mode of deposition of the graded suevite, the timing of the impact in relation with the marine transgression, as well as the dimensions of the original pre-erosion crater.
Results: Of the 6002 recorded clasts 63.6% are gneiss, 10.9% granite, 18.4% green melt, 5.5% white melt, 0.9% brown melt, and 0.6% quartzite conglomerate balls. Target rock clasts (i.e., gneiss, granite, and conglomerate) occur relatively evenly throughout the logged section (Fig. 1). The most obvious variation is seen for melt particles.
In a zone between 105m and 103m the plots become organized after having been chaotic below 105m. A clear reverse grading (i.e., reduction in clast size and sorting but increase in clast frequency) occurs between 103m and 81m. Then follows a normally graded interval 81-63m. In the interval 63-39.8m there is again a decrease in number of clasts towards the top. As this is not accompanied with an increase in clast size, it is more likely a consequence of increased matrix content (i.e., mud). At 63m occurs the first obvious change in roundness with a general increase in angularity towards the top of the interval. A drastic shift in the clast frequency (increase), size (increase), sorting (reduction), and lithology (high melt particle content) occurs at 39.8m. The interval 38.9-0m is characterized by a set of repeated graded beds (reverse and normal), although sorting is following a generally improving trend. With a delay of about 7m (39.8-33m) roundness is again increasing in the lower part of the interval, but decreases slightly to the top.
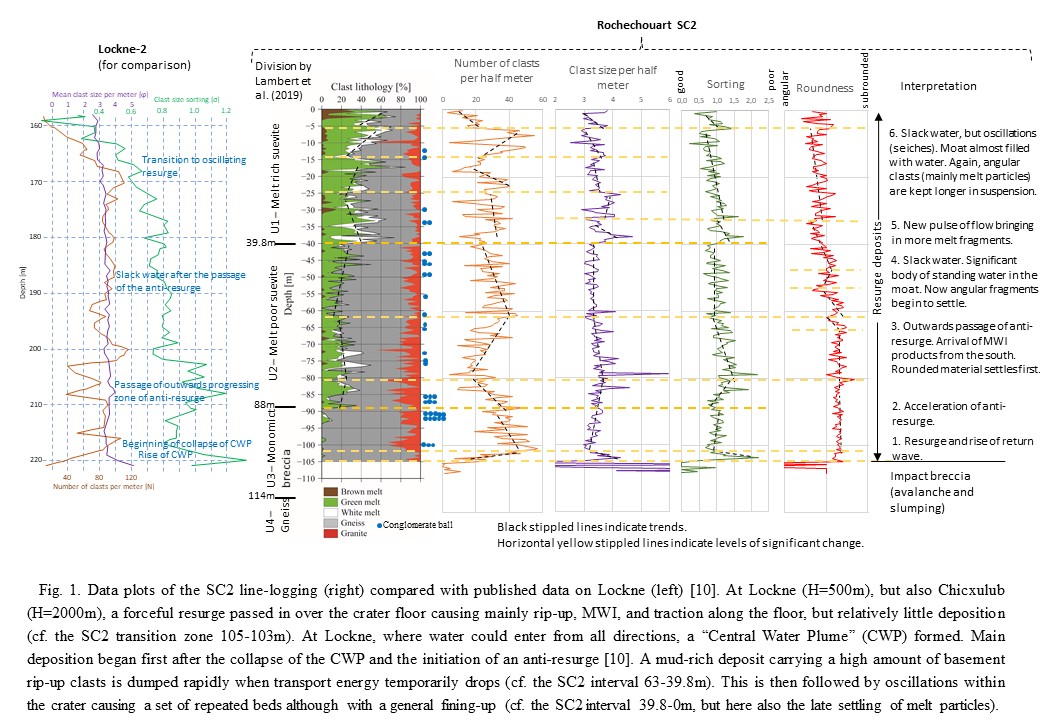
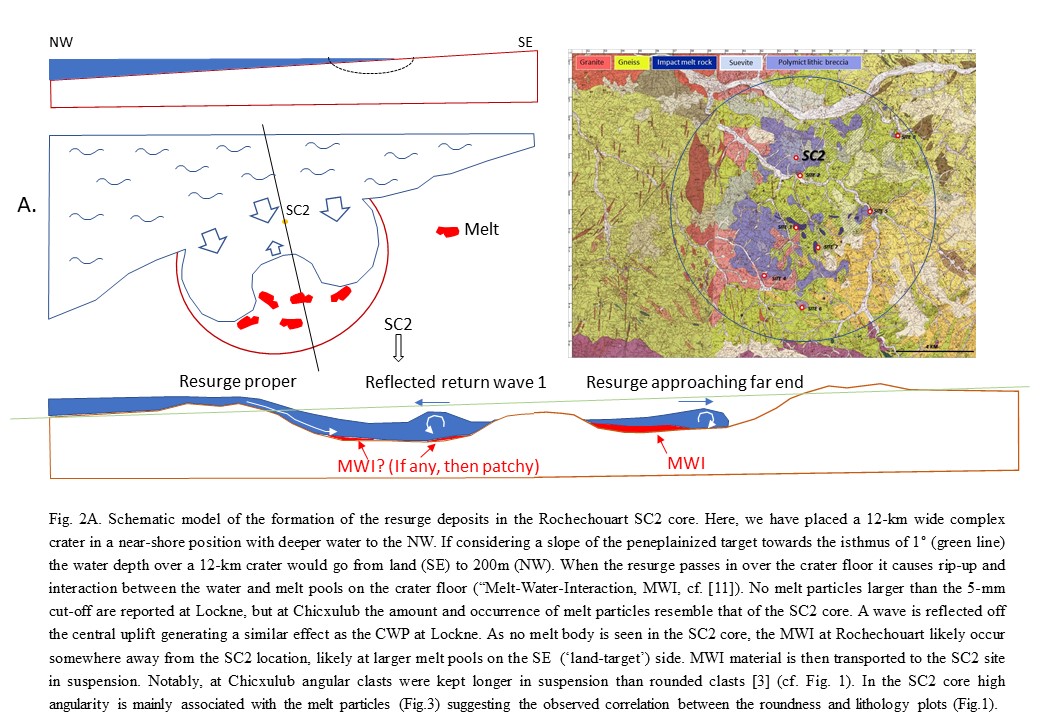
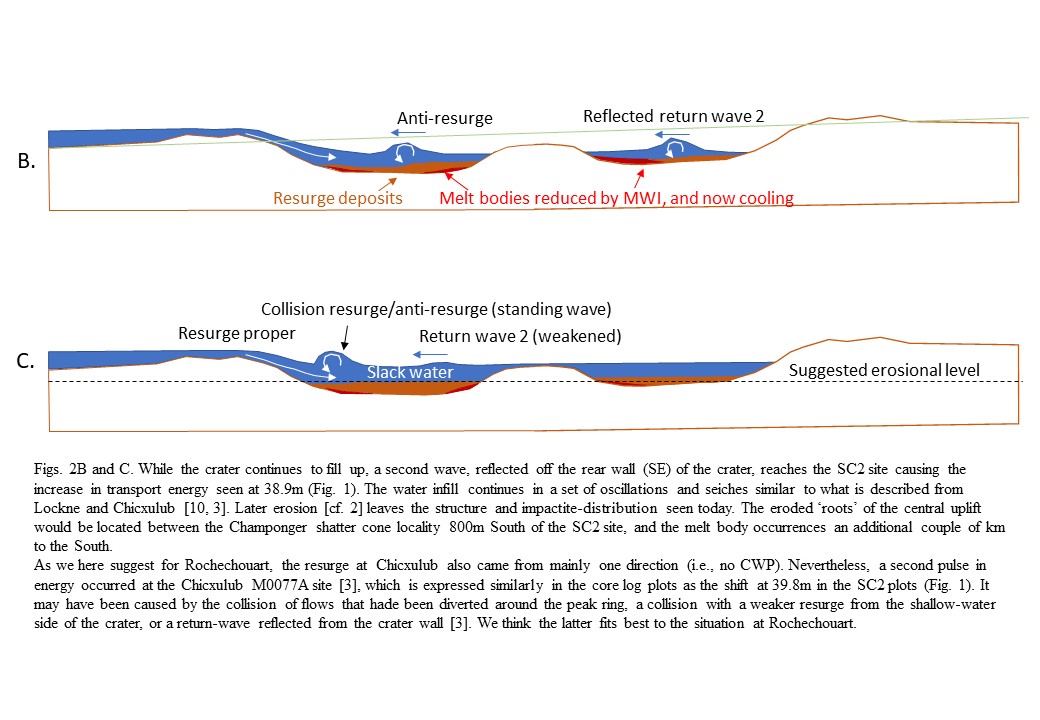
Discussion: The plots allow comparisons with published data on other resurge deposits [3]. Of those, the Lockne-2 core is most similar with respect to clast frequency, size, and sorting variations (Fig. 1). In addition, the Chicxulub M0077A core is comparable with respect to lithology distribution and roundness variation [cf. 3]. The chaotic appearance of the plots below 105m indicates avalanche and slump deposits [cf. 9]. Interval 105-103m represents a short transition zone with initiation of transport and deposition in water [cf. 3]. Suspension deposits begin at 103m and dominates upwards. Figures 1 (right column) and 2 describe the proposed depositional processes and the dynamics of the water flow.
Deposits such as in SC2, Lockne-2 and Chicxulub M0077A indicate a transport as hyperconcentrated flows [cf. 3] with 20-60%vol of material in suspension [12]. Considering the relatively low amount of clasts per meter (58) in SC2 compared with Lockne-2 (85) and Chicxulub M0077A (72) [cf. 3] despite a similar mean clast size (-ϕ 3.4), most likely the sediment load was in the higher end of that span. The overall thickness of the SC2 resurge deposits (>103m) and a sediment load of 50%vol gives a flow depth of ~200m. Numerical simulations of resurge flows indicate the depth of the target sea to be in the same order [13]. Less water would generate a complex set of debris flows, if at all able to pass the elevated rim [cf. 3]. Thus, we can confirm that the Rochechouart impact was marine [cf. 6]. The paleogeography map by [7] shows the rapid formation of the isthmus and deposition of “shallow- to deep- marine carbonates” in the area. However, the absence of any sediment clasts in the SC2 resurge deposits (except for conglomerate balls) indicate insufficient time between the transgression and the impact for formation of sedimentary rock. An impact during the transgression phase is envisaged and fit with the lower Rhaetian age of the impact [5].
Sedimentological studies of resurge deposits from marine-target craters have shown a relation between mean clast frequency (Nmean), impactor diameter (d) and target water depth (H) that allows the estimate of any of these variables when the two others are known [3]:
Nmean=-15(d/H) +100 Eq. 1.
Applying Equation 1 with = 58, H = 200m gives a projectile size of ~560m. A 500m iron projectile, as suggested by [14], generates, according to the impact-effect calculator down2earth.eu [accessed May 2021], a 12km wide crater. This correlates well with the main distribution of impactites in the Rochechouart structure. Therefore, this diameter is used in the process reconstruction in Figs. 2A-C.
Conclusions: Sedimentological analysis of the suevite deposits in the SC2 core near Chassenon confirms a shallow marine target environment for the Rochechouart impact. More generally the results can be used to further constrain the paleotopography and the erosional history of the Western edge of the French Massif Central, the timing of the event relative to the transgression, and the event magnitude.
How to cite: Ormö, J., Sturkell, E., and Lambert, P.: Ocean Resurge Deposits at the Rochechouart Impact Crater, France: Hints to Target Environment and Event Magnitude., Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-55, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-55, 2021.
Introduction
The Lockne crater, located in central Sweden, is a marine-target structure formed approximately 470 million years ago in an epicontinental sea [1][2]. The water depth at the time of the impact is estimated to be around 500 meters [3]. The nearly horizontal target rocks were comprised of, from top to bottom, ~50m of limestone, ~30m of dark, organic rich, shale, and Proterozoic crystalline basement [1]. The structure consists of a 7.5 km wide nested crater, in the basement, surrounded by a 14 km wide outer crater, where most of the sediment material was excavated [2]. Core drilling in the inner nested crater revealed crater-fill breccias composed mostly by sedimentary material, interfingered with crystalline breccia lens (Tandsbyn breccia) and resurge deposits (Lockne breccia and Loftarsone). The Lockne crater has been hypothesized to have been formed by a rubble-pile “pancake” shaped impactor that formed the Lockne-Målingen crater doublet [4]. The objective of this study is to understand, through numerical simulations, the Lockne crater formation based on different asteroid parameters such as dimensions, density, shape, and velocity.
Methodology
The formation of Lockne crater is being simulated by iSALE, an extension of the SALE hydrocode developed to model impact crater formation [5,6,7,8]. Current study focuses on iSALE-2D simulations with an axisymmetric approximation of the original impact problem. The model comprises an asteroid traveling at 20km/s impacting a three-layer target: (1) crystalline basement, (2) ~80 meters of limestone, and (3) 500 m of sea water. Two cases of asteroid shape were considered: a spherical asteroid of diameter 630m and a ‘pancake’ ellipsoidal asteroid with an aspect ratio of 8:1 between the horizontal and vertical axis. In both cases, asteroid damage was set to 1 representing a less cohesive and more fragmented impactor. To ensure comparison across the two cases, the asteroids had the same net mass (2.9 x10^11 kg) and kinetic energy (5.9 x10^19 J).
Results
The spherical asteroid scenario produces a crater of approximately 8 km in diameter and 2 km in depth (Figure 1), whereas the ellipsoid impactor produced a 12km wide crater with 3.5 km in depth. The crater in the ellipsoidal case has not stabilized yet, and the simulation is still running (Figure 2). As expected, the maximum pressure for the spherical impactor at 0.2 seconds is higher (at approximately 33 GPa) than that produced by the pancake impactor (at approximately 28 GPa). This is presented in Figure 3. Despite the differences in dimensions, the collapse of the ejecta curtain, overturn of rim flap, and subsequent outward tsunami formation occurs in similar timesteps in both cratering processes, at about 35-40 seconds. The spherical impactor scenario produces higher wave amplitudes and at about 50 seconds the sea water starts to return into the crater bowl. In the pancake-shaped impactor scenario, the waves amplitude are lower and a greater mass of water is displaced to longer distances in an outward direction from the crater (simulation is still running and resurge water is not visible yet). This is attributed to the pancake shape of the asteroid impacting the target over a wider area. In both scenarios, the proximal ejecta is composed sedimentary material interfingered with large blocks of the crystalline basement.
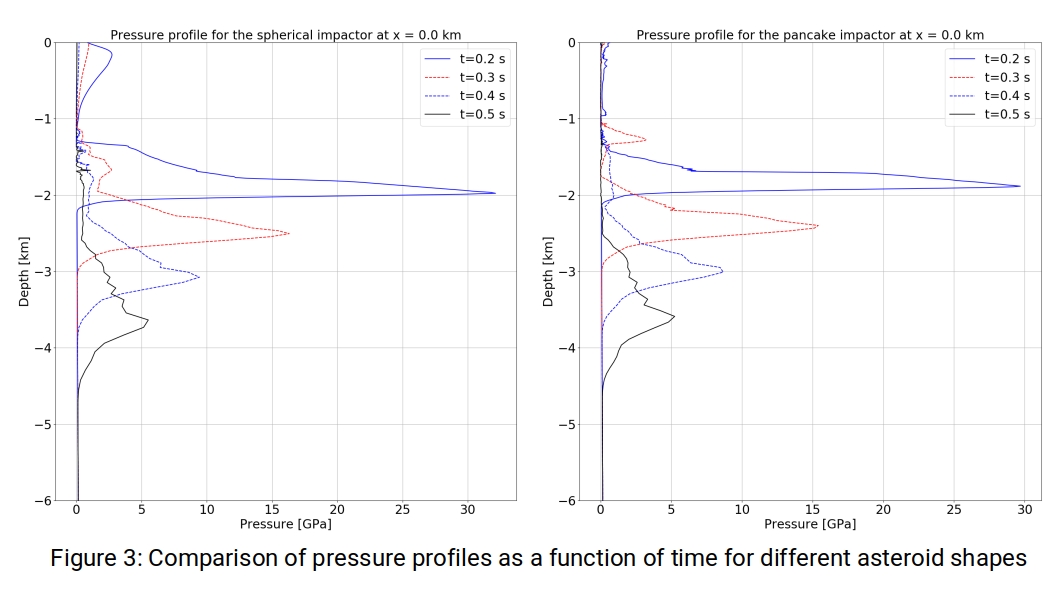
To systematically quantify the effect of asteroid shape and acquire more realistic impact conditions, new simulations are currently running with spherical and ellipsoidal impactors of varying aspect ratio (2:1, 3:1 and 4:1) at an impact speed of 13 km/s and 18 km/s. For a given impact speed, the total asteroid mass (and kinetic energy) is kept the same while the aspect ratio is varied. Additionally, for each combination of asteroid shape and impact speed, two different cases are considered: intact asteroid (with damage set to 0) and loosely packed asteroid (with damage set to 1).
References
[1] Lindström et al. (2005) Impact Studies, Springer 357-388 [2] Ormö et al. (2007) Meteoritics & Planet. Sci. 42, 1929-1943 [3] Ormö et al. (2002) JGR, 107, 31-39 [4] Sturkell E. and Ormö J., EPSC abstracts 2020, EPSC2020-956. [5] Melosh H.J. et al. (1992) JGR 97, no. E9, 14735-14759. [6] Ivanov B.A. et al. (1997) Int. J. Impact Eng. 20, 411-430. [7] Collins G. et al. (2004) MAPS 39, 217-231. [8] Wunnemann K. et al. (2006) Icarus 180, 514-527.
Acknowledgements: The authors are grateful to the CSIC financial support for international cooperation: I-LINK project LINKA20203 “Development of a combined capacity of numerical and experimental simulation of cosmic impacts with special focus on effects of marine targets”.
How to cite: De Marchi, L., King, D., Ormö, J., Sturkell, E., and Agrawal, V.: Numerical modeling of the Lockne impact crater with emphasis on the role of asteroid shape, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-445, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-445, 2021.
Introduction: The morphology of impact basins formed during the first 700 Ma after the Moon-forming event (e.g., [1-2]) is affected by the impactor's size and velocity, and the thermal state of the crust and upper mantle, which is related to the cooling history of the Moon (e.g., [3-5]). Due to alteration and erosion of structural surface features by subsequent impact flux, the size of given basins cannot be determined unequivocally. High resolution Bouguer gravity data from the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission [6-7] show a strong positive anomaly in the center, surrounded by a gravity low for impact basins located at the lunar farside. The relationship between the size of these gravity patterns and basin diameter may allow for estimating the impactor's size and thermal state of the Moon at the time of impact (e.g., [3, 5, 8]).
Previous studies (e.g., [7, 9]) showed that basin formation processes are followed by isostatic adjustment and cooling processes. As a result, basin structures undergo relaxation processes, coupled with modifications in gravity signature. Therefore, the direct comparison of GRAIL data with gravity data from numerical models of basin formation may be questionable.
We summarize results of our systematic numerical modeling study on the influence of the thermal state and impactor size on basin formation processes [5]. Using observed gravity data as constraints for our numerical basin formation models allows for estimating the thermal conditions and the size of the impactor at the time of impact for observable basin structures [5].
Based on this work we now aim at considering isostatic compensation processes and show preliminary results on how to investigate the problem.
Methods: In our previous work, we account for different impactor sizes, crustal thicknesses, and thermal states of the Moon. Different depth-temperature profiles represent the lunar thermal evolution at 4.5 Ga ("warm"), 4.1 Ga ("intermediate") and 3.8 Ga ("cold"), which correspond to approximate basin ages. We correlate modeled Bouguer gravity from our models of basin formation with observed gravity signatures of 16 lunar farside basins.
To evaluate the state of isostatic equilibrium in our best-fit models, we use as a first attempt the isostatic model assuming the Airy concept. Here, different topographic heights are accommodated by changes in crustal thickness. With this approach, we can estimate the location of the crust-mantle boundary for our best-fit models to evaluate the state of isostatic compensation.
Results: Figure 1 shows the transient crater (Dt) , the diameter of the largest crustal thickness (DLCT), and the diameter of the Bouguer anomaly from basin formation models (DBA-mod) as a function of impactor size (Limp). Apparently, Dt, DLCT, DBA-mod depend on the target's thermal state (indicated by the colors). For impactors larger than 40 km in diameter the thermal state affects the size of the Bouguer anomaly [5].
As examples, we discuss here the best-fit models for Korolev crater and Orientale basin: Figure 2 shows the model for the Korolev crater, assuming an impactor size of 50 km and a temperature profile at ca. 4.1 Ga. In Figure 3, the best-fit model for the Orientale basin formed by an impactor of 80 km in a cold lunar environment (3.8 Ga) is shown. The models are fitted to the observed gravity signal (Fig. 2a, 3a, dashed line). The green line (Fig. 2a, 3a) corresponds to the gravity anomaly derived from the basin formation model assuming constant densities in crust (ρc) and mantle (ρm) (Fig. 2b, 3b, left panel). The latter distinctly deviates from the density distribution in our basin formation models (Fig. 2b, 3b); however, we consider the usage of constant densities as a simple estimate of how Bouguer anomalies of our models may look like after cooling. The gravity signal (Fig. 2a, 3a; black line) based on the inhomogeneous density distribution due to the thermal expansion right after impact shows a much lower amplitude and a "plateau" in the basin center. A closer look to the temperature field (Fig. 2c, 3c) reveals that the "plateau" is directly related to the hot area of the temperature field.
In order to assess the isostatic equilibrium of the basin formation models with the inhomogeneous density distribution, we determine the position of the crust-mantle-boundary according to the Airy concept (Fig. 2b, 3b, orange line). Our preliminary results show that the Korolev impact structure is almost in isostatic equilibrium, whereas large changes in the crust-mantle-boundary have to be assumed for the larger Orientale basin.
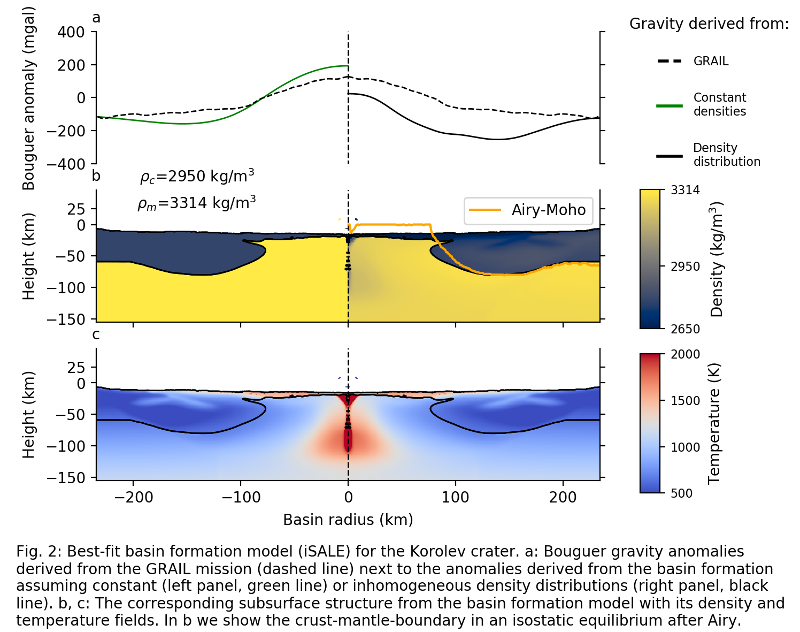
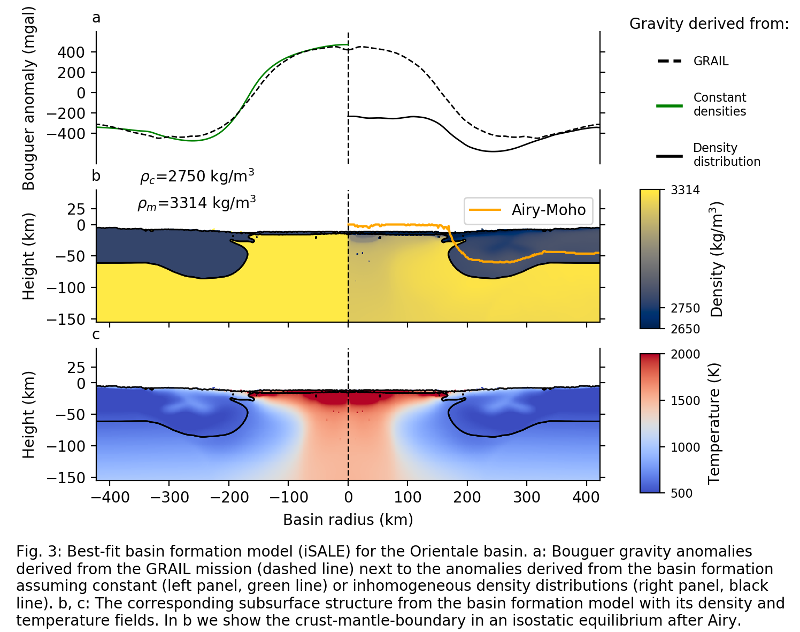
Conclusion: By assuming constant densities in the target, we are able to fit the observed and modeled gravity signatures. But this method of gravity fitting is questionable because the observed gravity data are based on the current subsurface density field, whereas the basin formation models show the density field directly after impact. We expect that cooling of impact structures between the last 4.4 Ga and 3.8 Ga directly affects the density distribution concomitant with isostatic compensation processes changing the position of the crust-mantle-boundary. Thus, the position of the gravity signal will also change.
Acknowledgements: We gratefully thank the developers of iSALE and the pySALEPlot tool. This work is funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Project-ID 263649064-TRR 170).
References: [1] Wilhelms, D.E. (1987) USGS Professional Paper 1348. [2] Morbidelli, A. et al. (2018) Icarus, 305, 262-276. [3] Miljkovic, K. et al. (2016) J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 121, 1695-1712. [4] Potter, R.W.K. et al. (2015) GSA Special Papers, 518, SPE518-506. [5] Lompa, T. et al. (2021) LPSC, Abstract #1254. [6] Zuber, M.T. et al. (2013) Science, 339, 668-671. [7] Melosh, H.J. et al., (2013) Science, 340, 1552-1555. [8] Neumann, G.A., et al. (2015) Sci. Adv., 1, e1500852. [9] Freed, A.M. et al. (2014) J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 119.
How to cite: Lompa, T., Holzrichter, N., Wünnemann, K., and Ebbing, J.: The evolution of the gravity signature of impact structures on the lunar farside, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-363, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-363, 2021.
Abstract
A highly degraded, pre-Nectarian lunar impact basin was proposed for the region between Bailly and Newton craters in 2000. However, a publication in 2010 suggested that there was no basin there. We utilize a combination of topographic and Bouguer anomaly basin fitting tools to provide evidence that the basin exists. A revised centre and diameter of the basin is given of 77°S, 41°W and 402 km respectively. The basin is in an interesting geological context as it straddles the rim of the South Pole Aitken basin.
1. Introduction
In 2000, whilst examining a Clementine nadir stereo derived digital elevation model (DEMs) of the Moon’s south pole region[1], an impact basin was found in a stereo anaglyph visualization of the topographic dataset (Fig 1), and used to find its location in the DEM and an image mosaic. The original position and dimension were quoted as 73°S, 57°W, and 330 km in diameter.
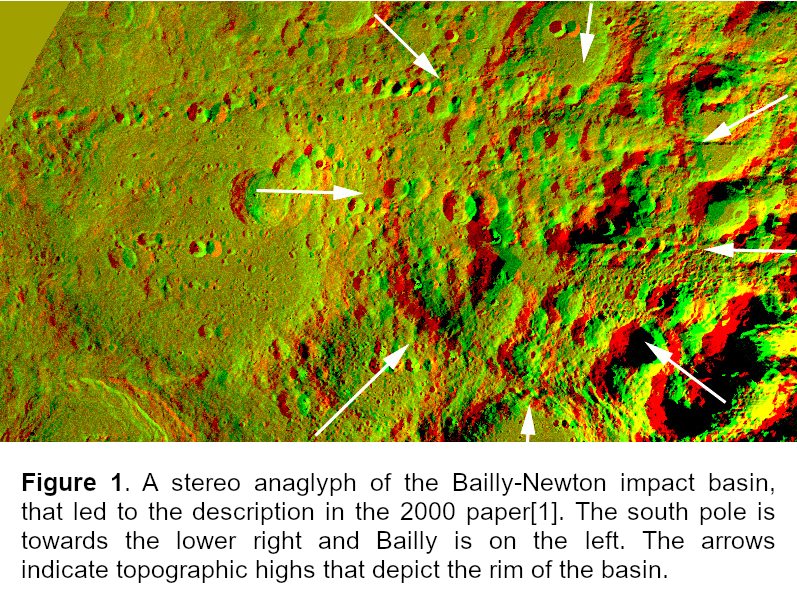
A subsequent study[2] found no evidence for a basin here. This used DEMs, hill shaded views, colour coding, perspective views, and slope maps. Using a variety of existing and new basin measuring tools, we show that there is a basin present after all.
2. Method
Three methods were used to fit a basin floor and rim to a topographic DEM (MoonTopo2600p)[3]: 1) rotational maximum height profile, 2) fitting the rotational topographic profile to three step arc tangent functions, 3) finding prominent peak maxima, ranking these and filtering the less prominent peaks out, leaving just those that should make up the basin rim. Three methods were also used to fit a basin using Bouguer anomaly data (GRGM1200B)[4] using the central mascon and surrounding low annulus: 1) finding prominent peaks maxima and ranking these and filtering out the less prominent peaks which make up the central mascon, 2) fitting the rotational Bouguer anomaly profile, similar to Baker et al.[5] but with two step arc tangent functions, 3) using an annulus method developed by Neumann et al.[6] with the annulus with inner and outer diameters set to 50% and 100% of the basin diameter, and an inner disc of 20% of the basins diameter. The difference between the annulus and the inner circle was a measure of the basin contrast.
These methods were tested out on lists of published basin tables, and found to vary in diameters found by each algorithm, for each basin, if for example the basin was on a slope or was sitting on some other large scale topographic features, this could skew the results. However, a combination of topographic fit and Bouguer peak methods seemed to produce results closest to published values[6]. However, plotting out all the basin ring diameters on the DEM and then using one’s eye to judge which diameter was most appropriate, was a practical solution.
3. Analysis of the Bailly-Newton Basin
Three different topographic basin measuring algorithms were applied to the DEM (Table 1) and three wildly different diameters were found. The peak method got locked onto the central topography in the basin and yielded an unrealistically small diameter for the basin – see inner blue circle in Fig 2. The rotational maxima algorithm also produced a result, the 2nd largest circle in Fig 2, that clearly does not relate to the true nature of the basin rim. The fitting to three step arc tangent functions though produced the largest diameter circle in Fig 2 and this neatly portrays the outer eroded rim of the basin.

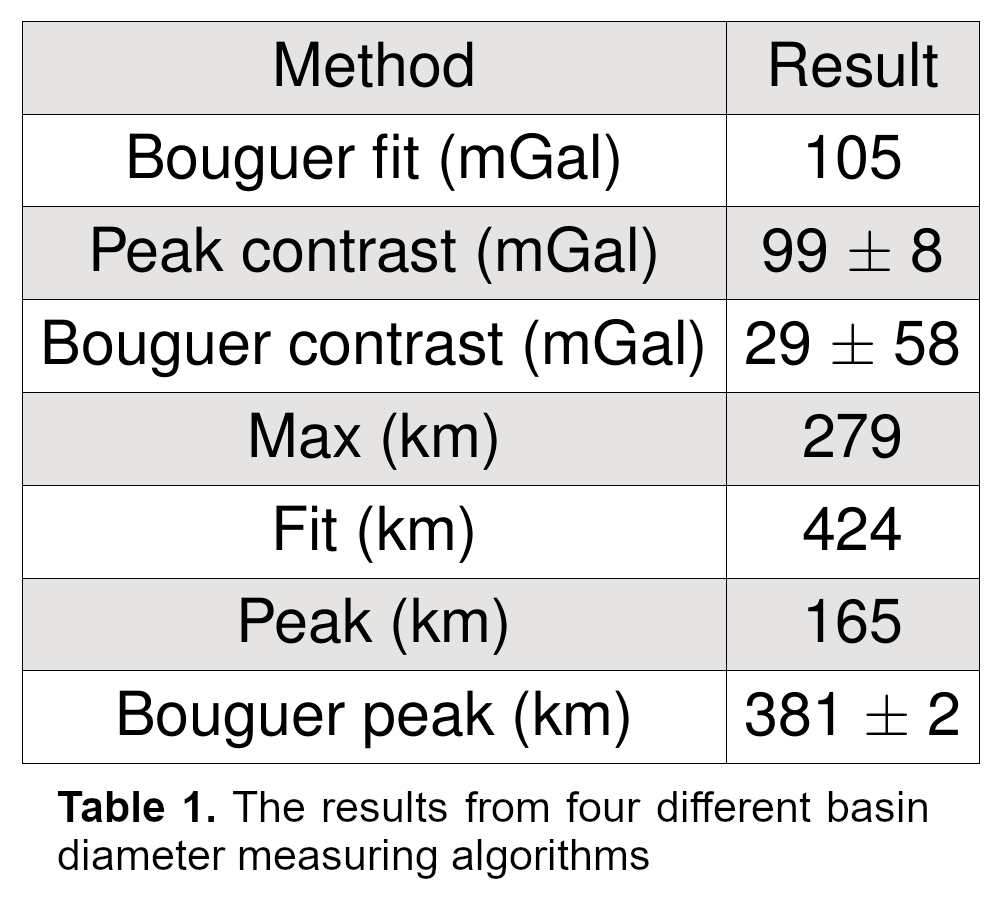
Concerning the Bouguer anomaly map of the same area, there is considerable noise, however once the Bouguer fit method is applied, a central mascon and surrounding annulus can be seen in Fig 3. The basin diameter derived by Bouguer peak algorithm is depicted by the 2nd largest circle in Fig 2. Using the topography in Fig 2 as a guide, the two outer circles appear to best fit the rim of the basin.
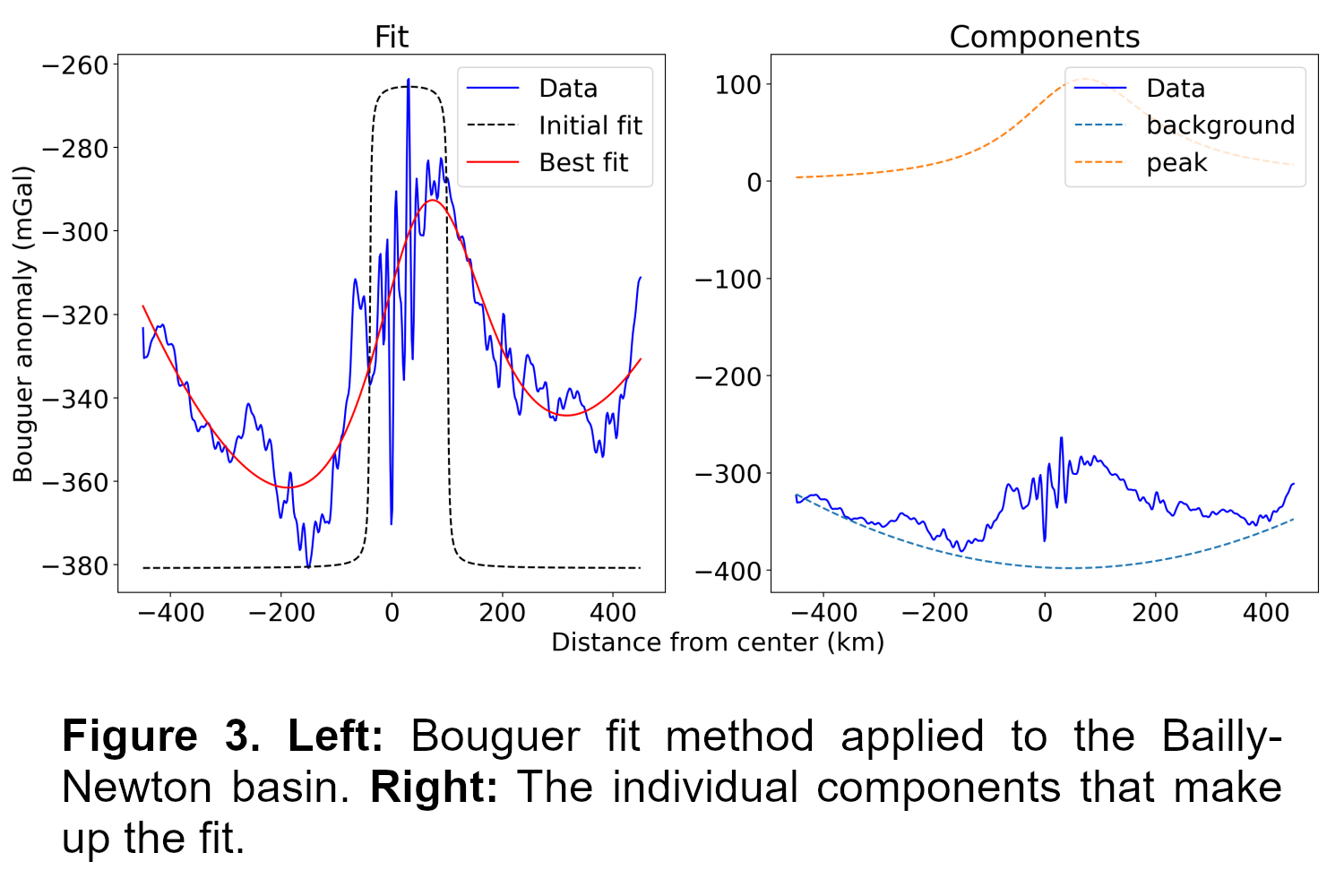
4. Discussion
Our analysis show that the Bailly-Newton basin is present and that it is larger than the estimate published in 2000, of 330 km namely, between 381 km and 424 km, depending upon which of the two best basin measuring method was used – with a mean 402 km. Although visual inspection of topographic data, slope maps, visualizations, can pick out obvious basins, a combination of algorithms applied to topographic and Bouguer anomaly data can identify more degraded basins. It is possible that the inclusion of evidence of other basin characteristics such as radial ejecta scour marks, and geological/geomorphological evidence[7] could help identify similar or more extensively degraded ancient basins.
References
[1] Cook et al., (2000) JGR (Planets), 105, p12,023-12,033. [2] Oberst et al., (2010) EPSC2010-827, [3] Wieczorek, (2015) Treratise on Geophysics (second edition), 10, p153-193. [4] Goosens et al. (2019) JGR (Planets), 125, e2019JE006086, [5] Baker et al., Icarus, 292, p54-73, [6] Neumann et al., (2015) Science Advances, 1(9), ISSN: 2375-2548. [7] Liu et al., (2020) 51st LPSC, abstract #1940.
How to cite: Aalhus, S., Cook, A., and Sheward, D.: Confirmation of the Bailly-Newton Impact Basin, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-724, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-724, 2021.
1. Introduction
The Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) mass extinction is marked globally by elevated concentrations of the platinum group elements (PGE), emplaced by a impact event 66.051 ± 0.031 Ma ago [1][2]. The 180- to 200-km-wide Chicxulub impact structure on the Yucatán Peninsula [3] is being considered as a possible impact crater that led to the global enrichment of PGE at the K-Pg boundary. The PGE signature (data from [4]) in the gray-green marlstone interval of Core 40R-1 recovered from Site M0077 on the Chicxulub peak ring in the Gulf of Mexico is distinctly different from a meteoritic component consistent with a chondritic impactor as well as the near-chondritic PGE abundance pattern at the European K-Pg boundary sites of Caravaca in Spain and Stevns Klint in Denmark.
2. Non-chondritic PGE abundance pattern at the Chicxulub impact structure
The PGE pattern (or inter-element ratios) from the upper transitional unit (TU; 616.58-616.60 mbsf) [4], Stevns Klint, Caravaca [5], Earth’s upper mantle, and crust [6][7], and the iron meteorite Mundrabilla [8] are shown in Figure 1. Unfortunately Rh was not determined. Significant differences can be seen, for example, in the Ru/Ir ratio (Table 1).
While the K-Pg sediments from Europe show a subchondritic Ru/Ir ratio of about 1.3, the suprachondritic Ru/Ir ratios of sediments from core 40R-1 range from about 2 to 4 (Figures 1-4).
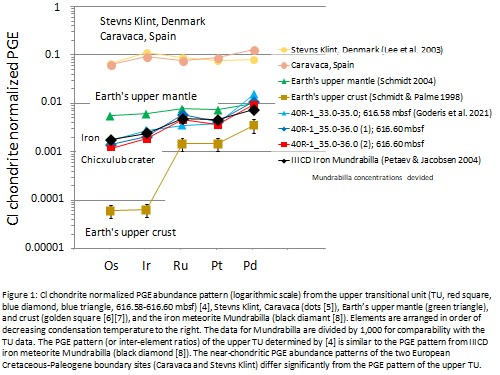
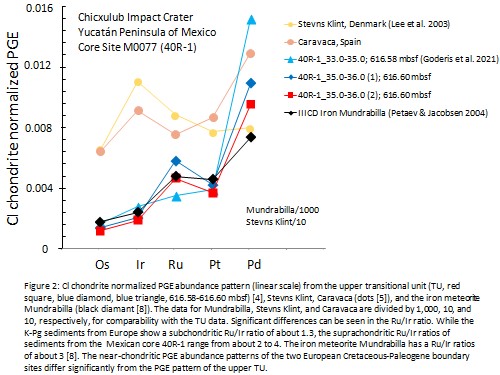
The Ru/Ir ratio of about 4 was measured on two subsamples from a depth of 616.6 mbsf at the University of Tokyo in Komaba using a Thermo Element XR HR-ICP-MS. The Ru/Ir ratio of about 2 was measured by ID-MS on one sample (616.58 mbsf) at the Vrije Universiteit Brussel [4]. The iron meteorites Mundrabilla and Duchesne have Ru/Ir ratios of about 3 and 5, respectively [8].
The signature of the upper TU from the drill core is similar to the PGE pattern from the irons Mundrabilla and Duchesne (Figure 4). This observation calls into question the Chicxulub impact structure as the source crater for the near-chondritic PGE ratios in European K-Pg boundary sites. The non-chondritic PGE ratios of the upper TU are evidence that the globally distributed iridium layer is not preserved in the Chicxulub impact structure. The most likely source for the PGEs in the upper TU of core 40R-1 sediments are Mundrabilla and Duchesne like iron impactors.
3. Future studies
The Ru isotope composition could be used as a powerful analytical tool alongside PGE ratios (especially the diagnostic Ru/Rh and Ir/Rh mass ratios [9]) to identify impactor signatures [10].
4. Conclusion
It seems to have been different projectile types and different temporal events [11][12], that left the near-chondritic PGE abundance patterns in Europe and the iron meteoritic abundance pattern in the sediments of the Chicxulub impact crater. When talking about synchronicity, it is easily overlooked that enormous time spans of ±31 ka (uncertainties) are meant for events that took place about 66 Ma ago. However, relative dating of individual events and their correlation is possible with lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy and can be supplemented, but not replaced, by radioisotope dating.
References
[1] Alvarez L. W., Alvarez W., Asaro F. & Michel H. V. (1980) Extraterrestrial cause for the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction. Science 208, 1095 - 1108.
[2] Renne P. R., Arenillas I., Arz J. A., Vajda V., Gilabert V. & Bermúdez H. D. (2018) Multi-proxy record of the Chicxulub impact at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary from Gorgonilla Island, Colombia. Geology 46, 547 - 550.
[3] Hildebrand A. R., Penfield G. T., Kring D. A., Pilkingston M., Camargo Z. A., Jacobsen S. B. & Boynton W. V. (1991) Chicxulub Crater: A possible Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary impact crater on the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico. Geology 19, 867 - 871.
[4] Goderis S., Sato H., Ferrière L., Schmitz B., Burney D., Kaskes P., Vellekoop J., Wittmann A., Schulz T., Chernonozhkin S. M., Claeys P., de Graaff S. J., Déhais T., de Winter N. J., Elfman M., Feignon J.-G., Ishikawa A., Koeberl C., Kristiansson P., Neal C. R., Owens J. D., Schmieder M., Sinnesael M., Vanhaecke F., Van Malderen S. J. M., Bralower T. J., Gulick S. P. S., Kring D. A., Lowery C. M., Morgan J. V., Smit J., Whalen M. T. & IODP-ICDP Expedition 364 Scientists (2021) Globally distributed iridium layer preserved within the Chicxulub impact structure. Science Advances 7, eabe3647.
[5] Lee C.-T. A., Wasserburg G.J. & Kyte F. (2003) Platinum-group elements (PGE) and rhenium in marine sediments across the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary: Constraints on Re-PGE transport in the marine environment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 67, 655 - 670.
[6] Schmidt G. (2004) Are high-temperature fractionations in the solar nebula preserved in highly siderophile element systematics of the Earth’s mantle? Meteoritics & Planetary Science 39, 1995 - 2007.
[7] Schmidt G. & Palme H. (1998) The concentrations of highly siderophile elements in Earth's upper crust as inferred from the compositions of large terrestrial impact melt sheets. 29th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #1273
[8] Petaev M.I. & Jacobsen S.B. (2004) Differentiation of metal‐rich meteoritic parent bodies: I. Measurements of PGEs, Re, Mo, W, and Au in meteoritic Fe‐Ni metal. Meteoritics & Planetary Science 39, 1685 - 1697.
[9] Schmidt G. (2019) Ru/Rh and Ir/Rh as diagnostic mass ratios for the identification of specific impactor compositions of terrestrial impact craters. Paneth Kolloquium, Nördlingen (Germany), Abstract #0009
[10] Schmidt G. (2019) Distinguishing different types of projectiles from terrestrial impact craters – Clearwater East (Canada) and Rochechouart (France) re-investigated. Large Meteorite Impacts and Planetary Evolution VI, Lunar and Planetary Institute Contribution No. 2136, Abstract #5006.
[11] Keller G., Stinnesbeck W., Adatte T. & Stüben D. (2003) Multiple impacts across the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary. Earth-Science Reviews 62, 327 - 363.
[12] Keller G. (2005) Impacts, volcanism and mass extinction: Random coincidence or cause and effect? Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, 725 - 757.
How to cite: Schmidt, G.: Chicxulub impact crater data from the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico re-interpreted: evidence for an iron meteoritic asteroid as impactor, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-49, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-49, 2021.
1. Introduction
The AIDA international collaboration, which includes the DART (NASA) and Hera (ESA) missions, aims to test the technology of deflection by a kinetic impactor and to enhance our understanding of small bodies in general. In the context of these missions, a spacecraft, DART, will impact the secondary of the 65803 Didymos system, Dimorphos, at the end of October 2022 [1]. The impact will eject asteroid material from the target surface, leading to a measurable change in the orbital period of the binary. A second, follow-up spacecraft, Hera, will arrive at the system several years after the impact to characterize the system and the impact consequences [2].
The objective of this study, which is conducted in the context of the NEO-MAPP project, is to model the collision of the kinetic impactor with Dimorphos and to predict the outcome of the impact with respect to parameters that are measurable by spaceborne and in-situ instrumentation provided by the Hera mission. We model the impact using two different numerical schemes: a continuum approach using iSALE-2D/-3D & a smooth particle approach using Bern SPH. Although all codes solve similar forms of conservation equations and use similar constitutive models, different numerical schemes can produce systematically different results. Hence, as a first step, accurate validation tests against laboratory experiments are conducted to improve the reliability of results from numerical modelling.
2. Method
iSALE-2D/-3D [3, 4] is a grid-based arbitrary Eulerian Lagrangian (ALE) code and is best suited to study crater formation and the propagation of shock waves from a high velocity impact into targets with a variety of different properties. On the other hand, Bern's grid-free Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) [5, 6] is most appropriate to study the ejection of material and processes where the entire target body is involved. Both codes include the simulation of material compaction (iSALE: ε-α model; SPH: P-α model) and different strength models. In this study, we employ the Drucker-Prager and the Lundborg rheology models to describe the strength of the material. For both codes, the ejection behaviour is analysed as described in [7,8,9], and the ejection data is used to determine the momentum transferred to the target for deflection (momentum enhancement factor β = ejecta + impactor momentum / impactor momentum). This approach was used previously for systematic parameter studies [9] and benchmarking studies [10]. To validate our shock physics codes, we compare our results against observations from a recent laboratory study [11], where PVC projectiles with a mass of ~25 mg were accelerated to velocities of 1-2 km/s, impacting glass beads, sand and regolith simulant targets. In a second step, we continue the benchmarking work done by the Hera impact working group [12] to detect, assess and remove deviations between two different numerical schemes, iSALE (in 2D and 3D) and Bern SPH at the scale of the DART impact.
3. Validation
We have simulated the crater formation in glass beads and regolith simulant with iSALE-2D at impact speeds of 2.4 km/s and 2.2 km/s, respectively. The glass beads target was modelled using a Drucker-Prager criterion with a coefficient of internal friction, f = 0.5 and an initial porosity of 35%. The regolith simulant used f ~ 0.8 and an initial porosity of 42%. We determine β-values of 2.9 and 1.4, which agree well with experimentally determined values of 2.7 and 1.3, respectively. In the glass beads target laboratory experiment, at ~0.5-1 ms after the impact, the ejecta curtain made an angle of 50-60°. In the case of the regolith simulant, at ~0.5 ms after the impact, the ejecta curtain angle was 30-40°. From our numerical models, we determined ejecta curtain angles 0.5 ms after the impact as 48° (glass beads) and 30° (regolith, Fig. 1). Both results agree with the lower bound of the experimental constraints.
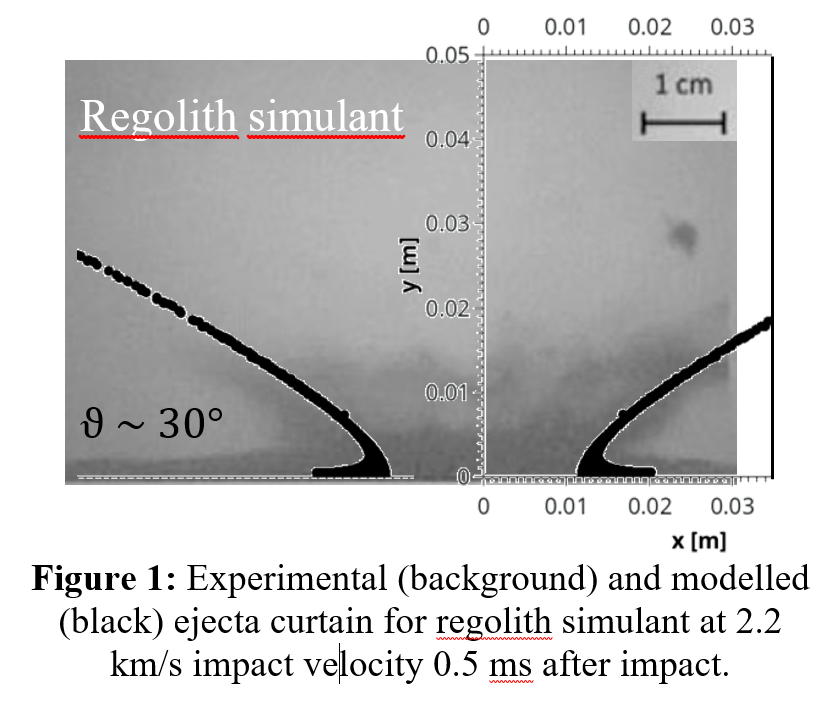
4. Benchmark
The first benchmark study focuses on the influence of target properties on the efficiency of the momentum transfer from the DART impact, β, for materials similar to the regolith simulant. The 600 kg projectile impacts targets with varying porosities, between 10 and 50%, and cohesions from 1 to 100 kPa, at a velocity of 6 km/s. The second benchmark study focuses on the influence of the impact angle on β for the 20% porosity case with 10 kPa cohesion at an impact velocity of 7 km/s.
In previous studies, we found generally good agreement between the results derived with iSALE and SPH [12, 13, 14]. However, for certain porosities the deviations between the results were larger (e.g., 20% porosity and 1 kPa cohesion), which may have been the result of discrepancies in the details of the crush curve used in each model. As a result, here we conducted new models with more consistent crush curves (Fig. 2).
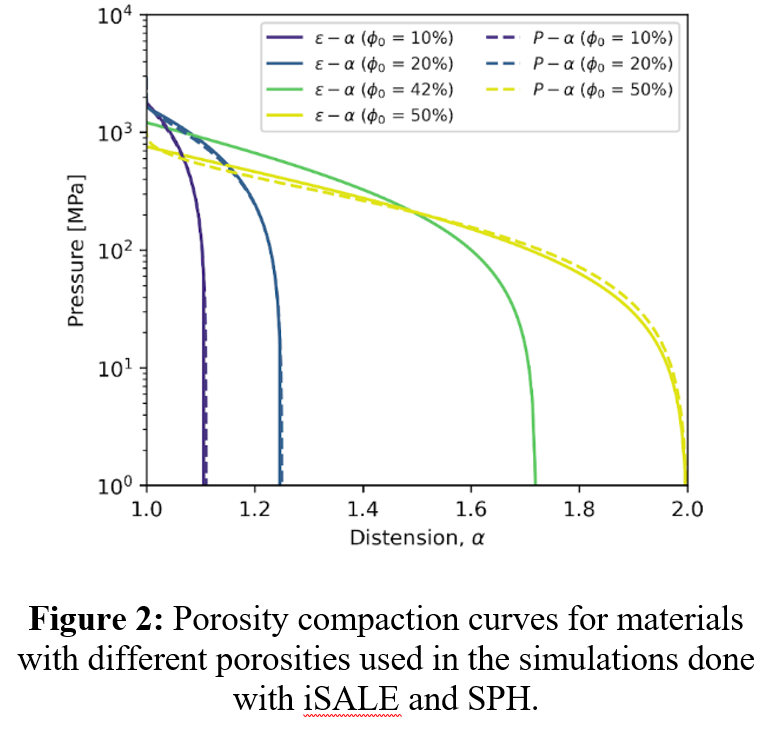
Varying the impact angle for a specific impact scenario and set of target properties shows a remarkably good agreement between the two codes (Fig. 3).
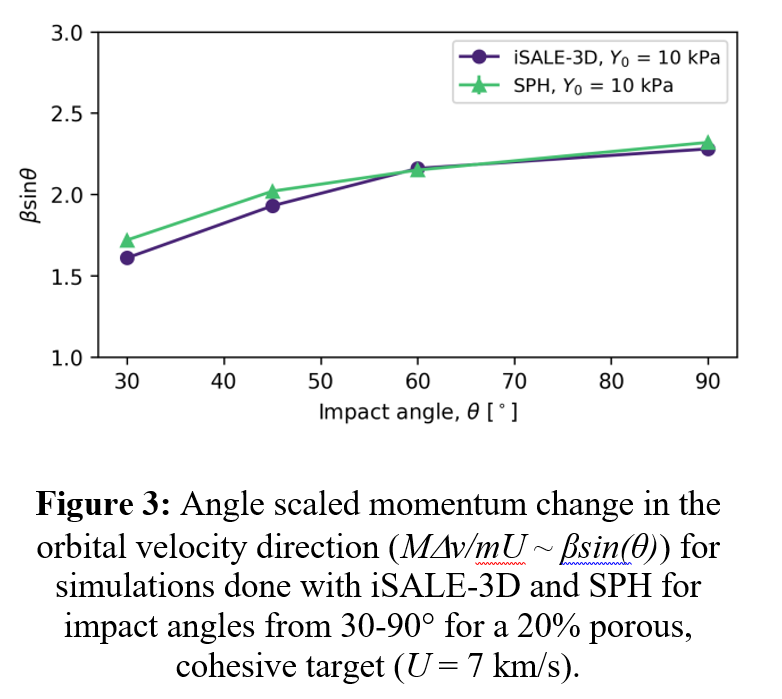
5. Summary
Our joint modelling and experimental approach to study the efficiency of asteroid deflection by a kinetic impactor shows that there is generally a good agreement between different numerical approaches and experimental work. The benchmark studies show that the results from the grid based iSALE (-2D/-3D) and the meshless SPH can deviate for similar initial porosities when the crush curves are not consistent, but they produce similar results when the same impact conditions are considered.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the developers of iSALE (www.isale-code.de). This work has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme, NEO-MAPP, grant agreement No. 870377.
References
[1]A.F.Cheng et al.,P&SS157(2018)104-115.
[2]P.Michel et al.,AdvSpaceRes.62(2018)2261-2272.
[3]K.Wünnemann et al.,Icarus180(2006)514–527.
[4]D.Elbeshausen et al.,Icarus204(2009)716–731.
[5]M.Jutzi et al.,Icarus198(2008)242–255.
[6]M.Jutzi,P&SS107(2015)3–9.
[7]M.Jutzi&P.Michel,Icarus229(2014)247-253.
[8]R.Luther et al.,M&PS53(2018)1705–1732.
[9]S.D.Raducan et al.,Icarus329(2019)282–295.
[10]A.Stickle et al.,Icarus338(2020)113446.
[11]S.Chourey et al.,P&SS194(2020)105112.
[12]R.Luther et al.,EPSC-DPS2019-1776(2019).
[13]S.D.Raducan et al.,52th LPSC(2021)#2548id1908.
[14]R.Luther et al.,7th PDC(2021)#122.
How to cite: Luther, R., Raducan, S. D., Jutzi, M., Wünnemann, K., Michel, P., Zhang, Y., Koschny, D., Davison, T. M., Collins, G. S., Schäfer, C., and Burger, C.: Simulating the Momentum Enhancement with iSALE and SPH: An AIDA Benchmark & Validation Study, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-225, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-225, 2021.
Carbonaceous asteroids, which are minor bodies but enriched in water and organics, have been extensively explored by HAYABUSA2 and OSIRIS-REx recently because they are thought to be the major carrier of volatiles to the inner planets in our solar system. The recent explorations revealed that two carbonaceous asteroids, Ryugu and Bennu, and their parent bodies suffered impact bombardments with a variety of impact energies. It has been hypothesized that Ryugu has lost a fraction of the volatiles due to some sorts of heating events [Kitazato et al., 2019]. In contrast, Bennu apparently did not suffer such a volatile loss [Hamilton et al., 2019]. Shock recovery experiments with metal containers performed in the 1980s suggested that chondritic meteorites could easily lose their volatiles during hypervelocity impacts [Tyburczy et al., 1986], leading to different impact histories being inferred to explain the difference in volatile contents. In this study, we revisited the total gas production during impact devolatilization of carbonaceous chondrite analog [Britt et al., 2019], hereafter referred to as CI simulant, with a two-stage light gas gun. We applied a new experimental technique for gas guns, which is referred to as the “two-valve method” [Kurosawa et al., 2019], to minimize the chemical contamination from the gun operation. The two-valve method allows us to investigate impact devolatilization in a fully open system where is the same geometry of natural impact phenomena.
Hypervelocity impact experiments were performed with a two-stage light gas gun placed at Planetary Exploration Research Center of Chiba Institute of Technology, Japan. An Al2O3 projectile with a diameter of 2 mm accelerated to two different impact velocities vimp = 3.7 km/s and 5.8 km s-1. Hereafter, we refer the two velocities as “the low vimp” and “the high vimp”, respectively. Helium gas was used to accelerate the projectile instead of frequently-used hydrogen gas to exclude the possibility that a trace amount of the gas for projectile acceleration causes the chemical reduction. A quadrupole mass spectrometer (QMS) was used to measure the composition and amounts of impact-generated gases.
The experimental results are summarized as follows: (1) The total gas production was limited only to a few wt.% of the projectile mass even at the high vimp, (2) the most abundant product was CO2 in all the shots, (3) the chemical composition, including CO/CO2 ratio and H2/CO ratio, did not depend on impact velocity, (4) the impact-generated vapor was depleted in sulfur with respect to the elemental composition of the CI simulant.
Here, we discuss about the controlling mechanism of impact devolatilization. Since the carbon source in the CI simulant is only crushed coal grains, which is mixed into the CI simulant as an analog for insoluble organic matters, the detected C-bearing gases, which are CO and CO2, must be produced due to oxidation of the organics in the CI simulant. Thus, the molar ratio of CO to CO2 is simply determined by the oxygen fugacity, which strongly depends on temperature, in the region where the devolatilization occurs. We could estimate the temperature of the devolatilization region by comparing the oxygen fugacity for the elemental composition of the CI chondrites [Schaefer and Fegley, 2017], suggesting that the temperature is 1,200–1,650 K at both high and low vimp. We also conducted shock physics modelling with the iSALE shock physics code [Amsden et al., 1980; Ivanov et al., 1997; Wünnemann et al., 2006; Collins et al., 2016]. We estimated post-shock residual temperature field after pressure release with the ANEOS serpentine by taking the endothermic decomposition of hydrous minerals and organics in the CI simulant into account. We found that the temperature in the iSALE was much lower than the temperature of the devolatilization region inferred from the CO/CO2 ratio. The large gap in the temperature between the experiment and the shock physics modelling indicates that a local energy concentration may be caused by velocity shear between the different grains with a large contrast in shock impedance. The above hypothesis about local heating is consistent with the low efficiency of impact devolatilization. Our experiment, shock physics modelling, and thermodynamic consideration suggest that hypervelocity impacts are not responsible for significant volatile loss from the parent body of Ryugu or from Ryugu itself [Kurosawa et al., Under review].
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by ISAS/JAXA as a collaborative program with the Hypervelocity Impact Facility. We appreciate the developers of iSALE, including G. Collins, K. Wünnemann, B. Ivanov, J. Melosh, and D. Elbeshausen. We also thank Tom Davison for the development of the pySALEPlot.
Key references:
Amsden, A., Ruppel, H. & C. Hirt. SALE: A simplified ALE computer program for fluid flow at all speeds. Los Alamos National Laboratories Report, LA-8095:101p (1980).
Collins, G. S., Elbeshausen, D., Davison, T. M., Wünnemann, K., Ivanov, B. A., and Melosh, H. J. iSALE-Dellen manual, Figshare, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.3473690.v2 (2016).
Hamilton, V. E. et al. Evidence for widespread hydrated minerals on asteroid (101955) Bennu. Nature Astronomy 3, 332–340 (2019).
Ivanov, B. A., Deniem, D. & Neukum G. Implementation of dynamic strength models into 2-D hydrocodes: Applications for atmospheric breakup and impact cratering. Int. J. Impact Eng. 20, 411–430 (1997).
Kitazato, K. et al. The surface composition of asteroid 162173 Ryugu from Hayabusa2 near-infrared spectroscopy, Science 364, 272–275 (2019).
Kurosawa, K., Moriwaki, R., Komatsu, G., Okamoto, T., Sakuma, H., Yabuta, H. & Matsui, T. Shock vaporization/devolatilization of evaporitic minerals, halite and gypsum, in an open system investigated by a two-stage light gas gun. Geophysical Research Letters 46, 7258–7267 (2019).
Schaefer, L., & Fegley, B. Jr. Redox states of initial atmospheres outgassed on rocky planets and planetesimals. The Astrophysical Journal 843, 120 (2017).
Tyburczy, J. A., Frisch, B., and Ahrens, T. J. Shock-induced volatile loss from a carbonaceous chondrite: implications for planetary accretion. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 80, 201–207 (1986).
How to cite: Kurosawa, K., Moriwaki, R., Yabuta, H., Ishibashi, K., Komatsu, G., and Matsui, T.: Do hypervelocity impacts on carbonaceous asteroids cause significant volatile loss?, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-508, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-508, 2021.
Introduction: NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) will impact the smaller component of the 65803 Didymos asteroid system, Dimorphos, and alter its orbital period around the primary, thus demonstrating the controlled deflection capabilities of near-Earth asteroids by a kinetic impactor [1, 2]. ESA’s Hera mission [2] will arrive at Dimorphos several years after the DART impact and provide a detailed characterization of the impact outcome, including the morphometry and morphology of the crater. Recent impact experiments and numerical studies [3–5] have shown that the kinetic impact efficiency depends strongly on the target properties and structure, and is non-unique (i.e., a number of target property configurations, such as different cohesion-porosity combinations, can result in the same deflection and a measure of the deflection alone can be interpreted in different ways depending on the target and impact properties). Therefore, for a successful interpretation of the DART impact outcome it is important to understand the influence of asteroid properties on the cratering process. Moreover, the DART impact outcome analysis will be based on numerical models, which require extensive and accurate prior validation.
Most previous impact experiments and the subsequent validation work of numerical models have focused on homogeneous targets [e.g., 6, 7]. However, it is unlikely that Dimorphos is homogeneous at the scale of DART impact. Here we present preliminary results from impact experiments and numerical simulations specifically designed to mimic asteroid surface materials and structures (e.g., layered targets, rubble piles). The experiments are performed at the Experimental Projectile Impact Chamber (EPIC) at Centro de Astrobiología CSIC-INTA, Spain.
Methods: The EPIC utilizes a 20 mm calibre compressed N2 (300 bar) cannon that launches projectiles at velocities up to ≈420 m/s and at angles of 20– 90◦ from horizontal [8]. The experiments, half- or quarter-space, are recorded with high-speed cameras and the resulting crater profiles are scanned in 3D with 0.5 mm resolution. Here we use the iSALE-2D [9] and the Bern SPH [10] shock physics codes to simulate the laboratory experiments. Both iSALE-2D and SPH include material models suitable for geological materials, various equations of state and porosity compaction models. We compare numerical models with impact experiments into targets with three different structures: homogeneous, layered and heterogeneous.
Results and discussion:
- Vertical impacts into homogeneous targets. These impact experiments were performed into dry beach sand ("slow pour" maximum compaction) and iron grit targets and the results are used to validate the ejecta curtain formation and crater size from 2D numerical models into homogeneous targets. This setup is also used as reference for comparison with more complex target settings.
- Layered targets. Recently visited asteroids (e.g. Itokawa, Ryugu) have been observed to have a layered structure (i.e., a layer of regolith overlying a much stronger and denser substrate). The effects of target layering on impact cratering in the strength regime have been studied extensively through laboratory experiments [e.g., 11] and simulations [e.g., 12]. However, it is possible that Dimorphos has a granular cohesionless upper layer and that cratering in this layer is gravity-controlled, much like Hayabusa2’s SCI experiment [13]. Little is known of the effects of layering in the gravity regime, however it is likely that the momentum transferred from the DART spacecraft can be both amplified or reduced, depending on Dimorphos’ layering configuration [12]. We carry out experiments with layers of different density (i.e., beach sand over iron grit) to simulate gravity-controlled cratering in layered targets. While much of the kinetic energy of the projectile is released in the weaker upper target, this material also requires relatively less energy to be cratered resulting in a concentric crater morphology. This crater morphology is well reproduced in our iSALE-2D numerical models.
- Complex target structures/"rubble piles". Variations in strength and density also occur in very heterogeneous objects such as rubble-pile asteroids. An irregular crater growth and, consequently, irregular ejection of material affect the asteroid deflection (e.g., unpredictable motions). Such irregularities are difficult to model numerically and require full 3D geometry, which is computationally expensive. Nevertheless, efforts to model rubble pile geometries in the context of DART are undertaken [14] and laboratory experiments are essential to validate such models. We have performed shots into targets with porous ceramic balls (simulating “boulders”) of approximately equal size and weight as the projectile embedded in a matrix of beach sand (“slow pour” maximum compaction) (Fig. 1). Experiment 1 had balls distributed uniformly and at regular intervals within the sand. Experiment 2 had the same configuration, but only in half of the target while the other half was beach sand only. Comparisons were then made with the reference shot in pure beach sand. There is now a very good fit between the reference crater (Exp3) and the part of the Experiment 2 crater developed in the pure sand target, and there is an equally good fit between the half of the crater developed in the “rubble-pile” part of the target and the crater from Experiment 1 (Fig. 2). The “boulders” in the target seem to affect the excavation flow lines, resulting in steeper ejection near the limit of the excavation cavity. This results in a more flat-floored and steep-walled crater (Fig. 2). Numerical simulation of Experiment 1 replicated the experimental result very well (Fig. 3). Balls placed in immediate proximity to the impact point were ejected and ‘rays’ were created in the ejecta blanket. Balls placed at about 3 ball diameters away from the impact point were displaced towards the crater rim, as also noted in the numerical simulation (Fig. 4).
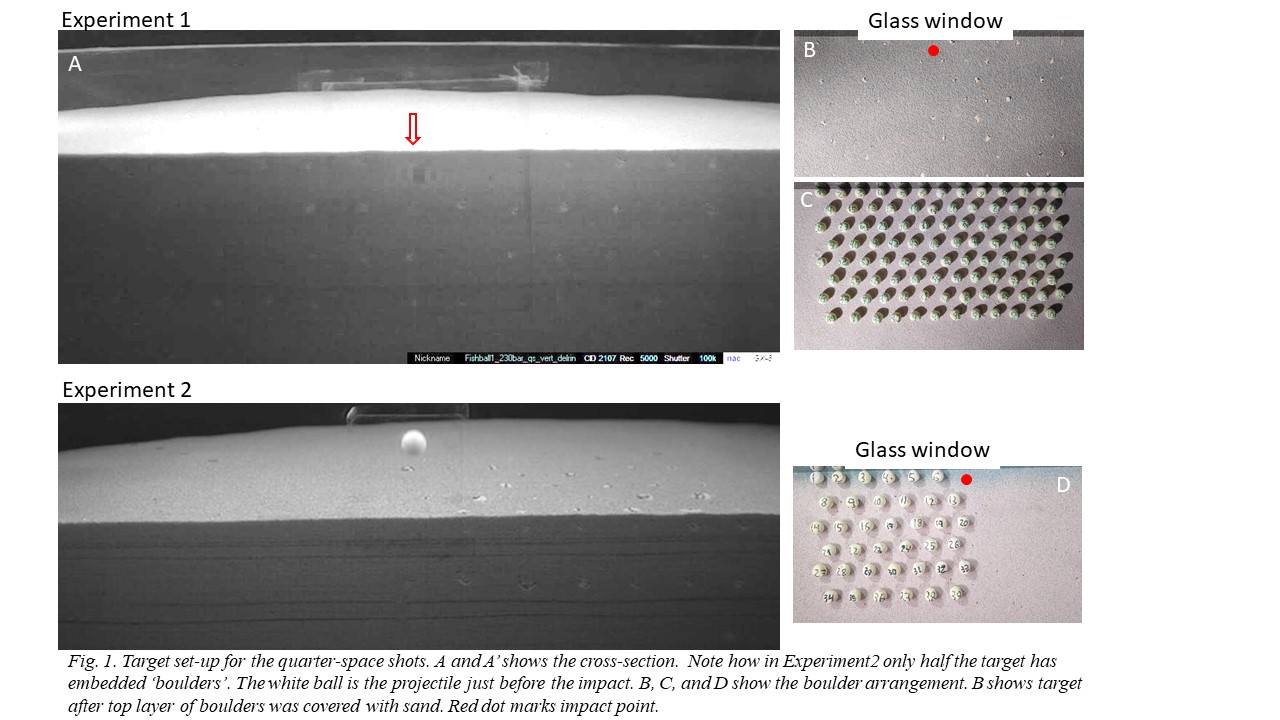
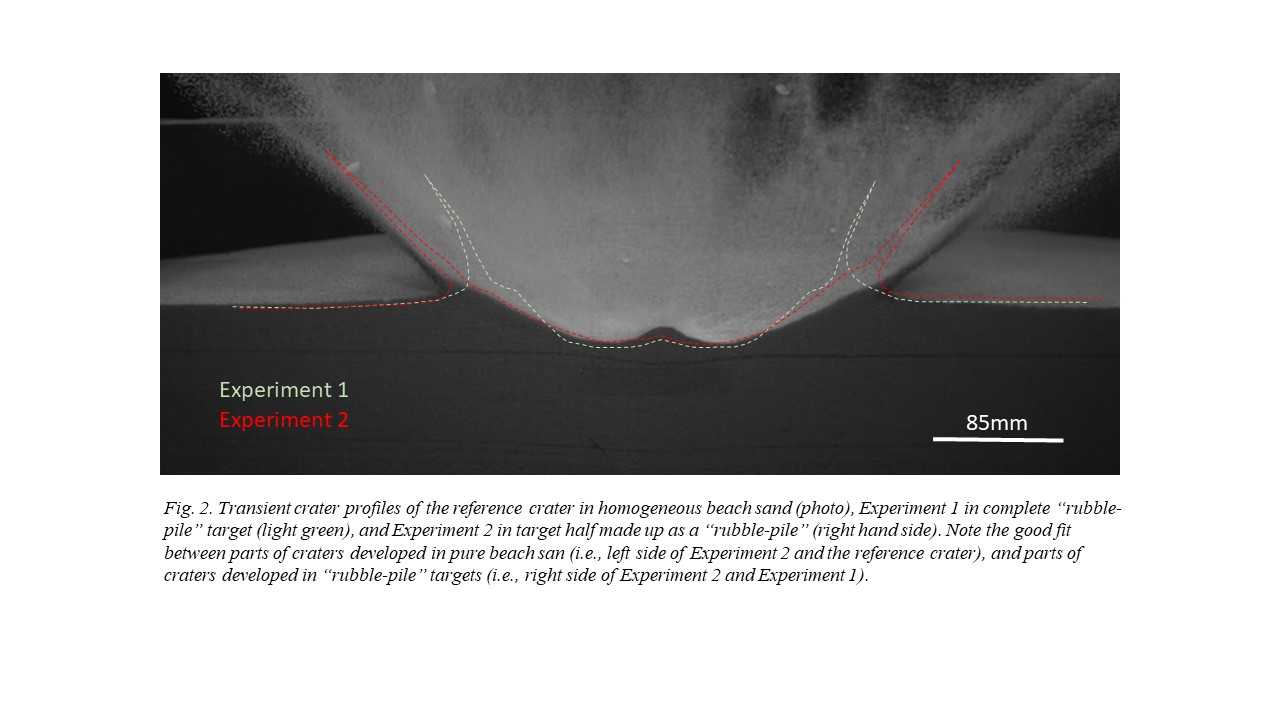
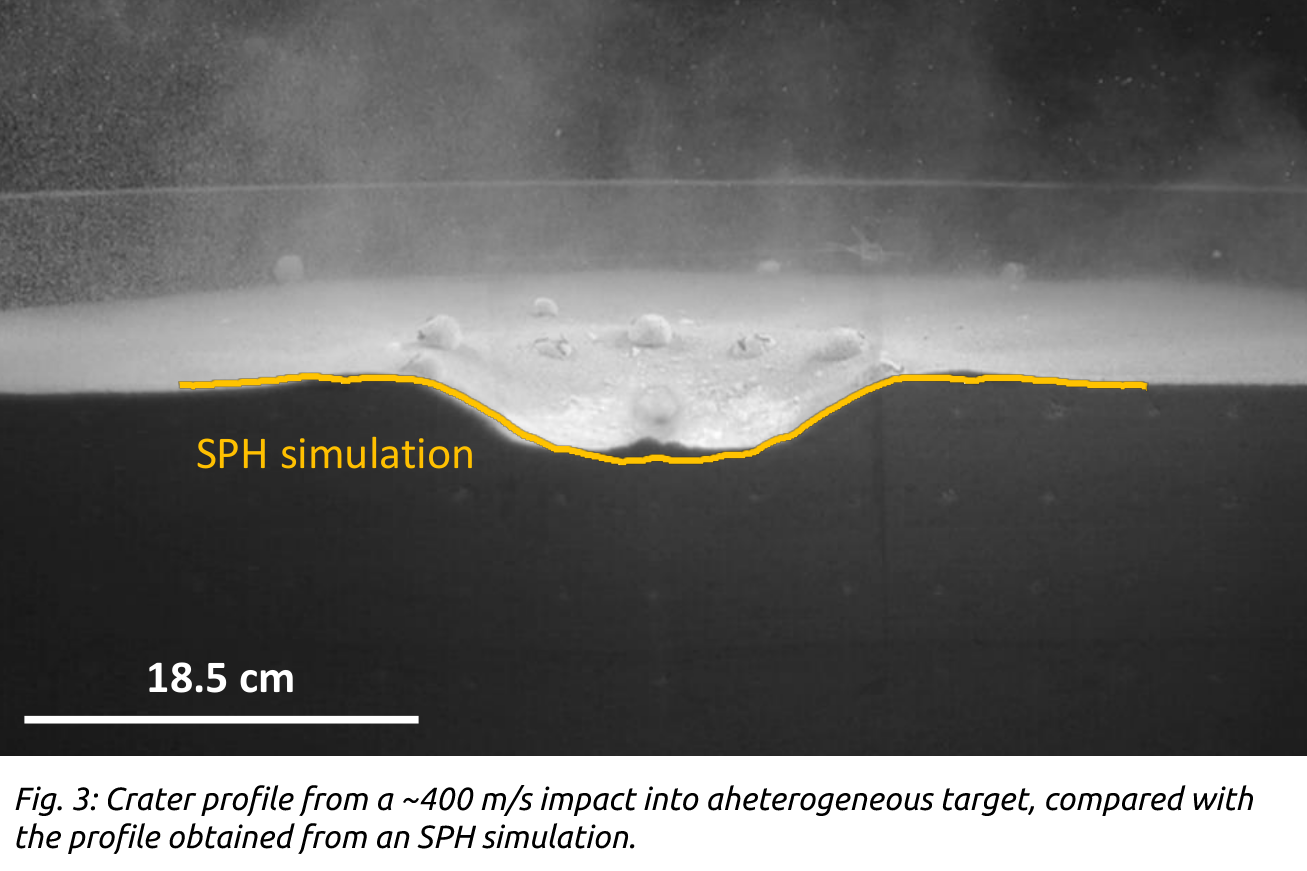
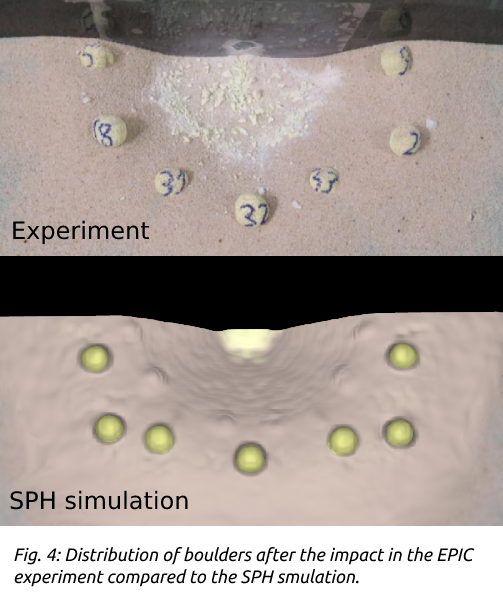
Conclusions: The impact experiments represent a first step in our work towards understanding the importance of target heterogeneities in the cratering process and impact momentum transfer. SPH simulations to reproduce these impact experiments are underway and preliminary results from the early cratering process show good agreement with the experiment.

How to cite: Ormö, J., Raducan, S. D., Luther, R., Herreros, M. I., Collins, G. S., Wünnemann, K., Jutzi, M., and Mora-Rueda, M.: Influence of Layering and Boulder Inclusions in a Granular Target on Crater Formation: Insight from Laboratory and Numerical Studies. , Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-587, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-587, 2021.
Keywords: Impact; asteroid surfaces; SSDEM; SPH.
Introduction: Impacts can modify the physical state of a substantial fraction of a target body. Studying the hypervelocity impact process and outcome is crucial in the interpretation of the history of a planetary body (Jutzi et al., 2015) and the design of asteroid deflection strategies based on the kinetic impactor technique (Raducan et al., 2019). Images returned by space missions show that small asteroids have complex surface morphologies with heterogeneous distributions of fine regolith and large boulders (e.g., Watanabe et al., 2019). To properly decipher the crater imprints on asteroid surfaces, we carried out numerical investigations to understand the effect of surface material properties (i.e., friction, cohesion) and the presence of large boulders on cratering processes.
Methods: We used a hybrid SPH-SSDEM framework to model the high-speed impact cratering (Zhang et al., 2021). The Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) is used to simulate the initial shock propagation and fragmentation stage (Jutzi & Michel, 2015). The outcome is then transferred into a Soft-Sphere Discrete Element Method (SSDEM) code (Zhang et al., 2018), which solves the ejecta evolution and crater growth in the later stages. This modeling framework is capable of simulating impacts from the beginning to the later stages when all ejecta are settled down, allowing capturing the final morphology of the resulting crater.
To make comparisons with the first impact experiment performed on an asteroid by the Hayabusa2 Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI; Arakawa et al., 2020), we conducted SCI-like cratering tests using the same impact condition (except using an impact angle of 0º) and Ryugu’s gravity field. The target is modeled as a 15-meter-radius granular bed held by a hemispherical ball. The particle-ball contact parameters are the same as those used for particle-particle contacts.
Results: As the SCI cratering analyses show consistencies with a very low-strength scaling law (Arakawa et al., 2020), we considered modeling the surface properties with three types of low cohesion (i.e., 0 Pa, 0.01 Pa, and 0.1 Pa) and four types of low to moderate friction angles (20°, 25°, 30°, and 33°). The results show that, in a monotonic manner, the diameter and depth of the resulting crater and rim decrease with a larger friction or cohesion (Fig. 1). Compared with the crater morphology of the SCI impact (i.e., crater diameter 14.5 ± 0.8 m and depth ~2.3 m, rim diameter 17.6 ± 0.7 m and depth 0.4 m), the case with C = 0.1 Pa and 𝜙 = 30° provides the best match. This suggests that the surface fine regolith on Ryugu near the SCI impact site would be likely to have a small amount of cohesion on the order of 0.1 Pa and moderate friction.
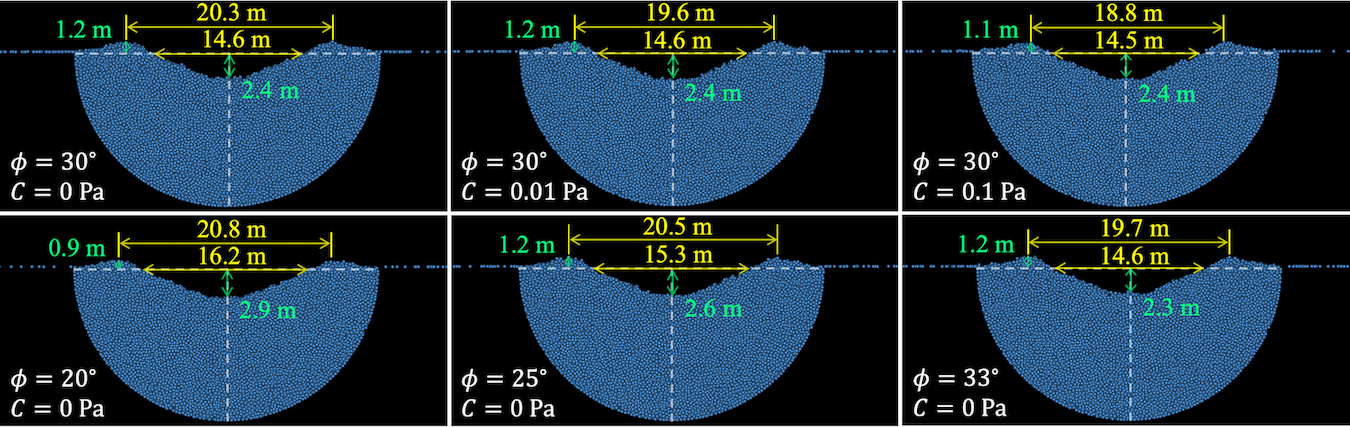
Figure 1 Crater morphology of SCI-like cratering tests. The material friction angle 𝜙 and cohesion C are indicated in the left bottom for each case. The crater/rim diameter and the crater/rim depth are highlighted by the yellow and green measurements, respectively. The dashed lines indicate the reference of the original surface and the central axis.
Nonetheless, the crater growth was undoubtedly affected by the surface morphology as observed during the SCI impact (Arakawa et al., 2020). To test the effect of the presence of boulders, we constructed a target with four boulders imbedded on its cohesionless granular material (Fig. 2d, e). As shown in Fig. 2, the velocity field of the target is significantly affected by these boulders. The growth of the left region was inhibited by the large block on the left side. The small boulders were elevated by the impact and displaced over 20 m. As the granular bed was mobilized by the impact and the movement of the large boulders, at the end, some granular materials were pushed out and the two large boulders sank into the bottom of the container. This sinkage behavior was not seen at the SCI impact site. This inconsistency may suggest that the subsurface area of this site could have large strength that inhibited the downward movement of large boulders, which is consistent with the formation of the small pit at the bottom of the SCI crater. However, the boundary effect of the simulations cannot be ruled out, and further tests are required.
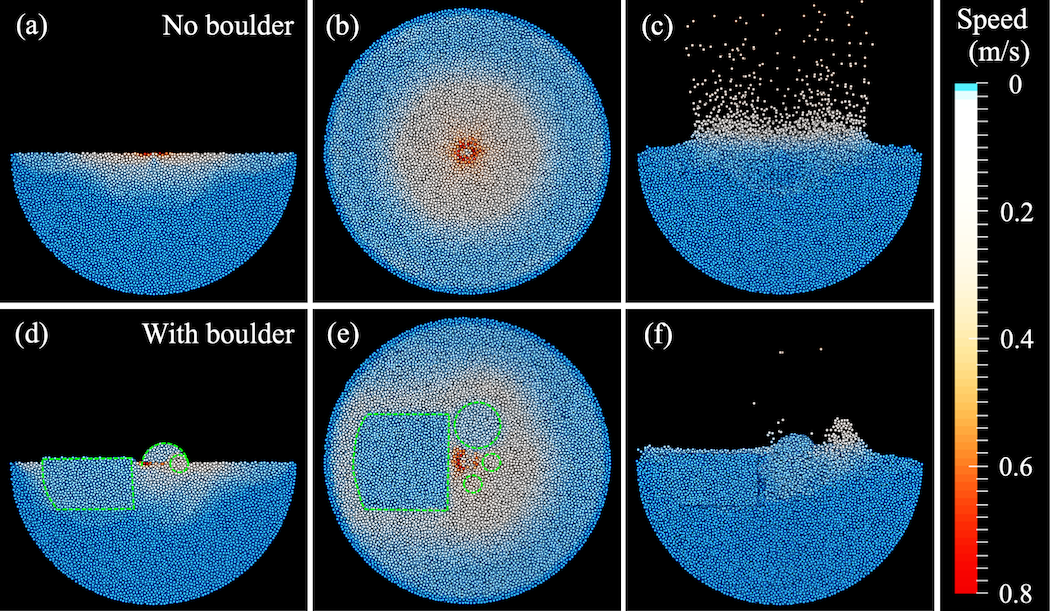
Figure 2 Velocity field at the beginning of the SSDEM-stage simulations (no boulder: a. side view of a cross-section , b. top view; with boulder: d. side view of a cross section, e. top view, where boulders are highlighted by the green dashed curves) and at 100 s (c.no boulder; f. with boulder).
Conclusion: Here we present the first step towards modeling impacts into realistic asteroid surface environments using well validated codes. These impacts are challenging to model and only limited number of impact scenarios have been studied so far. We found that the cratering outcome is very sensitive to the target material properties. Further tests against laboratory and in-situ experiments will be carried out to establish the relation between crater morphologies and surface properties, and understand the regolith and boulder dynamics in low-gravity environments. Moreover, comparisons to direct SPH calculations carried out to long times (Raducan & Jutzi, 2021) will allow to assess the differences between continuum and particle-based codes in the modelling of late-stage crater growth.
Acknowledgements: This project received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 870377 (project NEO-MAPP). Y.Z. acknowledges funding from the Doeblin Federation. Y.Z. and P.M. acknowledge funding support from the French space agency CNES.
References:
Arakawa, M. et al. (2020) Science, 368, 67–71.
Raducan, S.D. et al. (2019) Icarus, 329, 282–295.
Raducan, S.D. & Jutzi, M. (2021) 52nd LPSC, #1900.
Jutzi, M. et al. (2015) In: Asteroids IV (Michel P. et al., eds.) 679–699.
Jutzi, M. & Michel, P. (2014) Icarus, 229: 247–253.
Watanabe, S. et al. (2019) Science, 364(6437), 268–272.
Zhang, Y. et al. (2018) ApJ, 857, 15.
Zhang, Y. et al. (2021) 52nd LPSC, #1974.
How to cite: Zhang, Y., Jutzi, M., Michel, P., Raducan, S., and Arakawa, M.: Effect of material strength and heterogeneity on small asteroid cratering events, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-704, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-704, 2021.
Introduction: NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) aims to test a controlled deflection of a Near-Earth asteroid, by impacting the smaller component of the 65803 Didymos asteroid system, Dimorphos. ESA’s Hera mission [1] will arrive at Dimorphos several years after the DART impact and will perform detailed characterisation of Dimorphos and of the impact outcome.
Past studies of the DART impact outcome [e.g., 2–4] have shown that the amount by which Dimorphos can be deflected is strongly dependent on its surface, subsurface and internal properties. Moreover, [4] showed that in order to validate the predictive capabilities of our numerical models and to understand and ultimately reproduce the asteroid deflection technique, we need a measure of both the impact deflection efficiency (often referred to in terms of β, where β = change in momentum of the asteroid/impactor momentum) and the crater size and morphology. Small asteroids, of less than ~10 km in diameter, are believed to be rubble-pile objects, aggregates held together only by self-gravity or small cohesive forces [5]. Moreover, recent results of the SCI impact on Ryugu [6] inferred that at least the near-surface of the asteroid may not be dominated by strength and impact events are controlled to a large extent by gravity, despite its very low value. These findings might also be applicable to Dimorphos. Studies by [7] suggest that for a low cohesion target, an impact on the same magnitude as DART might have a large enough specific impact energy to cause global deformation of the target.
Here we numerically simulate DART-like impacts on weak homogeneous and rubble-pile asteroids that use realistic material models and aim to evaluate the resulting target morphology and the global shape change caused by such impacts. Additionally, we aim to quantify the deflection efficiency, given different target scenarios.
Numerical Model: Here we use Bern’s parallel Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) impact code [8, 9] to model DART-like impacts (500 kg projectiles at 6 km/s) on spherical asteroid targets, and track the evolution of the target for up to 2 hours after the impact. Bern’s SPH code has been previously validated against laboratory experiments and benchmarked against other codes [e.g., 10, 11]. Recently, the code has been validated against laboratory experiments of impacts into heterogeneous targets [12]. To quantify the effects of the target properties and structures on the post-impact morphology, degree of shape change and on the momentum transfer efficiency, we considered the following target scenarios:
1) Homogeneous spherical targets with low cohesion (Y0 = 0 to 50 Pa) and varying coefficient of internal friction (f = 0.4 to 1.0); To describe the shear response, the target material was modelled using a simple pressure-dependent strength model typical of pre-damaged rock materials [13]. The initial target porosity was kept constant at 40%.
2) Rubble-pile spherical targets with three different distributions of boulders, embedded into a cohesionless matrix material: 2a) grid distribution of 2.5 m in diameter boulders, with one boulder diameter spacing between each boulder in the x, y, and z directions; 2b) random distribution of 2.5 m boulders; 2c) Random distribution of boulders with random sizes between 2 and 10 m. In all rubble-pile target scenarios, the boulders had a tensile strength of YT = 1 MPa and the matrix material was modelled the same as in (1), with Y0 = 0 Pa and f = 0.6.
Results and discussion:
Homogeneous asteroids: The size and morphology of the DART crater is of paramount importance for determining the asteroid’s near-surface properties and structure. In the strength dominated impact scenarios, the cohesion is the dominant force that stops the crater cavity from growing. Therefore, with decreasing target cohesion, more material is displaced or gets ejected above escape speed. We found that for homogeneous asteroids, impacts into targets stronger than Y0~10 Pa create well defined bowl-shaped craters, while impacts into weaker targets create morphologies that do not resemble an impact crater anymore (e.g., Fig. 2, [14]). For these scenarios the curvature of the target also plays a major role. Fig. 1 shows the momentum enhancement factor, β, as a function of target cohesion, for four different coefficients of internal friction. Our results suggest that for a low friction, cohesionless target, the momentum enhancement can be as high as 6.
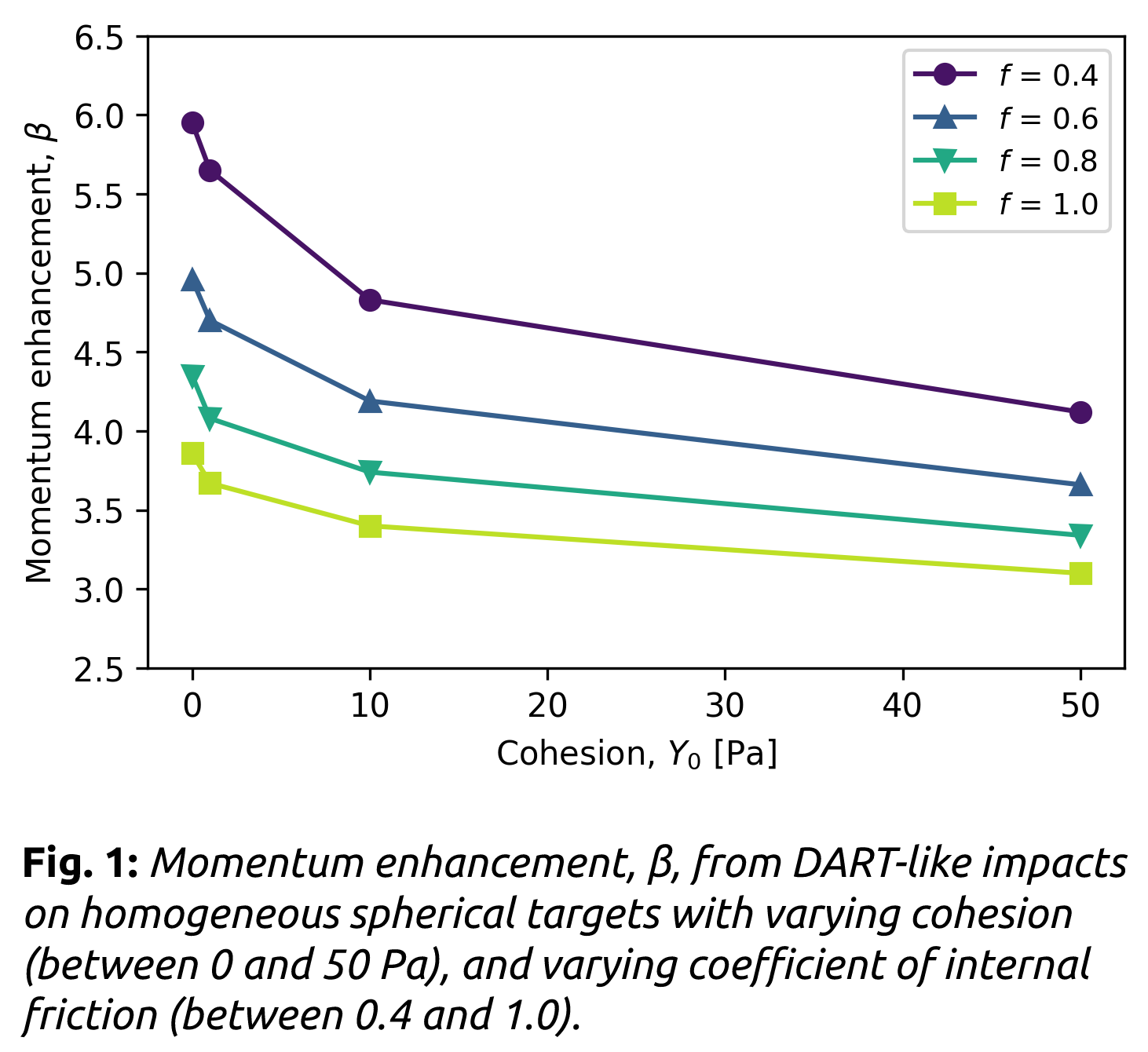
Rubble-pile asteroids: Fig. 2 shows the final target morphologies from DART-like impacts into a (1) cohesionless homogeneous target and (2a, b, c) rubble-pile targets with different boulder size-frequency distributions. In all four impact scenarios, the DART impact produced target morphologies that are dissimilar to cratering and changed the global morphology of the asteroid. Initial simulation results revealed that the presence of boulders in the target can decrease the deflection efficiency by up to 40% compared to an impact into a homogeneous target. At the same time, the initial boulder size-frequency distribution on the surface of the asteroid seems to also influence β.

Conclusions: The DART impact on cohesionless spherical bodies is likely to produce morphologies that are dissimilar to cratering and change the global morphology of the asteroid. Our modelling results together with future Hera mission observations will provide constraints regarding the evolution of the shapes and structures of small asteroids. Future work will investigate impact events into low-cohesion asteroids with more diverse asteroid shapes and boulder distributions.
Acknowledgements: This work has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 870377.
References: [1]Michel, P. et al. (2018) Adv Space Res. 62:2261–2272. [2]Jutzi, M. & Michel, P. (2014) Icarus, 229:247–253. [3]Raducan, S.D. et al. (2019) Icarus, 329:282–295. [4]Raducan, S.D. et al. (2020) Planet. and Space Sci. 180:104756. [5]Richardson, D.C. et al. (2002) Asteroids III, 501–515. [6]Arakawa, M. et al. (2020) Science, 368:67–71. [7]Jutzi, M. et al. (2017) A&A, 597:A61. [8]Jutzi, M. et al. (2008) Icarus, 198:242–255. [9]Jutzi, M. (2015) Planet. Space Sci, 107:3–9. [10]Jutzi, M. et al. (2009) Icarus, 201:802–813. [11]Raducan, S.D. et al. (2021) LPSC,1908. [12]Ormö, J. et al. (2021) LPSC,1965. [13]Collins, G.S. et al. (2004) Meteorit. Planet. Sci, 39:217–231. [14]Raducan, S.D. & Jutzi, M. (2021) LPSC,1900.
How to cite: Raducan, S. D. and Jutzi, M.: Asteroid-scale consequences of the DART impact: the role of target strength and heterogeneity, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-623, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-623, 2021.
JUICE, JUpiter ICy moons Explorer, the ESA mission planned to be launched in 2022 and to arrive at Jupiter in 2029, will make detailed observations of Jupiter and three of its largest moons. One of its goals is to improve the current estimates of Ganymede surface age [2].
Ganymede was observed firstly by Voyager 1 and 2 in 1979, and then by Galileo between 1996 and 2000 through six flybys, which revealed that the surface has two main types of terrains, which differ in albedo, crater density, and surface morphology [4]. The first one, the “dark” terrains, is low albedo terrains, covered by regolith material, and heavily cratered. The second one, the “light” terrains, has higher albedo and lower crater density, suggesting a younger age. They can occur as smooth elongated and polygonal shaped areas, or as grooves. An accurate chronology for Ganymede can therefore provide information about resurfacing and the evolution of the surface, including the extent of the cryovolcanism [3].
As part of the future activities, we make new crater counts to be then used to refine current Ganymede crater-based chronology. The quantitative and statistical analysis of impact crater populations is the primary tool to derive absolute ages of planetary and small body terrains. Further information to improve surface landform interpretation and crater counts can be derived from the crater morphological “freshness”, which may represent a first qualitative hint to the relative ages of individual craters and the surrounding area.
The goal of this project is to improve Ganymede crater chronology using the most updated understanding on the current and historical impact flux resulting from recent dynamical models. In this work, we will present our results in i) improving the geological mapping of the Ganymede surface, and in ii) deriving a revised crater database for Ganymede.
The present global image mosaic of Ganymede is available at a resolution of ~1 km/pixel. Being only 74% of the surface at a resolution better than 2 km/pixel, either image resampling or degradation was applied [1], [4]. We select the areas of Ganymede acquired at the highest resolution (<100 m/pixel).
On the existing global geological map [1], [4], we performed cartographic refinement to better define the contours of the geological units used in this study. Crater counting is then performed by selected impact structure by means of photo-interpretation (e.g., primary vs secondary, degradation degree, peculiar morphology, ejecta blanket, etc.). In Figure 1, we show a sample of the regions we analysed, while in Figure 2 we report the respective cumulative plots.
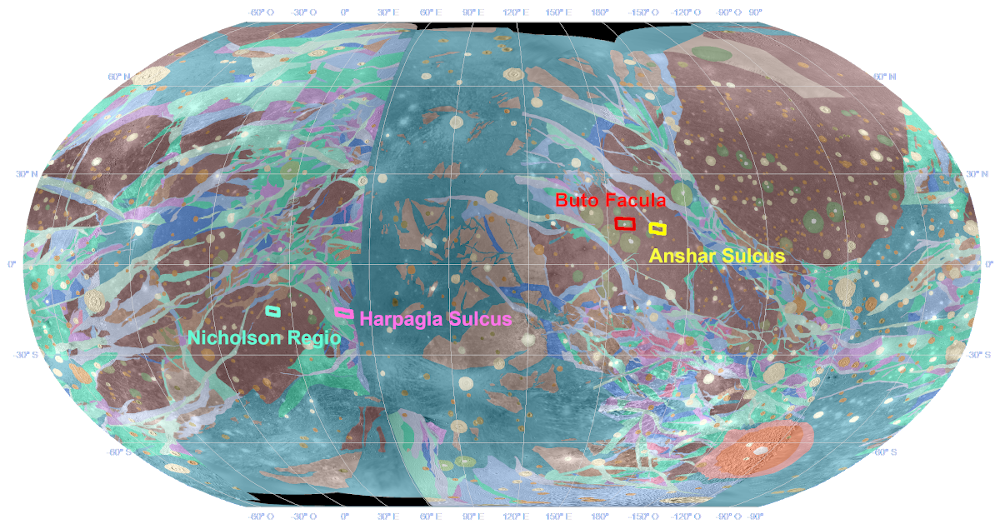
Fig. 1. Ganymede with overlaid the geological interpretation of its terrains (modified from Collins et al. 2013; Patterson et al. 2010). The four boxes refer to the areas of counts: Nicholson Regio in water green, Harpagia Sulcus in pink, Buto Facula in red, and Anshar Sulcus in yellow. The map is a Robinson projection, centred at 110°.
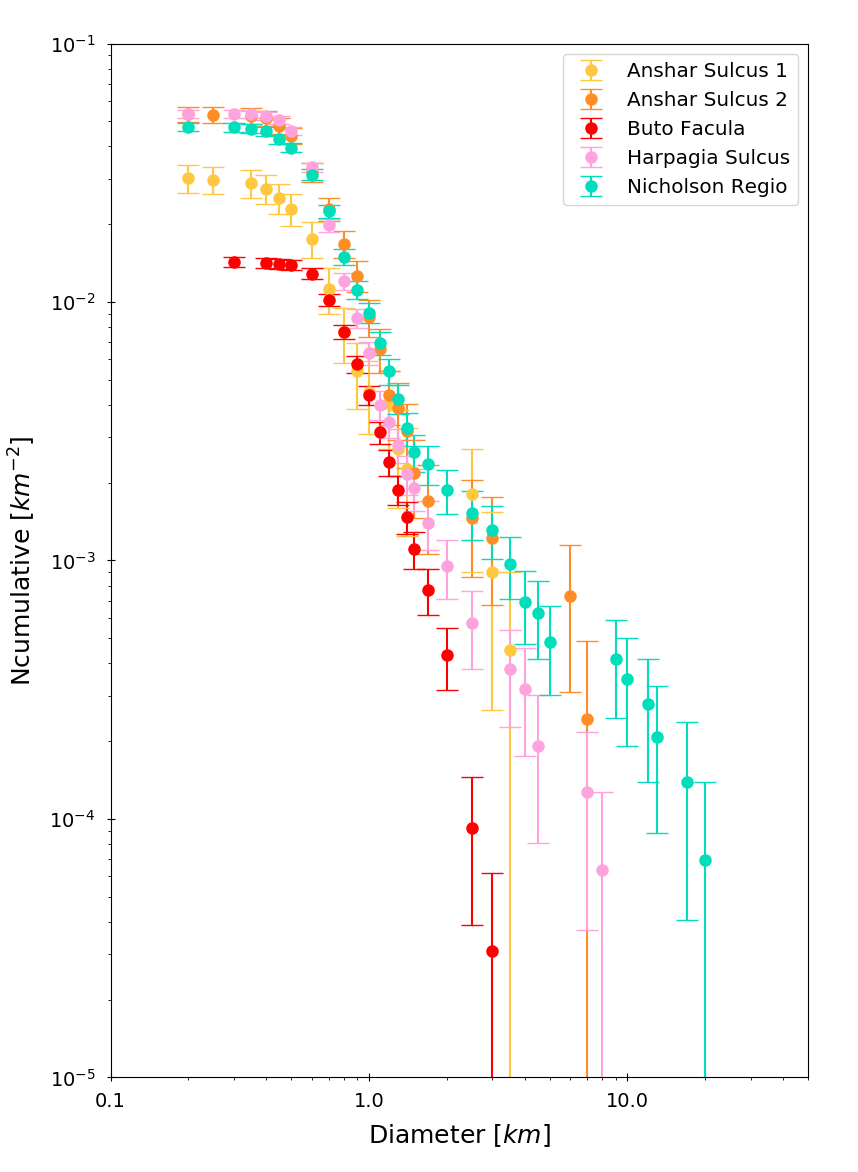
Fig. 2. The plot shows the comparison of the crater counts on the regions marked in Figure 1, represented as a cumulative distribution.
The precision of crater counting is crucial to derive reliable age estimates. Factors affecting the shape of the crater size−frequency distribution are: (i) contamination due to secondary craters and/or volcanic structures; (ii) ejecta blanketing; (iii) superposition, abrasion, and infilling; (iv) image resolution; and (v) illumination conditions.
We quantitatively estimate the accuracy of our counts by selecting sub-areas for which we have images available also at a spatial resolution better than a factor of five. We made there a second additional count, and made a direct comparison of the craters counted in these sub-areas when using either the image at lower or higher resolution.
As displayed in Figure 3, we found that craters counted in the low resolution images are often larger than the true value, due to a poor identification of the crater rim. Moreover, we marked as primary a number of crater-like features, which display a circular shape with an inner shadow in the low resolution image, but they then turn out to be an erroneous detection when cross-checking in the high resolution image.

Figure 3. Harpagia Sulcus at ~116 m/pixel (top) and ~16 m/pixel (bottom). The two boxes in this figure emphasize two of the main errors found in crater detection.
References.
[1] Collins et al.: Global geologic map of Ganymede. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3237, scale 1:15,000,000, http://pubs.usgs.gov/sim/3237/, 2013.
[2] Palumbo et al. (2014): JANUS: The Visible Camera onboard the ESA JUICE mission to the Jovian system. 45th LPSC, abstract #2094.
[3] Pappalardo, R.T., et al.: Geology of Ganymede, in: Bagenal, F., Dowling, T., McKinnon, W. (eds), “Jupiter”, Cambridge University, Press, Cambridge, UK, pp. 363–396, 2004.
[4] Patterson, G.W. et al.: Global geological mapping of Ganymede. Icarus, Vol. 207, pp. 845–867, 2010.
How to cite: Martellato, E., Marchi, S., Galluzzi, V., Palumbo, P., and Rotundi, A.: Ganymede Cratering Record, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-576, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-576, 2021.
We present Earth-based observations of Jupiter from 1994 and 2009, which respectively capture the effects on Jupiter’s atmosphere by the impacts of Comet D/Shoemaker-Levy 9 (SL9) and the impact by an unknown object whose visible impression on Jupiter’s appearance was discovered by Anthony Wesley. Previous studies have suggested the 2009 impactor was by an asteroid on the basis of differences in Jupiter’s atmospheric response compared to the 1994 impact by SL9. These differences include detections of 9.1-μm silicate features in the 2009 impact site (Orton et al., 2010, Icarus 211, 587-602) and the fact the 2009 debris field shrank faster (Hammel et al., 2010, ApJL 715, L150-L154), both of which suggest the 2009 impactor was more rocky/refractory in composition. However, Schenk et al. 2004 (Jupiter: The Planet, Satellites and Magnetosphere, Bagenal, Dowling, McKinnon, 427-456) state that comets are orders of magnitude more likely to impact Jupiter than asteroids since Jupiter should have cleared its orbit a long time ago. Thus, either (1) the 2009 impact was caused by an asteroid and therefore a statistical fluke, (2) Jupiter-Family Comets (JFCs) are a highly heterogeneous population, with some containing rocky/refractory interiors hidden from remote-sensing, or (3) there is a population of asteroids among bodies classified as JFCs. In order to explore these hypotheses, we performed a comparative spectral re-analysis of broadband imaging and low-resolution spectra measured during/after the 1994 and 2009 impacts. The comparison used consistent procedures for reduction and calibration of the data, atmospheric models, radiative-transfer software and spectroscopic line data in order to facilitate direct comparisons between 1994 and 2009 events.
How to cite: Sinclair, J., Orton, G., Krishnamoorty, M., Fletcher, L., Hora, J., Lisse, C., Palotai, C., and Hayward, T.: The 2009 Wesley impact: Asteroidal or Cometary?, Europlanet Science Congress 2021, online, 13–24 Sep 2021, EPSC2021-140, https://doi.org/10.5194/epsc2021-140, 2021.
Please decide on your access
Please use the buttons below to download the presentation materials or to visit the external website where the presentation is linked. Regarding the external link, please note that Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
Forward to presentation link
You are going to open an external link to the presentation as indicated by the authors. Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
We are sorry, but presentations are only available for users who registered for the conference. Thank you.
Please decide on your access
Please use the buttons below to download the presentation materials or to visit the external website where the presentation is linked. Regarding the external link, please note that Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
Forward to session asset
You are going to open an external link to the asset as indicated by the session. Copernicus Meetings cannot accept any liability for the content and the website you will visit.
We are sorry, but presentations are only available for users who registered for the conference. Thank you.

